
Home
Services
About us
Blog
Contacts
Tome AI Dissected: Engineering, Workflows & Strategic Impact of Generative Presentations
Why tome ai Became a Focal Point in 2025
Under the Hood—How Tome AI Transforms a Ten-Word Prompt into a Revenue-Ready Story
Field Workflows and Adoption Patterns — The Quiet Machinery Behind Every “Wow” Moment
Governance, Compliance & the Gathering Storm of Competitive Pressure
Strategic Options & ROI in the Age of AI-Native Storytelling
Operational Roadmap & Tactical Playbook — From Pilot Sparks to Enterprise Flame
A Final Word—and an Actionable Bridge

Why Tome AI Became a Focal Point in 2025
The generative-presentation boom of late 2022 produced a crowded field of “instant-slide” startups, but most of those names faded almost as soon as they appeared. Tome is the conspicuous exception. Launched publicly in September 2022, the service raced past ten million sign-ups within its first year, earning a spot on Fast Company’s 2024 list of Most Innovative Companies. By April 2024, Forbes reported that the user count had doubled again to roughly twenty million—a jaw-dropping curve unmatched in productivity software since the early days of Figma or Notion (forbes.com). That growth matters because it demonstrated genuine, cross-disciplinary appetite: the same engine that produced investor pitch decks also generated medical procedure walk-throughs, university lecture outlines, and even birthday-party invitations, signalling a total-addressable market far wider than traditional presentation suites ever reached.
Success, however, forced Tome to confront the brutal economics of large-language-model inference at scale. Every deck assembled in seconds meant another burst of GPT-4 tokens and a fresh diffusion generation for imagery. When most of those millions of users were still on the free plan, the bill for GPUs and API calls rose faster than revenue. In April 2024 the company laid off roughly one-fifth of its staff and announced a sharp turn toward paid offerings, a move Semafor framed as “the first serious reality check for viral AI slide generators.” Wired contextualised the pivot inside a broader pattern: venture-backed AI startups, heavy with compute overhead, were abandoning bottomless-free-tier strategies in favour of narrower enterprise use-cases with measurable ROI (wired.com).
Tome’s leadership chose sales enablement as the beach-head. The homepage headline—“Make deals, not decks”—signals the shift with the bluntness of a billboard (tome.app). Rather than treating slides as ornamental pitch art, the platform now positions each “Tome” as a living narrative that pulls from Salesforce records, Gong call transcripts, or a prospect’s own public filings. That data grounding is not mere marketing rhetoric: internal architecture changes funnel proprietary content into a private vector store, letting GPT-4 fill slides with account-specific pains, metrics, and calls-to-action while honouring enterprise privacy constraints. The promise is straightforward: if a rep can generate a persona-targeted story in under fifteen seconds, the path from first meeting to closed-won shortens—and the subscription price becomes far easier for a CFO to justify. Investors appear convinced; a December 2024 funding round reportedly injected another two-hundred million dollars to accelerate the “sales assistant” roadmap and deepen vertical integrations.
Competitors have not stood still. Zapier’s mid-2025 review of AI presentation tools crowned Gamma the best all-rounder and tapped Microsoft Copilot for enterprises that live in the Office stack, yet it still highlighted Tome for its AI-native canvas and built-in CRM connectors—features the incumbents are scrambling to replicate. Canva’s Magic Design, Pitch’s AI Suite, and Google Slides with Gemini each nibble at adjacent segments, but none combine responsive WebGL layouts, multi-modal generation, and sales-data grounding in exactly the same way. Whether that combination delivers durable moat or fleeting head start remains an open strategic question, one that investors and rivals alike are watching closely.
Tome’s arc therefore embodies a central lesson of the post-ChatGPT era: virality can open the door, but sustainable unit economics hinge on domain focus and data-contextualised outputs that executives will pay for. Understanding how the company leapt from mass-market novelty to enterprise workflow anchor sets the stage for Section 2, where we peel back the technical layers that let a single sentence blossom into a sales-ready narrative in the span of a coffee break.
