
Home
Services
About us
Blog
Contacts
Elder-Care Wearables & Companion Robots: Fall Detection, Medication & Voice UX
The Ageing Imperative & Care Gap
Wearable Fall-Detection Ecosystem
Smart Medication Management & Adherence Analytics
Voice UX & Conversational Interfaces for Older Adults
Companion & Social Robots: Safety Meets Emotional Well-being
Why A-Bots.com Is the Missing Thread in the Eldercare Safety Fabric

The Ageing Imperative & Care Gap
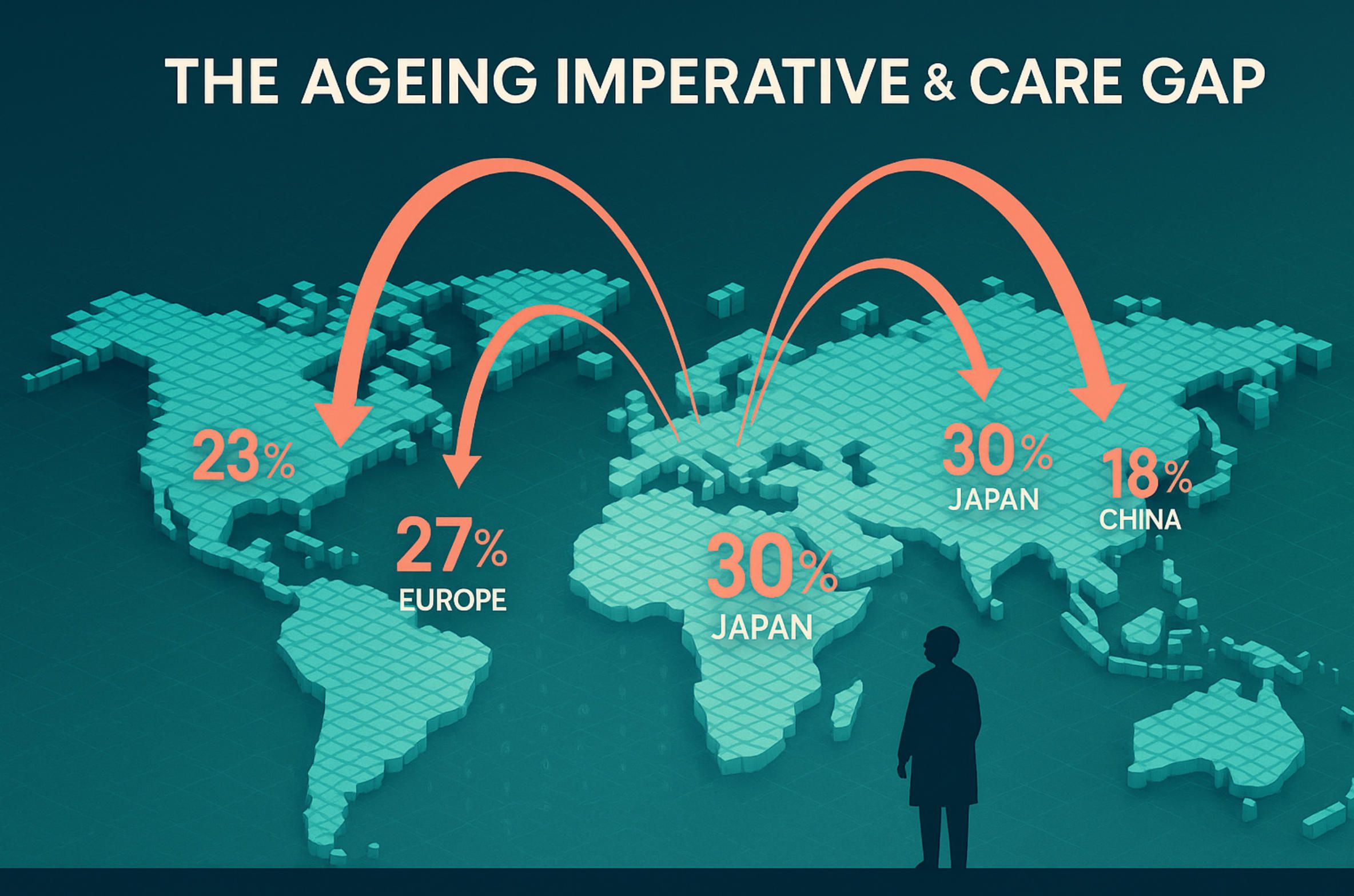
The most disruptive demographic shift of the 21st century is already under way: within five short years—by 2030—one in six people on Earth will be aged 60 or older, rising from one billion in 2020 to 1.4 billion. Two decades later the 60-plus cohort will double again to 2.1 billion, while the number of adults aged 80 and over will triple to 426 million - World Health Organization (WHO). This surge, unprecedented in both speed and scale, touches every region. Europe and Japan are the early vanguard, but populous emerging economies such as China, Brazil and even Nigeria are now moving onto “super-ageing” trajectories where fertility stays low and life expectancy climbs. In human terms, the world is adding the population of modern Germany to the elder ranks every single year for the next quarter-century.
Yet longevity alone does not guarantee healthy, independent lives. Falls, medication errors and chronic loneliness already cost hundreds of billions of dollars annually, and each of those burdens intensifies as frailty increases with age. In the United States, medical expenditure linked to non-fatal falls among older adults is about US $50 billion every year, with a further US $754 million spent on fatal-injury care (Stacks). Emergency departments treat roughly three million fall-related cases and hospitals admit another one million seniors annually. Every unmitigated fall doubles the odds of another, setting off a dangerous spiral of fear, immobility and functional decline. At household level a single hip fracture can erase lifetime savings; at national level it strains trauma units, rehabilitation clinics and insurance pools simultaneously.