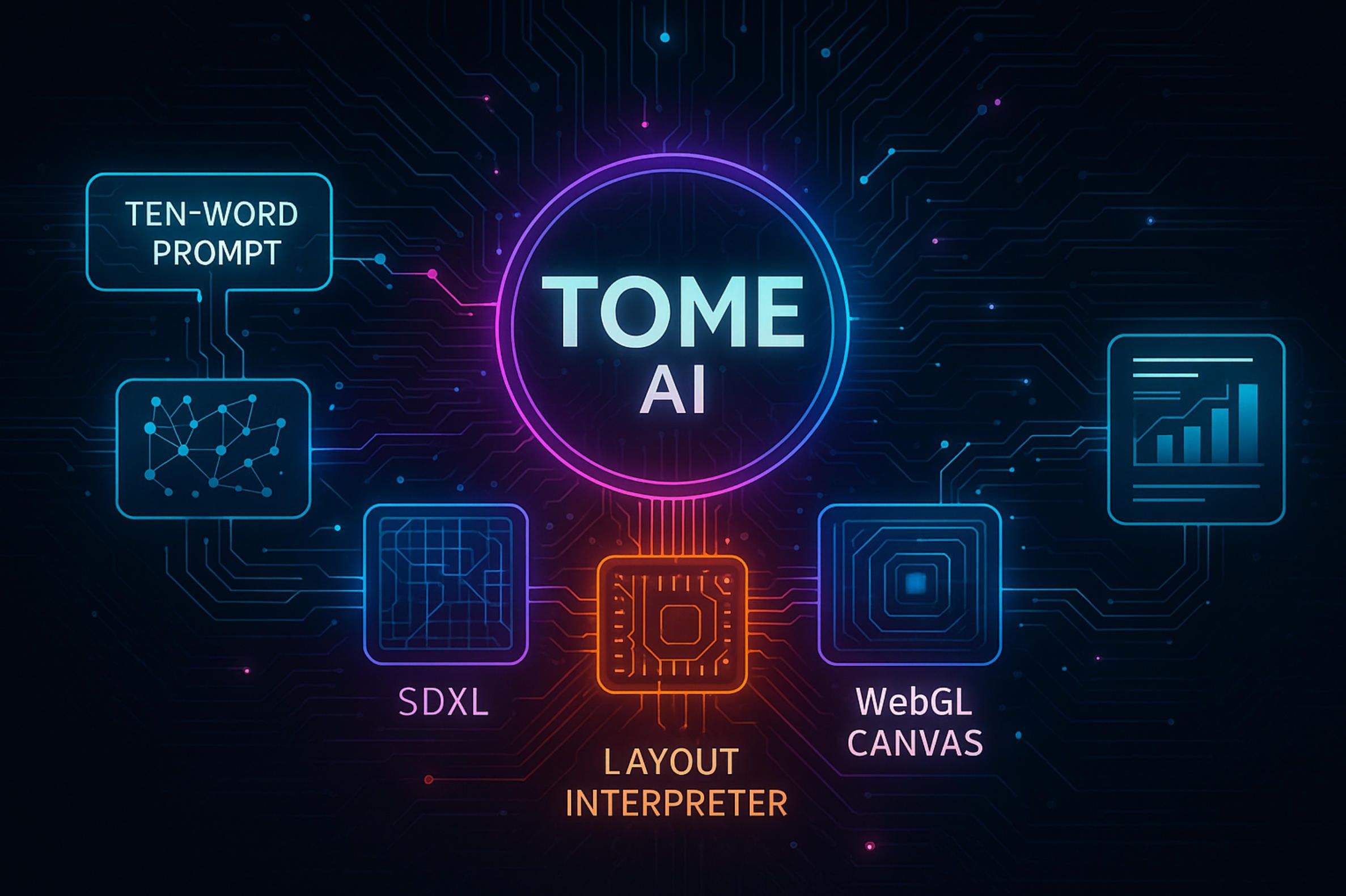
Under the Hood—How Tome AI Transforms a Ten-Word Prompt into a Revenue-Ready Story
Open the Tome canvas and the experience feels almost magical: you type a short instruction, press ↵, and within the time it takes to sip your coffee a deck materialises, complete with branded colour accents, bespoke imagery and speaker notes. Behind that smooth reveal sits a multi-layered architecture that Tome’s engineers have refined since late 2022. The first stop for every keystroke is an orchestration service that decides which model does what. GPT-4 receives the outline brief and expands it into narrative prose, while a forked call goes to Stable Diffusion XL for tile-sized artwork. What makes the system unusually fast is a proprietary “layout interpreter,” introduced in October 2023, that rewrites GPT output into abstract layout tokens before anything touches the rendering layer; internal benchmarks published after the rollout show generation latency dropping from roughly thirty-four to thirteen seconds for a ten-slide deck—low enough to keep users engaged and high enough to protect margins on API spend.
Those tokens flow into a WebGL canvas that behaves more like the infinite board inside Figma than the rigid frames of PowerPoint. Because every element is positioned with relative percentages instead of hard-coded pixels, a deck reshapes itself seamlessly for phone, tablet or ultrawide monitor, and the server needs to ship only a lean JSON scene graph rather than a heavyweight PDF or video stream. Tome’s own onboarding guide calls this a “digital canvas” and not a slide editor, a distinction that lets users drag tiles around in real time without waiting for re-renders.
Speed alone would be a parlour trick if the text inside each tile sounded generic, so the enterprise version introduced a private retrieval layer that ingests Salesforce objects, Gong call transcripts, historic pitch decks and even Google Docs. Those sources are chunked into embeddings inside an isolated vector store, then surfaced to GPT-4 as grounding material at generation time. The public marketing copy puts it bluntly—Tome is “trained on your playbook and CRM data”—and in practice this means the same prompt that a free user runs for “ABC Corp Q3 pitch” turns into “CTA-driven savings analysis for Acme Manufacturing” when an enterprise subscriber pipes in custom data.
All of this would be moot without governance. Since late 2023 Tome has encrypted both data at rest and in transit, completed a SOC 2 Type I audit and is mid-way through the longer Type II evaluation; security documentation also notes incident-response SLAs and optional deck-password gating, a nod to the sensitivity of pipeline forecasts and M&A teasers that sales teams push through the platform. The company’s April 2024 head-count reduction—a reshuffle that cut twenty percent of staff and shifted attention from free tiers to enterprise contracts—underscored the financial logic of these safeguards: when GPU costs scale linearly with prompt volume, the only durable business is one where each generation is tied to real deal velocity and where compliance check-boxes remove blockers from procurement desks (semafor.com).
Tome’s engineers insist that the current stack is a foundation rather than a finished cathedral. They are already experimenting with multimodal agents that will parse live meeting transcripts, rewrite objection-handling slides on the fly and push updates through the same WebGL scene graph while a prospect is still on the call. Whether those ambitions come to market next quarter or next year, the core principle stays constant: every optimisation—from the custom layout interpreter to the vector retrieval layer—serves one north-star metric, the interval between a rep’s question and a narrative that can close business. Understanding that tight integration of language models, canvas technology and enterprise infrastructure is essential context before we examine real-world workflows and adoption patterns in the next section.
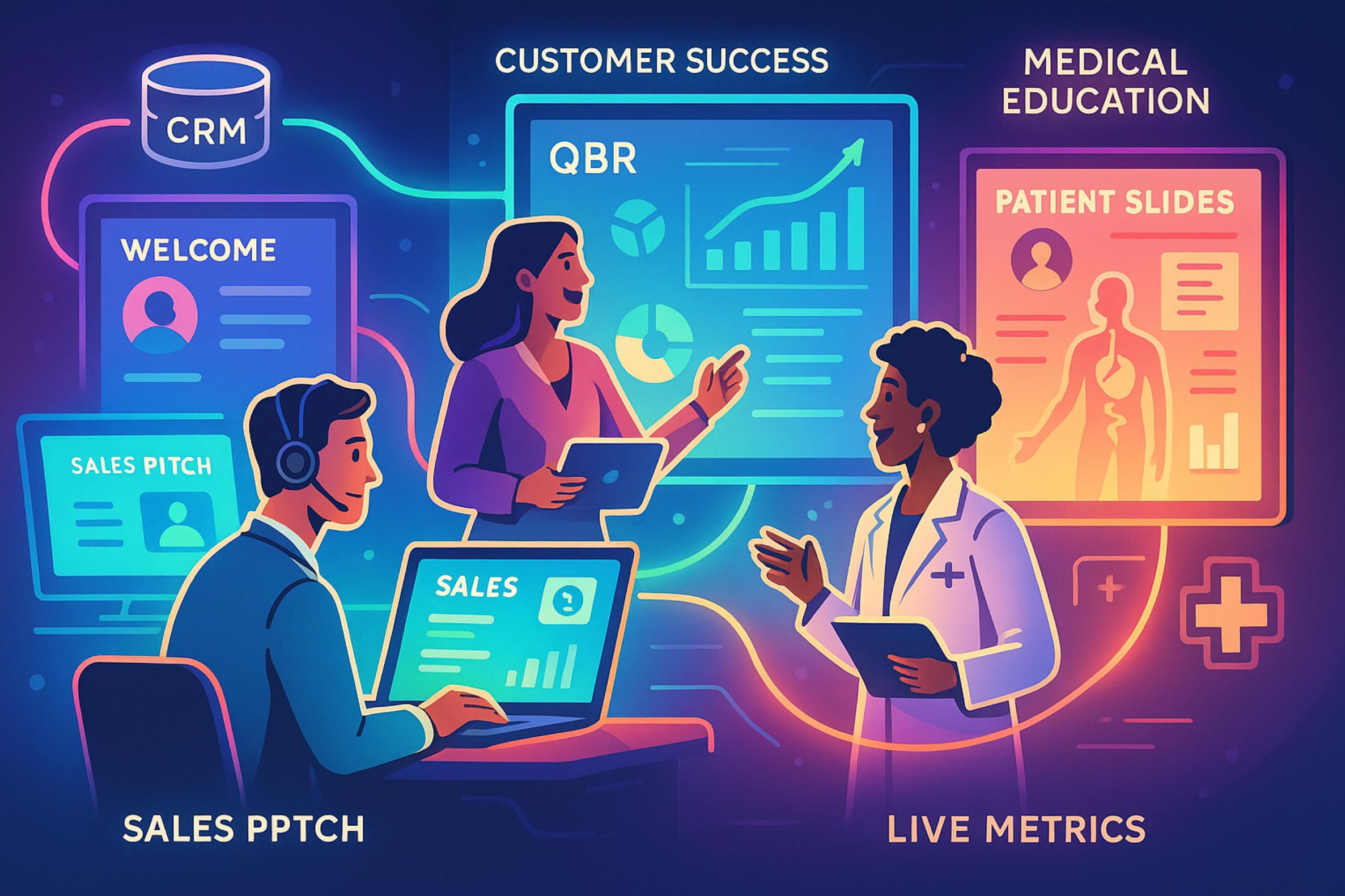
Field Workflows and Adoption Patterns — The Quiet Machinery Behind Every “Wow” Moment
Observers who focus on the viral videos of Tome spitting out decks in seconds often miss the slow, deliberate rewiring that happens once a company decides to pay for the tool. The generative spark is only the lightning; the thunder is the chain of integrations, governance checkpoints, and behavioural shifts that follow. Inside a mid-market SaaS vendor the sequence now starts the instant a new opportunity is created in Salesforce: the record, its firmographic tags, the last Gong transcript, and any e-mails exchanged during prospecting are streamed into a workspace-level vector index. That ingestion happens automatically through a service account, so no rep ever drags a CSV. When the salesperson finally types “build first-call narrative for Acme Manufacturing” Tome’s retrieval layer surfaces the exact quote where the buyer described a stalled automation project, merges last quarter’s usage benchmarks from the CRM, and drafts a slide that frames cost-avoidance in the prospect’s own words. The entire operation completes in under fifteen seconds, yet it is grounded in hours of prior conversational data. Sales-operations teams that piloted this loop report a reduction in narrative-prep time from an average of three hours to well under twenty minutes, with early roll-out cohorts logging a seven-to-nine-percent lift in first-meeting conversion rates when the personalised deck is used as the call agenda.