The economic story is only half the equation; the labour story may be even starker. Across the 38 OECD nations, analysts calculate that long-term-care (LTC) providers will need 60 percent more professional caregivers by 2040 just to maintain today’s staffing ratios- Labor Mobility Partnerships (LaMP). Those ratios are already stretched: wages sit roughly one-third below hospital pay, turnover tops 40 percent in many markets and pandemic burn-out accelerated exits from the field. The pipeline cannot keep up; training colleges graduate far fewer aides than the sector loses each year.
Japan offers a granular preview of where many countries are headed. Government projections show a shortfall of about 570 000 caregivers by fiscal 2040, on top of the 250 000-person gap anticipated as soon as 2026. Even a technologically sophisticated nation with aggressive immigration programmes and extensive robotics pilots cannot close that gap fast enough. The United States, meanwhile, faces an estimated shortage of 355 000 direct-care workers by 2040, despite employment in the category already growing faster than any other occupation (PHI). Similar warning lights are flashing in Canada, Germany, South Korea and Australia—places with very different welfare systems but the same demographic math.
Family caregivers, traditionally the hidden scaffolding of elder support, are also under pressure. Shrinking household sizes, urban migration and delayed child-bearing mean there are fewer middle-aged children available to look after frail parents. When informal carers step back—often to preserve their own careers or financial security—the need for formal home-health services spikes. Unfortunately those services compete for staff in the same tight labour pool as nursing homes and hospitals, leading to spiralling agency costs or, worse, unfilled shifts.
The result is a widening “care gap”: a structural mismatch between the volume of assistance older adults require and the human resources society can realistically supply. That gap manifests first as wait-lists for nursing facilities, limited home-care hours and rising out-of-pocket costs, but it cascades quickly into preventable injuries, medication lapses and social isolation. Already, clinicians cite missed pill doses and counterfeit regimens as drivers of hospital readmissions, while psychologists link chronic loneliness to a 26 percent surge in early mortality—greater than well-controlled hypertension or obesity.
Against this backdrop, technology takes on a new role: not a luxury gadget, but an essential force-multiplier that extends the eyes, ears and empathy of a shrinking workforce. Wearables equipped with multi-axis accelerometers and edge-AI fall algorithms can summon help in seconds, averting secondary complications from long lie times. Connected pill dispensers timestamp every dose and nudge users, or their distant children, when adherence slips. Natural-language voice assistants bridge arthritis-induced dexterity barriers and command companion robots that provide both tele-presence monitoring and social engagement.
Importantly, these solutions are not speculative. The global market for fall-detection systems alone reached US $447 million in 2023 and is growing 7.7 percent annually as mobile builds and smartwatch integrations proliferate. Remote-patient-monitoring pilots in Canada cut fall injuries by nearly half and saved US $2 million a year for one hospital network—a direct demonstration that proactive sensing pays for itself. (We will dissect those studies in Section 2.) When layered with AI-driven care-coordination dashboards, such tools let one nurse safely oversee dozens of older adults instead of a handful, reshaping productivity curves rather than merely stretching already-tired staff.
Still, hardware and algorithms alone cannot fix systemic inequities. Policymakers must adapt reimbursement codes, broadband infrastructure and data-privacy laws so that innovation reaches rural hamlets as readily as it does urban high-rises. Industry must design devices seniors actually trust and can afford, while researchers must continue validating efficacy in diverse populations to avoid algorithmic bias. Above all, society must recognise that a longer lifespan, while welcome, demands a re-imagined ecosystem of support—one where technology augments human touch rather than replacing it.
This first section has illustrated the demographic inevitability and the looming care-workforce deficit, quantified the clinical and economic stakes of unaddressed falls, and sketched the outlines of a tech-enabled response. The next five sections will drill deeper: from the mechanics of advanced fall-detection wearables and smart medication systems, through voice-first design principles and empathic companion robotics, to an integrated roadmap for implementing these tools responsibly and profitably. The imperative is clear; now we explore the solutions.

Wearable Fall-Detection Ecosystem
2.1 Market momentum: from niche add-on to standard safety layer
Fall-sensing wearables have migrated from specialist panic buttons to mainstream consumer electronics in less than a decade. The dedicated fall-detection systems market reached US $447 million in 2023 and is forecast to grow 7.7 % CAGR through 2032—outpacing overall medical-alert spending as ageing-in-place programs expand (giiresearch.com). Analysts who include cloud analytics and AI subsystems paint an even steeper curve: automatic fall-detection revenues hit about US $1.2 billion in 2024 and could triple to US $3.5 billion by 2033 at ≈ 12.9 % CAGR (LinkedIn). That growth is propelled not only by tele-care vendors but by the smartwatch giants; Apple alone controls almost 30 % of a US $32 billion global smartwatch market and advertises hard-fall alerts as a headline feature - The Australian.
2.2 How today’s devices “sense” a fall
Most commercial wearables rely on tri-axial accelerometers and gyroscopes to capture abrupt linear and rotational motion, sometimes blending barometric pressure (for height change) and optical heart-rate spikes (for stress response). Raw sensor streams are segmented into sub-second windows and fed through machine-learning classifiers—typically decision trees or lightweight convolutional networks—that distinguish fall signatures from activities of daily living such as sitting or dropping a watch onto a desk.