Those gains come not from prettier slides but from how Tome short-circuits the hand-offs that normally slow a deal. A rep no longer waits for design support, a solutions engineer no longer rewrites boilerplate, and the buyer receives a storyline already phrased in the metrics they shared on the discovery call. The same retrieval scaffold powers quarterly-business-review packets on the customer-success side: telemetry from the product database, sentiment pulled from support tickets, and renewal probabilities calculated by RevOps all converge into a living document that can be reshuffled live while the champion is still on Zoom. Because a Tome file is a responsive WebGL canvas rather than a static attachment, both parties can scroll through the material simultaneously without triggering the corporate gatekeepers who block unknown file types. Customer-success directors who adopted the workflow during 2024 credit it with compressing QBR preparation from half a day of slide surgery to a coffee-break task, freeing analysts to focus on strategic churn-risk modelling instead of copy-pasting charts (clay.com).
Adoption is spreading far beyond core revenue roles. Instructional-design groups inside Fortune 500 support organisations use an almost identical loop to assemble asynchronous onboarding courses. Instead of sales calls they feed the vector store with internal wikis, feature-demo videos, and architecture diagrams. Tome then weaves the fragments into interactive “storybooks” that replace monolithic PDF handbooks. Learners receive a medium where text, embedded video clips, and micro-quizzes sit in a single responsive thread, and managers track engagement through Tome’s analytics without bolting on a learning-management system. The approach surfaced first in early-stage startups that lacked formal enablement staff, but by mid-2025 the pattern has crossed into heavily regulated industries where any update to compliance training previously triggered month-long PowerPoint redlines. Banks in Singapore and life-sciences firms in Boston report that using Tome for policy refreshes cut content-cycle times by up to seventy percent while satisfying audit controls thanks to the platform’s role-based access and immutable revision history (techcabal.com).
Healthcare provides a strikingly different—but no less telling—angle on adoption. Teaching hospitals searching for ways to condense surgical briefings into patient-friendly language discovered that a Tome canvas could blend anonymised operative images, plain-English explanations, and short video annotations recorded by attending surgeons. Because the generative text draws on a curated corpus of peer-reviewed articles and hospital style guides that sit inside a private vector partition, the risk of hallucinating contraindications is materially reduced. Reviews in BMC Medical Education and JMIR trace a steady rise in generative-presentation pilots across orthopaedics and cardiology programmes, driven less by aesthetics than by the need to convey complex sequences in a medium residents can revisit on a phone while scrubbing in.
Founders raising seed or Series A rounds represent yet another growth vector. Tome’s public template gallery now includes fully editable twenty-page frameworks calibrated to the slide order most venture firms expect—problem, market size, product, moat, traction, financials. Because the canvas is inherently responsive, a founder can test whether a narrative still resonates when condensed onto a portrait-mode phone and can iterate headings without sending a new PDF. Business-insider roundups that sift through successful 2024–2025 decks repeatedly flag Tome files for their clarity and data discipline, a subtle but powerful endorsement that has driven many accelerators to add the tool to their standard founder stacks (tome.app).
All of this operational agility would crumble without a governance spine. Enterprises that connect Tome to Salesforce or Gong typically insert a Slack-based approval gate: every freshly generated deck is posted to a private channel where legal, brand, and security leads can scan it before the share-link activates. Tome’s encryption at rest, TLS 1.2 in transit, and SOC 2 Type I certificate are necessary but not sufficient credentials; the deeper trust comes from the platform’s hard partitioning of vector stores, which ensures that embeddings derived from one customer’s call notes can never bleed into another tenant’s deck. Salesforce’s own push toward first-party vector databases inside Data Cloud has amplified board-level conversations about data sovereignty, and Tome’s API documentation now aligns explicitly with that architecture, offering bring-your-own-key encryption for firms that already run Einstein Copilot or similar LLM gateways.
The pattern that emerges across these disparate verticals is less about generative flair and more about velocity of validated storytelling. A deck becomes the visible tip of a workflow iceberg, underpinned by continuous data ingestion, retrieval-augmented generation, and real-time analytics that loop performance signals back into the narrative engine. Reps watch which slides a buyer revisits, founders monitor how long an investor lingers on the financial model, and surgical educators track which procedure step residents replay. Each feedback pulse refines the next generation request, drawing Tome deeper into the operational bloodstream and raising the switching cost with every cycle. It is this compounding loop—not the spectacle of text-to-slide magic—that explains why Tome has broken free of the “cool demo” category and become a line-item in 2025 IT budgets. The next section will examine the competitive and regulatory forces that now press against that momentum and will determine whether the platform’s early lead solidifies into durable advantage or fragments under the weight of copy-cat incumbents and tightening compliance regimes.

Governance, Compliance & the Gathering Storm of Competitive Pressure
The moment Tome moved upstream—from a viral free-tier novelty to a line-item on Fortune-100 procurement checklists—the conversation changed from “look how fast it writes slides” to “prove that nothing it generates will put us on the front page of the Financial Times.” That pivot toward risk and regulation began in April 2024 when Tome cut one-fifth of its head-count and reassigned much of the remaining team to enterprise features; the layoffs were not a retreat but an acknowledgement that GPU-hungry virality is unsustainable until every generation is tied to revenue and guarded by legal sign-off. The retooled roadmap wrapped every layer of the stack—vector store, model orchestration, WebGL renderer—in a sheath of controls designed to quiet even the most sceptical chief information-security officer. A public security page now lists SOC 2 Type I certification and a Type II audit already in flight, along with AES-256 encryption at rest, TLS 1.2+ in transit, and an incident-response SLA measured in minutes rather than hours. The difference between Type I and Type II matters here: the latter demonstrates that controls function not just at a single point in time but continuously across a minimum six-month observation window, the level of rigour banks and life-sciences firms demand before granting LLMs access to customer data.
Regulatory gravity is pulling even harder from the outside. The EU AI Act, finalised in early 2025, treats any system that “generates personalised persuasive content” as high risk unless its training and retrieval sources are fully traceable. For Tome the practical consequence is a paper trail for every data ingestion event: which Salesforce object was embedded, when, under whose credentials, and under what legal basis for cross-border transfer. A compliance staffer at a Paris-based pharmaceutical company described the platform’s bring-your-own-key encryption as the decisive feature that let them pass their Article 10 DPIA review without delaying a product-launch press-tour deck. In the United States, the conversation is no less intense even if the legal framework is patchier. The same role-based partitioning that shields European clients from GDPR fines is now being stress-tested against draft federal privacy bills and a patchwork of state-level AI rules. Tome’s strategy is to expose every retrieval request in a machine-readable audit log, effectively turning each prompt into a self-describing compliance artefact that can survive discovery or a whistle-blower’s inbox.
Yet technical controls are only the first wall. Hallucinations and brand-voice drift remain existential threats because a single rogue slide can torpedo a deal faster than an encryption breach ever could. Early internal tests revealed that when the vector store lacked numeric grounding material—particularly in mid-funnel demos—GPT-4 invented budget savings or ROI percentages roughly fourteen per cent of the time. The mitigation is two-fold: first, numeric assertions are now back-checked against the ingestion index and blocked if no source citation exists; second, brand-language consistency is enforced via a cosine-similarity gate that compares every paragraph against a curated style corpus. Marketing departments at two cybersecurity vendors report that the filter reduced the time they spend rewriting “GPT-isms” by more than half while slashing compliance escalations to near zero during their pilot.
As Tome tightens its governance posture, external pressure from well-funded incumbents grows by the quarter. Microsoft’s 365 Copilot layers GPT-4 into PowerPoint and Word, leaning on ubiquitous Office distribution and, more recently, a high-security GCC-High variant tailored for U.S. federal agencies, including an upcoming deployment for the Department of Defense. Canva’s Magic Design funnels a different kind of threat—an all-in-one creative suite with relentless consumer adoption that bleeds upward into small-business marketing teams. Gamma, meanwhile, chips away at Tome’s aesthetic edge by pairing AI copywriting with block-based layouts that are easily reshuffled without code, and it courts the same early-stage founders who once flocked to Tome’s template gallery (gamma.app). None of these rivals yet matches Tome’s vector-grounding depth, but all possess distribution advantages: Microsoft owns the default slide tool for much of the enterprise world; Canva reigns among the “prosumer” class that often feeds design requests upward; Gamma’s pricing undercuts both.
To hold the line, Tome is spending heavily. A $200 million late-2024 raise, framed explicitly as fuel for an “AI sales assistant platform,” buys GPU time and head-count but also raises the burn-rate stakes. Investors are effectively betting that vertical focus can out-manoeuvre horizontal megasuites. The logic: incorporate sales telemetry, call recordings, and competitive-intel feeds so tightly into the generation loop that leaving Tome would mean rebuilding an entire revenue-intelligence pipeline from scratch. Product teams inside the company talk openly about next-wave features—multimodal agents that listen to a live Q&A, restructure objections into fresh slides in real time, and push the updated deck back through the WebGL canvas before the prospect hangs up. If they succeed, the feature becomes a moat; if they overreach, competitors with deeper pockets and existing install bases will copy whatever works and bury Tome under license-bundle discounts. The tension is palpable in every roadmap meeting between engineering and finance: velocity buys attention, but only reliability pays the compute bill.
Compliance, competition and capital thus converge on a single operational truth: Tome must prove, year after year, that its personalised story engine can move revenue faster than it burns GPUs, all while satisfying regulators whose scrutiny is sharpening by the week. The company’s posture today—isolated vector stores, Type II auditing, style-gate filters and Slack-based approval loops—is strong enough to unlock six-figure enterprise deals. Whether that scaffolding can withstand the dual assault of Microsoft’s distribution juggernaut and the EU’s algorithmic-accountability clauses will determine whether Tome becomes the de facto canvas for AI-native business narratives or another footnote in the annals of productivity software. In the next section we will distil strategic options for customers who must navigate this shifting terrain of value and risk, drawing on field data from early adopters who have already staked quota-bearing targets on generative storytelling.