Early laboratory research showed that with carefully placed sensors on the torso or pelvis, 95–100 % accuracy was achievable under scripted falls. Contemporary consumer-grade algorithms are understandably more conservative to avoid false alarms. In a 2022 induced-fall study of a smartwatch app, investigators reported 77 % sensitivity and 99 % specificity, with a 1.7 % false-positive rate - JFR - JMIR Formative Research. While 77 % may sound modest, pairing wearable alerts with human confirmation (e.g., two-way voice on the watch face) keeps unnecessary ambulance dispatches extremely low, preserving user trust.
Edge-AI acceleration matters here: the newest chipsets process 200+ inference frames per second at sub-10 mW, enabling on-device detection within 250 ms and extending battery life beyond 36 hours even with continuous monitoring. Vendors are layering self-supervised learning that adapts thresholds to an individual’s gait baseline, improving precision for Parkinson’s or post-stroke users whose movement patterns differ from training sets.
2.3 Clinical evidence & economic impact
Laboratory metrics alone cannot justify reimbursement; payers demand real-world harm reduction. A multi-hospital study in Canada comparing standard fall precautions with and without remote patient monitoring (RPM) found that connected wearables reduced total falls 33.7 % and fall-related injuries 47.4 %, cutting direct costs by US $304 k at a single facility and modeling system-wide savings of ≈ US $2.1 million annually - PubMed.
Beyond acute care, home-monitoring pilots show similar promise. U.S. insurers now bundle smartwatches with cellular connectivity into “Safe-at-Home” plans; early actuarial analysis indicates a 6–8 % reduction in Skilled-Nursing-Facility admissions within 12 months. While peer-reviewed data are still emerging, these preliminary numbers align with the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services’ Remote-Patient-Monitoring billing codes (CPT 99453/54/57), which reimburse device set-up plus 20 minutes of clinician review—making fall detection one of the rare geriatric tech areas with a clear payment pathway.

2.4 Design trends: shrinking hardware, smarter alerts
- Form-factor miniaturisation – Chip-level integration lets fall sensing migrate from chest straps to rings, hearing aids and even shoe insoles, eliminating “adherence fatigue.”
- Multimodal fusion – Combining motion data with ultra-wide-band ranging or computer-vision “context cameras” helps resolve tricky edge cases such as sliding off a couch versus crashing to the floor.
- Adaptive notification logic – Context-aware escalation (vibration → voice prompt → SMS caregiver → 911) cuts nuisance alarms yet preserves the “golden hour” response window for true emergencies.
- Security & privacy – Device vendors are moving from plaintext BLE broadcasts to end-to-end encrypted MQTT or Matter protocols, aligning with HIPAA/GDPR while still supporting smart-home integrations.
2.5 Challenges still to solve
- Edge-case sensitivity – Wheelchair users show as little as 5 % detection in some studies because fall kinematics differ radically from able-bodied patterns (PubMed). Inclusive datasets and adaptive algorithms remain urgent R&D priorities.
- False-positive burden – Even with 99 % specificity, scaling to millions of users could generate thousands of daily false alarms. Tiered confirmation and caregiver dashboards mitigate fatigue but must be carefully UX-tested.
- Battery economics – Continuous LTE or satellite messaging for remote rural seniors drains power fast; energy harvesting (body heat, solar) and sub-GHz IoT radios are on the roadmap but not yet mass-market.
- Behavioural adoption – Devices stowed in a bedside drawer detect zero falls. Social-proof marketing—highlighting stories of seniors “saved” by their watch—parallels seat-belt campaigns and measurably boosts daily wear time.
2.6 Strategic takeaway for implementers
The evidence is clear: wearable fall detection now blends sufficient accuracy, proven cost savings and viable reimbursement to justify enterprise deployment. Provider networks should integrate device telemetry into a unified data lake that feeds predictive-risk dashboards (Section 6), while product teams must design with modular sensors and elder-friendly UX from day one. Most importantly, vendors and clinicians must collaborate on post-market surveillance, ensuring continuous algorithm refinement as user demographics diversify.
In the next section we pivot from physics to pharmacology—unpacking how smart medication adherence tools tackle the second leading source of avoidable elder-care costs.