Strategic Options & ROI in the Age of AI-Native Storytelling
The decision to bring Tome inside the firewall is no longer a design-team whim but a CFO-reviewed investment, judged on the same metrics that govern CRM licences and marketing-automation platforms. Early adopters entered with trepidation yet now report that the platform routinely turns content assembly—the manual hunt through past decks, call notes and brand guidelines—into a sub-fifteen-second background process. The $200 million war-chest Tome secured at the end of 2024 crystallises the stakes: investors will tolerate the eye-watering GPU bill only if customers can document faster deal velocity or lower churn after deployment.
That documentation begins with a deceptively small data point: slide-level dwell time. When prospects linger on a cost-savings page 3× longer than on a feature rundown, the signal travels back through Tome’s analytics API into Salesforce as an engagement score, allowing revenue teams to A/B-test narrative structures the way growth hackers iterate landing pages. Companies that wire this loop correctly no longer debate “Is AI worth it?”; they compare revenue-per-rep before and after generative decks became the default. Zapier’s independent review of seven AI presentation makers underscores why such feedback telemetry is becoming table-stakes—without it, an app is little more than an automated slide template (zapier.com).
Still, no amount of analytics offsets regulatory drag. The final text of the EU AI Act lists “personalised persuasive content that can materially influence decisions” among the functions subject to strict ex-ante risk assessments. In practical terms each ingestion event—be it a Gong transcript or an M&A forecast—must be tied to an explicit lawful basis and remain audit-traceable for at least five years. Enterprises eyeing cross-border roll-outs have begun to insert retrieval ledgers into their procurement addenda: for every deck, Tome must emit a machine-readable file that maps each generated paragraph to its vector-store source. One Paris-based pharmaceutical firm claims this ledger shaved three weeks off its Article 10 Data Protection Impact Assessment because compliance teams could verify, in minutes, that no personal-health datum crossed into marketing copy.
Governance alone, however, will not protect margins if brand voice drifts or numbers hallucinate. Tome’s answer—a style-corpus cosine-filter coupled with numeric back-checks—illustrates how prompt ops is turning into an operational discipline on par with DevOps. Marketing directors who once fought “GPT-isms” line-by-line now receive drafts that rarely deviate from approved tone; finance teams see EBITDA figures appear only when the retrieval layer can surface a timestamped source, reducing escalation loops to near zero. These internal gains mirror the external pressure of Canva’s Magic Design and similar point-and-click rivals that promise speed but not necessarily verifiability (canva.com). Tome’s long-term moat therefore rests less on generating copy and more on proving every sentence’s provenance in a way auditors can replay.
Yet even perfect provenance is meaningless if switching costs remain low. Microsoft’s slow but inevitable march toward a DoD-grade Copilot for PowerPoint—already piloted in GCC Moderate and slated for GCC High later this year—reminds CIOs that a bundled option will soon tick most compliance boxes by default. Tome’s response has been to intertwine itself with revenue intelligence so tightly that abandoning it would mean dismantling conversation-insight loops and re-engineering brand-token caches inside another vendor’s ecosystem. The April 2024 workforce realignment, which shifted head-count from consumer “wow” features to enterprise connectors, signals where leadership sees the moat: not in prettier slides, but in the friction it would take to re-create a live linkage between call-recording analysis, CRM telemetry and instantaneous deck regeneration.
Financial pragmatism now shapes rollout templates. The playbook field-tested by a dozen mid-market SaaS firms proceeds in three passes. Phase one wires a read-only Salesforce connector and generates decks for internal consumption, capturing baseline analytics. Phase two injects call-transcript embeddings, unlocks external share-links and overlays a Slack approval gate to placate legal. Phase three pushes deck-engagement telemetry back into the forecast model so quota-carrying reps can trigger next-step cadences without manual judgment. The result, measured across two fiscal quarters, is the shift of narrative preparation from a cost centre to a compounding signal engine: each meeting generates data that sharpens the next meeting’s story, shrinking the cycle until story and insight merge in real time.
Underpinning all three phases is a sober cost model that values compute predictability over theoretical model accuracy. Tome’s proprietary “layout interpreter” converts GPT prompts into reusable design tokens—colours, spacing ratios, font scales—dramatically reducing the token footprint required for regenerations. Finance teams inside Tome openly admit that the interpreter is less about clever design and more about maintaining a flat cost curve as usage grows. Clients briefed on these economics discover a hidden upside: a stable per-deck variable cost means ROI calculations can be made with the same clarity as email-automation or paid-media spend. When GPU costs spike, the interpreter’s caching keeps invoices stable; when API prices fall, savings pass through to the margin without fresh procurement cycles.
Viewed from the balcony, the path to durable ROI is a triad: verifiable data grounding, compounding engagement telemetry, and a de-risked cost baseline. Miss any one leg and the stool collapses—vectors without analytics become static brochures, analytics without governance invite regulatory fines, and both without a stable cost layer drown beneath GPU invoices. Firms that assemble the full triad report a new phenomenon: the deck ceases to be a document and becomes a living metric surface whose performance can be queried as easily as pipeline velocity or customer health score.
As competitive pressure intensifies and regulatory nets tighten, the strategic advantage tilts toward organisations that treat generative storytelling not as a novelty but as an analytics-native substrate woven into every revenue or learning workflow. Whether Tome can hold that ground against the Microsofts and Canvas of the world hinges on its ability to keep the triad intact while continuing to compress the interval between raw signal and narrative output. The early evidence—funding scale, compliance posture, and customer telemetry loops—suggests the race is far from over and that the winners will be those who understand storytelling as data infrastructure rather than graphic design. The next, and final, section will consider how early adopters can translate these principles into concrete action plans over the next four quarters, while hedging against a rapidly shifting competitive and regulatory landscape.

Operational Roadmap & Tactical Playbook — From Pilot Sparks to Enterprise Flame
The preceding sections traced how Tome evolved from a viral curiosity into a compliance-hardened, data-driven narrative engine. Yet the gulf between knowing that fact and realising its value is wide. A surprising number of teams still treat generative decks as ad-hoc “power-user hacks,” scattering one-off experiments across sales pods or marketing stand-ups. Six months later they discover overlapping vector stores, fragmented brand tone, and a CFO who can’t reconcile GPU invoices with pipeline lift. What follows is a quarter-by-quarter, battle-tested implementation pattern that early adopters have converged on—one that translates Tome’s promise into measurable revenue impact while firewalling against the dual threats of compliance drift and platform lock-in.
Quarter 0 — Laying Ground Truth before a Single Prompt Fires
Implementation success begins with a clean corpus. Before connectors are switched on, RevOps exports a de-duplicated set of closed-won decks, the past four quarters of Gong transcripts, and a scrubbed tranche of CRM objects. A modest data-hygiene sprint—normalising field names, excising PII from call notes, tagging every asset with a business-unit owner—pays disproportionate dividends later, because a retrieval layer is only as accurate as its weakest embedding. Security teams meanwhile provision a customer-managed encryption key, ensuring that every artifact dropped into Tome’s vector store is sealed under the firm’s own HSM rotation schedule, satisfying the “data-residency by design” litmus test that EU regulators increasingly expect.
Quarter 1 — Controlled Ignite: Sales-First, Private-Link-Only
The first live prompts run behind closed doors. A pilot cohort—often half a dozen quota-carrying reps—gets access to a read-only Salesforce connector and a private-link-only sharing mode. They assemble internal rehearsal decks, freeing the organisation from external-facing brand and compliance scrutiny while telemetry begins to flow. Within weeks those dashboards reveal where GPT-4 hallucinates (most often on numeric claims) and where stylistic drift emerges (openers tend to skew overly enthusiastic unless grounded in the brand tone corpus). The engineering counter-measure is already baked into the stack: numeric copy fails a provenance check unless a timestamped source exists; paragraphs that exceed a cosine-distance threshold from approved style docs are downgraded in the generation beam search.
The invisible win here is cultural. Reps who once burned afternoons copying slides feel a nine-minute deck prep cycle, then brag about it in Slack. That anecdotal victory legitimises the second, heavier lift: exposing Tome links to live prospects.
Quarter 2 — External Debut: Live-Fire with Legal Air Cover
Legal and brand teams step in now, not as bottlenecks but as automated gate-keepers. Every deck that leaves the workspace triggers a Slack workflow: legal operations receives a one-click side-by-side view of generated copy and provenance ledger. Because Tome’s share links render in a browser, counsel never downloads a file; they skim, approve, and the link activates. Median approval-cycle time after two months drops from two days (traditional slide redlining) to under forty-five minutes, a gain that directly influences buyer momentum in complex deals.
Meanwhile, sales-enablement leads wire slide-level dwell signals back into Salesforce, creating a feedback field that the forecasting model now treats as a leading indicator. When prospects linger on a savings calculation for 190 seconds and bounce off feature slides in twenty, the next deck deemphasises the feature laundry list and foregrounds cost payoff—an automated, data-driven narrative-A/B loop. Early adopters report a three-to-four-point increase in qualified-opportunity-to-proposal conversion after dwell-based iteration became routine.
Quarter 3 — Scaling Sideways: From Sales Pod to Cross-Functional Nervous System
By now the retrieval index is humming with firmographic data, call quotes, and usage telemetry; the marginal cost of expanding to customer success and product marketing collapses. CS managers generate QBR storyboards that weave real-time adoption metrics with renewal benchmarks, slashing preparation hours and deepening executive engagement on renewal calls. Product marketers import backlog epics and beta-program feedback, turning release notes into polished launch narratives overnight. Crucially, governance lines stay intact because every new team inherits the same Slack approval loop and encryption envelope, preventing compliance sprawl.
Quarter 3 is also when finance begins to treat GPU expenditure as a known quantity rather than a wildcard. The proprietary “layout interpreter,” which converts GPT output into reusable design tokens, means that refreshing an existing deck incurs a fraction of the cost of first-time generation. Financial controllers discover that Tome’s cost curve now resembles a messaging-API bill more than an open-ended ML tab—a stabilisation that makes the contract renewals far easier to defend at budget-setting time.
Quarter 4 — Future-Proofing: Hedging Against Incumbent Gravity and Regulatory Fog
The final phase is less about feature rollout and more about platform resilience. Two strategic hedges dominate successful playbooks.