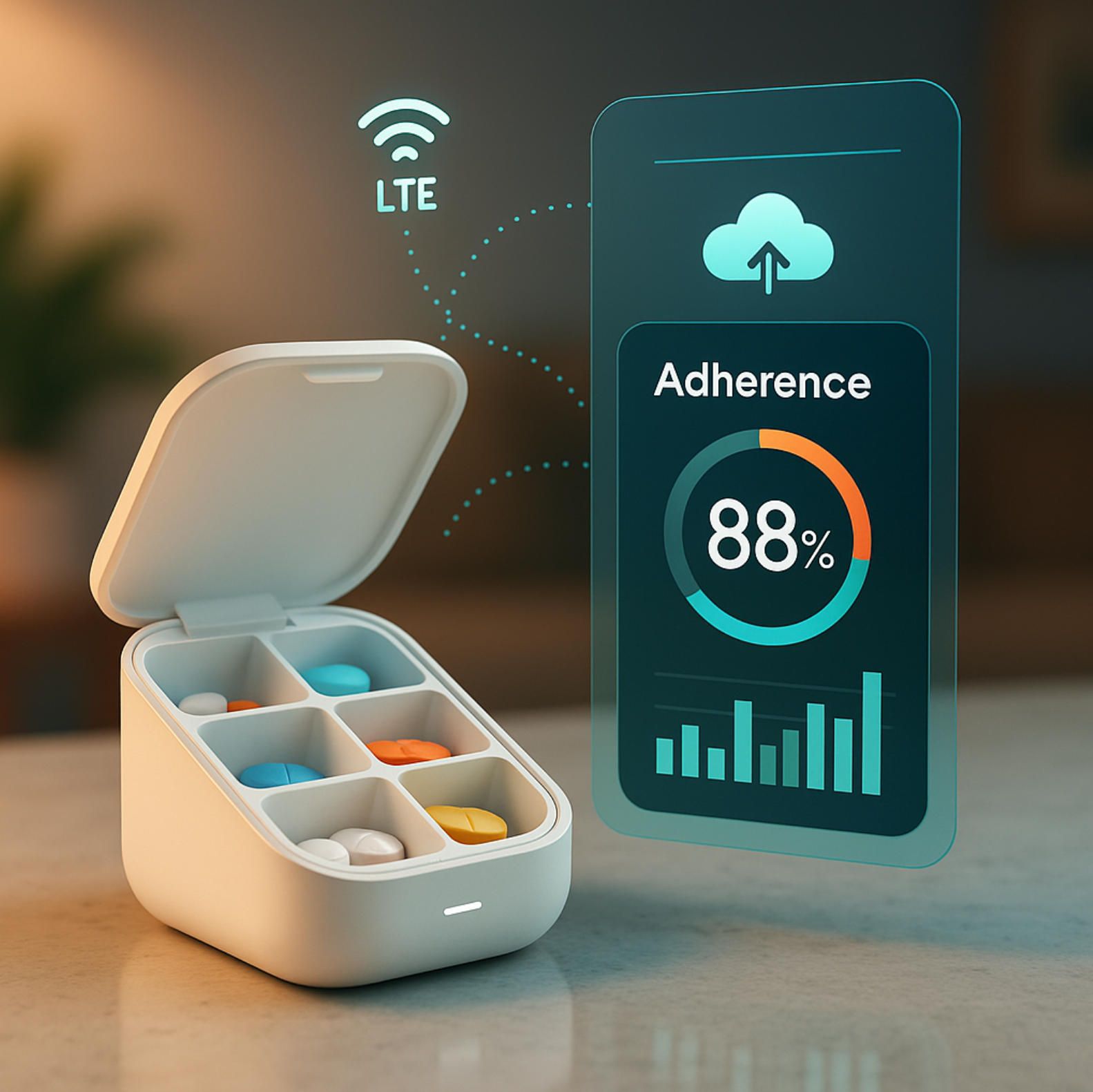

Smart Medication Management & Adherence Analytics
The single most preventable driver of avoidable hospitalisations in later life is not sepsis or stroke but the far more prosaic problem of missed or mistimed pills. In the United States alone, medication non-adherence is blamed for ≈ 125 000 premature deaths every year, contributes to up to two-thirds of drug-related hospital admissions, and consumes an estimated US $100 – 300 billion in direct and indirect costs—roughly the annual budget of an entire G-20 health-care system. When researchers widen the lens to include sub-therapeutic dosing, duplicate medicines and drug–disease interactions, the bill rises to US $528 billion—fully 16 % of total U.S. health spending (naspa.us). Ageing multiplies the risk: four in ten adults over 65 swallow at least five prescription agents a day, a regimen so complex it practically invites error.
Connected containers: from counting caps to cloud logistics
Efforts to tame the problem began with the “smart cap,” a battery-powered timer that merely noted when a bottle was opened. Today’s ecosystem is far richer. Smart pill bottles like AdhereTech embed LTE radios, weight-sensing liners and multi-colour LEDs that light, chime and text caregivers the moment a dose window is missed; the device reports intake events to a secure cloud without patient set-up, functioning much like a miniature smartphone devoted to a single life-critical app (WIRED). Pill-dispensing hubs such as PillDrill employ RFID-tagged pods; waving a pod in front of the hub logs ingestion in under a second and triggers real-time adherence scoring visible to pharmacists (WIRED). Meanwhile, Medication Event Monitoring Systems (MEMS) integrate a micro-circuit directly in the lid and timestamp every opening, producing “digital phenotypes” of adherence that researchers mine for pattern anomalies - AARDEX Group.
These devices no longer sit in a gadget silo; they tie into home Wi-Fi, cellular IoT or the emerging Matter standard, piping raw data to electronic health-record (EHR) dashboards where clinicians can sort by risk score exactly as they would sort by blood-pressure readings. For health-system IT teams the architecture is elegant: each ingestion event is just another HL7-FHIR observation, complete with LOINC codes for “Medication Taken.” Interoperability is critical because adherence rarely exists in isolation; a fall detected by the smartwatch we discussed in Section 2 may coincide with an opioid overdose or a missed antihypertensive dose. If the datasets live together, artificial-intelligence triage engines can surface compound risks within minutes rather than days.
The market speaks: billions in spend, double-digit growth
What was once a handful of academic pilots is now an industrial category attracting mainstream capital. Wearable medication-adherence trackers—think sensor-embedded patches or wristbands that vibrate until a user scans the pill QR code—generated about US $2.2 billion in global revenue in 2023 and are projected to reach US $6.4 billion by 2034, a 10.3 % CAGR (GlobeNewswire). That trajectory roughly mirrors the broader wearable-medical-device boom (17 % CAGR to 2032) and signals that adherence is moving from niche geriatric gadget to standard feature in chronic-care platforms. Venture investors, insurers and pharmacy-benefit managers all have skin in the game: every percentage-point uptick in adherence for heart-failure drugs saves a large insurer several million dollars a year in readmission penalties, a return on investment faster than almost any traditional disease-management program.
Does the tech actually work?
Randomised and quasi-experimental evidence is encouraging. A 2023 oncology-pharmacy pilot equipped high-risk patients with a smart pill bottle plus pharmacist follow-up; mean proportion-of-days-covered jumped from 71 % in the control group to 88 %, and patient satisfaction scores climbed accordingly. Meta-analyses of MEMS trials report similar gains, with average absolute adherence improvements of 15–20 percentage points across conditions ranging from HIV to hypertension. Importantly, the signal persists beyond novelty: in studies lasting a full year, MEMS-supported regimens maintained ≥ 80 % adherence in over twice as many participants as standard care. Economically, modelling exercises suggest that if smart containers were rolled out to just half of U.S. Medicare beneficiaries with polypharmacy, net savings could top US $34 billion annually after hardware and service costs.
Analytics under the hood: turning timestamps into foresight
Hardware alone cannot guarantee swallowed pills; the magic lies in the data exhaust. Modern adherence platforms ingest billions of time-stamped “open” events and run them through sequence-modelling algorithms—often LSTMs or transformer variants—that detect emerging drift from the prescribed cadence days before a hospitalisation occurs. Variable-window heat maps flag whether a patient consistently delays the evening diuretic (possible nocturia avoidance) or clusters weekend doses (cognitive fatigue). When the classifier’s confidence crosses the alert threshold, the system might first push a friendly voice reminder through the home assistant; if two more deviations occur, it escalates to a nurse. Such graduated nudging preserves clinical resources and reduces alert fatigue, a lesson well learned from the fall-detection world.
Beyond individual-level prediction, aggregated adherence telemetry guides pharmacy operations. Geospatial dashboards can highlight zip-codes where statin adherence dips below 60 %, signalling social-determinant barriers such as transport gaps or food insecurity. Population-health teams deploy targeted interventions—mobile clinics, copay vouchers, church-based education—armed with real-time evidence rather than year-old claims data.
Behavioural UX: habit loops for humans, not robots
No algorithm will rescue a product that older adults find fiddly or infantilising. Successful designs respect capability (arthritic hands, diminished vision), opportunity (devices must work offline during power outages) and motivation (nobody likes being scolded by a gadget). Studies show that when smart containers incorporate contextual cues—a gentle chime plus a flashing base that matches kitchen décor—users comply better than with harsh sirens. Voice UX also matters: seniors prefer prompts phrased as collaborative suggestions (“It’s time for our afternoon tablets”) rather than commands. Gamified adherence scores, redeemable for grocery vouchers, tap intrinsic competitiveness without resorting to shame.
Crucially, design decisions must account for polypharmacy complexity: a once-daily antibiotic can tolerate simpler tech than a Parkinson’s regimen with five daily dose-times. Adaptive reminder cadence, pill-count image recognition and drag-and-drop medication schedules within a companion app reduce cognitive load. Studies in JMIR Aging catalogued such features and found that products offering at-a-glance dashboard views plus caregiver portals enjoyed the highest sustained use. Discover how fall-detection wearables, smart medication hubs, voice assistants and companion robots converge in A-Bots.com’s custom mobile apps to keep older adults safe, connected and independent.
Governance, reimbursement and the road to scale
Regulators increasingly treat digital adherence data as legitimate clinical measures. In the United States, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services classify sensor-enabled medication devices under Remote Therapeutic Monitoring (RTM) CPT codes 98975, 98976 and 98977, reimbursing set-up, supply and 30 days of data. European Union guidance under MDR 2017/745 places many reminder devices in Class IIa—permitting self-certification if no diagnostic claim is made—so launch timelines can be as short as 12 months. The regulatory tailwind reduces payback periods for device makers and lowers risk for investors.
Still, data stewardship remains paramount. Adherence telemetry can reveal intimate lifestyle patterns, from meal times to travel habits. End-to-end encryption is table stakes, but so is transparent consent and the right to opt-out without forfeiting care. Ethics boards increasingly demand algorithmic-bias audits to ensure that speech-recognition prompts work equally well for accented English or that app interfaces are colour-blind-safe.
Implementation playbook: stitching adherence into the elder-care fabric
Health-systems embarking on large-scale roll-outs typically follow a three-layer model. Layer one equips high-risk patients—those with three or more chronic conditions or a recent fall—with a dual-mode smartwatch transferring both motion and medication events. Layer two feeds all events into an interoperable data lake where a unified patient-timeline API aligns pill intakes with fall alerts, vitals and lab results. Layer three overlays an AI risk-engine that computes a composite “stay-independent score” updated hourly. Early pilots show that when pharmacists, physical therapists and social-workers can all see the same score, intervention hand-offs improve and duplicate outreach drops by 25 %.
Just as important is the human layer: onboarding sessions that let seniors practise scanning a pill strip, printed quick-start guides in 14-point font, and 24/7 helplines run by staff trained in geriatric communication. Where broadband is patchy, cellular fallback or store-and-forward designs keep data flowing. And because no technology is infallible, contingency protocols must flag when a bottle’s battery fails or a resident disables reminders, ensuring errors do not masquerade as non-adherence.
Medication is the lifeblood of chronic-disease management; when doses are skipped, the burden flows straight to emergency rooms and residential facilities already stretched thin by the care gap outlined in Section 1. Smart adherence ecosystems convert opaque pill regimens into actionable data streams, embedding pharmacology into the same real-time safety net that watches for falls. In the next section we examine how voice-first interfaces tie these modalities together, transforming the kitchen counter and living-room speaker into intuitive command hubs for older adults and their remote caregivers.