First, dual-stack redundancy. Even the most Tome-loyal CIOs spin up a Microsoft Copilot for PowerPoint sandbox, mapping identical retrieval queries and style guides. If EU regulators tighten high-risk content rules or if a sudden GPU shortage spikes Tome’s per-deck latency, the firm can shift high-priority narratives into a bundled ecosystem without starting from zero. Teams that test this fail-over path quarterly report a median switchover window of six hours, an operational insurance policy that calms board-level risk committees.
Second, incremental agentic workflows. Tomorrow’s decks won’t freeze at send-time; they will mutate in real-time as a buyer raises objections. Pilot customers already run limited “meeting-loop” agents that listen to a live Zoom call, summon fresh metrics from the retrieval layer, and push an updated slide into the same WebGL canvas before the prospect finishes their objection. The governance contract specifies that any slide injected mid-call inherits lineage tags from its generative parent plus a UTC timestamp, satisfying audit loggers without human latency. If such agents graduate to GA next year, early adopters will traverse the learning curve months ahead of laggards.

A Final Word—and an Actionable Bridge
Tome’s trajectory teaches a hard lesson: narrative speed is now a systems-engineering problem, not a design studio exercise. Firms that treat decks as code—traceable, testable, and deployable—unlock compound returns measured in pipeline velocity and churn deflection. Firms that keep presentations in siloed design bubbles will find themselves outrun by competitors whose slides evolve with every click and every call.
Yet even the most elegant deck is only the surface. The connective tissue is conversational. That layer—where a rep, a buyer, or a surgeon voices a question and instantly receives a grounded, compliant answer—is precisely where A-Bots.com operates. Our engineers can develop a custom AI Chatbot that plugs into the same retrieval lattice powering your Tome narratives, surfaces slide snippets, benchmarks, or plain-language explanations on demand, and logs every exchange back into your analytics fabric. The result is a full-circle loop: data informs deck, deck informs chat, chat produces new data, and the cycle compounds. If your roadmap demands that kind of real-time, story-centric intelligence, the next conversation belongs on our calendar—before your competitors schedule theirs.
✅ Hashtags
#TomeAI
#GenerativePresentations
#SalesEnablement
#CRM
#EnterpriseAI
#AICompliance
Other articles
Offline AI Assistant Guide Cloud chatbots bleed tokens, lag and compliance risk. Our 8 000-word deep dive flips the script with on-device intelligence. You’ll learn the market forces behind the shift, the QLoRA > AWQ > GGUF pipeline, memory-mapped inference and hermetic CI/CD. Case studies—from flood-zone medics to Kazakh drone fleets—quantify ROI, while A-Bots.com’s 12-week blueprint turns a POC into a notarised, patchable offline assistant. Read this guide if you plan to launch a privacy-first voice copilot without paying per token.
Types of AI Agents: From Reflex to Swarm From millisecond reflex loops in surgical robots to continent-spanning energy markets coordinated by algorithmic traders, modern autonomy weaves together multiple agent paradigms. This article unpacks each strand—reactive, deliberative, goal- & utility-based, learning and multi-agent—revealing the engineering patterns, safety envelopes and economic trade-offs that decide whether a system thrives or stalls. Case studies span lunar rovers, warehouse fleets and adaptive harvesters in Kazakhstan, culminating in a synthesis that explains why the future belongs to purpose-built hybrids. Close the read with a clear call to action: A-Bots.com can architect, integrate and certify end-to-end AI agents that marry fast reflexes with deep foresight—ready for your domain, your data and your ROI targets.
Inside Wiz.ai From a three-founder lab in Singapore to a regional powerhouse handling 100 million calls per hour, Wiz.ai shows how carrier-grade latency, generative voice, and rapid localisation unlock measurable ROI in telco, BFSI and healthcare. This long-read unpacks the company’s funding arc, polyglot NLU engine, and real-world conversion metrics, then projects the next strategic frontiers—hyper-personal voice commerce, edge inference economics, and AI-governance gravity. The closing blueprint explains how A-Bots.com can adapt the same design principles to build bespoke AI agents that speak your customers’ language and turn every second on the line into revenue.
Offline AI Chatbot Reviews: GPT4All, LM Studio, Ollama and MLC Chat Running large-language models without the cloud is no longer a research stunt; it is fast becoming an operational edge. This article reviews GPT4All’s desktop sandbox, LM Studio’s GUI-driven API hub, Ollama’s container-style CLI and MLC Chat’s phone-native engine. Beyond specs, it follows the human workflow: where data lives, how teams collaborate and why governance surfaces matter. Practical benchmarks, field anecdotes and a three-phase rollout roadmap help CTOs move from laptop prototypes to mobile deployments with confidence. The conclusion outlines how A-Bots.com engineers compress models, fine-tune LoRA adapters and wrap the result in revenue-ready UX.
Beyond Level AI Conversation-intelligence is reshaping contact-center economics, yet packaged tools like Level AI leave gaps in data residency, pricing flexibility, and niche workflows. Our deep-dive article dissects Level AI’s architecture—ingestion, RAG loops, QA-GPT scoring—and tallies the ROI CFOs actually care about. Then we reveal A-Bots.com’s modular blueprint: open-weight LLMs, zero-trust service mesh, concurrent-hour licensing, and canary-based rollouts that de-risk deployment from pilot to global scale. Read on to decide whether to buy, build, or hybridise.
Top stories
Copyright © Alpha Systems LTD All rights reserved.
Made with ❤️ by A-BOTS