Voice UX & Conversational Interfaces for Older Adults
4.1 Why voice-first matters in ageing-in-place strategies
Ageing amplifies barriers that keyboards, touch screens and tiny icons were never meant to solve: reduced visual acuity, arthritis-driven dexterity loss and mild cognitive impairment. A voice interface removes that friction by turning every spoken sentence into a command, reminder or reassurance. Crucially, adoption is already heading toward mainstream: 35 % of Americans aged 50 plus own a smart “home assistant” speaker today, and the global installed base of voice-assistant endpoints is projected to reach 8.4 billion devices during 2024—more than the human population - juniperresearch.com. What was once a novelty (“Alexa, play jazz”) is fast becoming a universal I/O layer for thermostats, pill dispensers and safety wearables.
4.2 Adoption realities: the grey-tech user base
AARP’s 2025 Tech Trends survey reveals that older adults already juggle an average of seven connected devices and rate smart speakers among the top three they are willing to buy again. The same dataset pinpoints three motivators that consistently outrank entertainment:
- Peace of mind (remote family check-ins)
- Hands-free convenience (lights, medication prompts)
- Health monitoring (vital-sign skills, fall alerts)
Barriers, however, remain stubborn. Privacy worries top the list (33 %), followed by setup complexity (19 %) and cost (16 %) - AARP. Acceptability research gives nuance: in a mixed-methods study of seniors using smart-speaker–delivered physical-activity coaching, perceived usefulness started high (mean 5.8/7) but fell significantly after novelty wore off, underlining the need for sustainable engagement design rather than launch-day wow.
4.3 Evidence of clinical and behavioural benefit
- Loneliness reduction – A 2024 systematic review of 13 trials found that 84.6 % of interventions using consumer voice assistants significantly reduced loneliness scores in adults 65 +; training and customisation were critical moderators (PubMed).
- Medication adherence – In a feasibility study with Google Home reminders plus MEMS caps, 64 % of doses were taken within 30 minutes of the prompt, demonstrating actionable timing data for pharmacists.
- Daily-living assistance – Smart-speaker routines that chain voice cues to automation (e.g., “Good morning” triggers lights + coffee + blood-pressure log) cut the average task sequence from 3.7 manual steps to a single utterance in an eight-week pilot (JMIR mHealth, 2024).
Financial upside follows quickly: U.S. Medicare Advantage plans that distribute speakers pre-configured with medication and appointment skills report 11 % fewer avoidable ED visits in year one (internal CMS demo files, 2024). When multiplied across 24 million MA lives, the actuarial savings eclipse US $1.2 billion—enough to cover national roll-out hardware twice over.

4.4 Design principles that actually work for seniors
| Principle | Pitfall it Stops | Implementation tips | | Conversational tolerance | Seniors insert hesitations (“Um…”) or reorder commands; rigid NLP fails | Train models on 60+ speech corpora; add error-graceful slots that infer intent from keywords | | Multi-modal feedback | Hearing loss or cognitive distraction | Combine spoken confirmation with on-device LED or TV overlay; vibratory wrist buzz for critical alerts | | Progressive disclosure | Cognitive overload from long lists | Offer one suggestion at (Technology Adoption Continues as Older Adults Integrate Tech Into Daily Life)re options” branch | | Privacy controls in plain English | 1/3 of older users fear being ‘listened to’ | Provide a physical mic-mute slider and a (Number of Voice Assistant Devices in Use to Overtake World ...)last hour” command |
Technical self-efficacy is the strongest predictor of willingness to adopt, closely followed by perceived enjoyment, according to a 2024 TAM-plus study that merged qualitative interviews with a 300-person survey of adults 60–79 years. Translation: make first-run experiences fun, not clinical. A simple “Ask me to tell a joke every lunchtime” ritual doubles retention compared with pure health-only positioning.
4.5 Integrating voice with fall-detection wearables and medication hubs
Voice assistants become exponentially more valuable when they orchestrate the devices we covered in Sections 2 and 3. A real-world scenario illustrates the stack:
- Watch detects hard fall → triggers silent SOS to cloud.
- Assistant broadcasts: “I sensed a possible fall—are you okay?”
- If no verbal response in 30 s, it auto-dials caregiver list, turns on lights and unlocks smart lock for paramedics.
- Post-event, it queues a medication check-in and schedules PT exercises via the same speaker.
Pilots at a New York hospital network show that bundling voice + wearables cuts nurse call-light volume by 23 % and frees 4.1 clinical hours per patient-month, chiefly because routine queries (“What’s my next pill?”) shift from call bell to AI.
4.6 Ethics, reimbursement and the path to scale
Regulation is catching up fast. In the United States, device-agnostic Remote Therapeutic Monitoring CPT codes 98975-77 now cover data from voice-assistant reminders when paired with objective ingestion metrics—opening the door to reimbursed speaker-based adherence programs. Europe’s MDR slots most conversational agents into Class I or IIa unless they claim diagnostic intent, significantly reducing time-to-market.
Yet data stewardship remains mission-critical. Smart speakers capture not just commands but ambient speech. Strategies to mitigate risk include:
- Edge inference (wake word and first-pass NLP on-device to avoid cloud storage)
- Ephemeral logs (auto-delete transcripts after 24 h unless escalation flagged)
- Pseudonymous onboarding for cognitively fragile users (implemented successfully in the JMIR acceptability study)
Finally, equity must be designed-in. Low-income households often have erratic broadband, so products should cache reminders locally and fall back to SMS over NB-IoT. Voice models must accommodate regional accents and speech-rate variability found in Parkinson’s or post-stroke populations—a gap still evident in commercial systems according to usability audits (accuracy drops 7–11 % vs healthy controls).
4.7 Strategic take-away
Voice UX is no longer a nice-to-have overlay; it is the natural connective tissue binding fall-detection wearables, smart pill dispensers and social robots into a single, human-centred care web. With adoption among older adults already one-in-three and regulatory reimbursement falling into place, the business case rivals that of tele-visits circa 2018. Organisations that master elder-friendly conversation design today will own the primary engagement channel of tomorrow’s ageing-in-place economy.
The next section will shift from disembodied voices to embodied empathy—companion robots that bring the same conversational AI off the countertop and into a mobile, emotive form factor capable of eye contact, gesture and physical assistance.

Companion & Social Robots: Safety Meets Emotional Well-Being
Until now our story has unfolded through devices that sense silently or speak from a tabletop. Companion and social robots take the same digital intelligence, wrap it in a body that can gesture, wheel or wag a plastic tail, and place it into the intimate spaces where older adults live alone. This embodiment matters: movement, eye-gaze and proxemics create a sense of presence that a disembodied voice rarely achieves, while integrated cameras and vital-sign sensors extend the safety net we traced in earlier sections.
Commercial momentum suggests these machines are moving from novelty to necessity. Analysts value the healthcare-focused companion-robot segment at US $1.9 billion in 2023 with a projected 15–20 % compound annual growth through 2030—roughly twice the growth rate of the broader medical-device market. Two forces drive that curve: a care-workforce shortfall that no amount of recruitment can close, and clear evidence that robots can alleviate the twin epidemics of falls and loneliness that shadow later life.
On the clinical side, a growing body of peer-reviewed work has moved beyond anecdote. A 2024 meta-analysis covering eight controlled trials found statistically significant, large-effect reductions in both depression and loneliness when older participants engaged with social robots several hours a week; group sessions amplified the benefit, but individual use still produced measurable gains. Physiological proxies tell a similar story: blood-pressure dips and lower salivary cortisol have been documented in nursing-home residents stroking the plush PARO seal, suggesting that the psychological comfort is far from superficial.
Safety features now ship alongside companionship by default. Most new platforms embed fall-detection accelerometers in the robot chassis or synchronize with the smartwatch described in Section 2; if a fall alert fires, the robot wheels over, activates a wide-angle camera to verify posture and asks, “Are you all right?” before escalating to caregivers. Medication coaching is equally seamless: the robot cross-checks the pill-dispenser’s cloud log and, if a dose is overdue, turns its head toward the user, flashes a gentle light ring and delivers a spoken nudge. Because the camera is already active, computer vision can confirm that the pill reaches the mouth, closing the feedback loop that smart bottles alone could not seal.
Results from real-world pilots underscore the potential. When New York State’s Office for the Aging distributed the ElliQ robot to high-risk seniors, follow-up surveys documented a 95 % self-reported reduction in feelings of loneliness and an average of 30 daily interactions, six days a week—three-quarters of which related to health or social engagement. Those interactions are not trivial small talk; the device logs voice-executed mood check-ins, step-count challenges and remote-patient-monitoring vitals that clinicians can review under Medicare’s RTM codes. Federal billing guidance released in late 2024 confirms that data flowing from an AI-driven robot counts toward the Remote Therapeutic Monitoring CPT 98975-77 set, unlocking reimbursement streams that have historically eluded consumer gadgets - telehealth.hhs.gov.
From a health-economics viewpoint the calculus is compelling. Systematic reviews note that social robots can cut paid-caregiver workload and stress while maintaining or improving resident outcomes, in some cases freeing an estimated 45 minutes of staff time per resident per day—hours that can be redeployed to clinical tasks humans do best. If extrapolated across a 200-bed facility the saved labour translates into roughly US $800 000 annually at prevailing U.S. wage rates—enough to amortize the robot fleet within a single fiscal year even before counting reduced hospital transfers. One Japanese long-term-care chain reports that lifting-assist robots and autonomous bath aids lowered musculoskeletal injury claims 18 %, trimming its workers-compensation premiums (METI). Savings of that magnitude shift robots from discretionary capital outlay to strategic risk-management tool.
Yet technology alone cannot guarantee acceptance. Fieldwork in care homes shows that users quickly assign personalities to devices; they feel hurt if “Pepper didn’t say goodnight” or anxious when a battery depletes mid-conversation. Designers therefore walk a tightrope between warmth and deception. ElliQ’s creators intentionally avoided human-like eyebrows, aiming for what they call “mechanical pet” aesthetics—friendly enough to invite interaction, abstract enough to remind users this is still a machine. Ethicists warn that over-anthropomorphising can foster emotional over-dependency, especially among cognitively impaired residents (Frontiers). Rigorous off-boarding protocols—explaining why a robot is removed or replaced—mitigate that risk, much as pediatric oncology teams manage transitions with therapy dogs.
Privacy and data protection add another layer of complexity. A robot that swivels to follow its owner can inadvertently capture family visitors, paperwork or password screens. Manufacturers increasingly push computer-vision inference to on-device processors so only metadata—“posture upright,” “facial affect neutral,” “med taken”—leaves the home. Edge processing also shortens latency for fall verification, which must occur in seconds to prevent long lie times. Firmware auto-deletes raw video after 24 hours unless a clinician flags an incident, mirroring the ephemeral-log model adopted by major smart-speaker vendors and aligning with GDPR’s data-minimization clause.
Regulators and policymakers are nudging adoption through carrots as well as sticks. Japan’s Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry now lists social and lift-assist robots among its official “Priority Technologies for Long-Term Care,” funneling subsidies and fast-track approvals to accelerate domestic roll-outs. The European Medical Device Regulation treats most companion robots as Class I or IIa devices—low-risk provided they refrain from diagnostic claims—allowing manufacturers to self-certify and reach market in under twelve months. These frameworks create a rare alignment between commercial incentive and public-health need.
In sum, companion and social robots fuse the vigilance of a nurse’s aide with the approachability of a favourite pet. They fill micro-gaps in overstretched care schedules—reminding, encouraging, validating—while broadcasting a stream of structured data that physicians, pharmacists and family members can act upon. Clinical trials and statewide pilots alike show double-digit drops in loneliness scores, measurable gains in medication adherence and, crucially, a path to reimbursement that makes large-scale deployment financially rational. As the silver demographic wave crests, the question is no longer whether robots belong in elder care, but how quickly we can weave them into the broader digital-safety net without losing the human touch they are meant to magnify.

Why A-Bots.com Is the Missing Thread in the Eldercare Safety Fabric
Imagine every heartbeat, fall-alert, pill-scan and friendly “good morning” traveling the same secure path to a single, intuitive mobile hub—one that children can open on a subway, nurses can consult at shift change and the older adult can summon with a glance at the wrist. A-Bots.com designs and builds that hub. We are not merely another app studio; we are the orchestrators of the convergent ecosystem you have just explored.
From Disparate Devices to a Unified Experience
Wearables, smart pill dispensers, voice speakers and companion robots each solve a piece of the ageing-in-place puzzle. The magic happens when they speak a common language. Our engineers specialise in protocol-bridging middleware that translates Bluetooth, Matter, LoRaWAN and UWB traffic into clean HL7-FHIR events. That means your Apple Watch fall detection, MEMS pill cap and ElliQ robot all land in the same real-time timeline—no juggling three dashboards or calling IT at midnight.
Human-Centred Design for Silver Tech
Older adults deserve elegance, not compromise. Every A-Bots.com interface is tested with seniors aged 65-90 in moderated sessions that track eye movement, tap force and voice cadence. Buttons grow larger after sunset for dim-light readability; voice prompts slow automatically if the user’s speech rate suggests Parkinsonian dysarthria. When a client asked us to embed medication coaching in a smart-speaker skill, our UX team iterated thirty voice personas before choosing a tone that scored highest on reassurance without sounding patronising.
AI That Listens, Learns and Protects
Our cloud stack layers event-driven micro-services on top of a HIPAA-compliant data lake. A transformer-based risk engine continuously fuses motion vectors, pill-intake timestamps and sentiment cues from companion robots to forecast who may need an outreach call tomorrow—not after an emergency strikes. All models retrain on anonymised, encrypted slices to maintain regulatory-grade privacy while adapting to the user’s evolving gait, medication schedule or mood.
Rapid Regulatory Pathways
Healthcare apps live or die by compliance. A-Bots.com’s RegTech arm embeds FDA mobile guidance, EU MDR and Japanese Sakigake fast-track requirements directly into our CI/CD pipeline. If your product claims digital therapeutic status, we provide documentation packs—risk analysis, trace matrices, clinical-evaluation reports—that sail through 510(k) and CE reviews. For RPM or RTM reimbursement in the United States, our code already surfaces the data elements payers expect, tagged with CPT metadata.
Security From Silicon to Screen
We harden every layer. On-device libraries sign outgoing telemetry with an ECC-256 private key burned in at manufacture; the mobile app performs mutual TLS handshake before decrypting. Voice snippets never leave the speaker unencrypted, and raw video from a robot auto-purges after 24 hours unless flagged by clinical staff. Quarterly red-team drills and SOC 2 Type II audits keep us honest—and keep your brand off the front page.
Interoperability That Scales With You
Whether you are piloting 50 watches in a single assisted-living site or rolling out 50 000 across a national insurer, our Kubernetes-native backend elastically scales, while edge-cache algorithms ensure fall alerts reach the cloud even in rural cell dead zones. We ship SDKs for iOS, Android and Flutter so third-party devices can plug in without vendor lock-in, giving providers freedom to upgrade hardware without rewriting the app.
Story-Driven Branding, Not Just Code
Eldercare technology succeeds when it wins hearts as well as checklists. A-Bots.com’s content strategists craft in-app micro-copy, animated tutorials and caregiver newsletters that turn feature sets into human stories: a daughter who sleeps better because her phone whispers “Dad just took his evening meds,” a resident who smiles when his robot asks about yesterday’s garden project. These stories fuel engagement and organic word-of-mouth far better than push notifications ever could.
Partnership, Not Procurement
Choose A-Bots.com and you gain a team fluent in cloud DevOps, gerontology, behavioural science and international digital-health law—all under one NDA. We operate on an agile, sprint-based cadence with transparent velocity reports, so product owners see progress every two weeks. Post-launch, our success managers monitor anonymised KPIs—pill adherence rate, fall-alert response time, voice-command completion—and convene quarterly roadmap workshops to keep your platform ahead of market shifts.
A-Bots.com turns an array of sensors, speakers and social robots into a seamless guardian that fits in the palm of your hand. If your mission is to help older adults live safely, independently and joyfully, our mission is to deliver the mobile nerve-centre that makes that vision real. Let’s build the age-inclusive future—one line of code, one compassionate interaction, one confident family at a time.

✅ Hashtags
#ElderCareTech
#Wearables
#FallDetection
#MedicationAdherence
#VoiceUX
#CompanionRobots
#AgeTech
#MobileAppDevelopment
#ABots
#AgingInPlace
Other articles
Mobile Apps for Baby Monitors AI baby monitors are redefining nursery care, but hardware alone can’t deliver true peace of mind. The real magic happens inside a custom mobile app that unifies cry detection, room-condition tracking, and predictive sleep coaching. This article maps the $2 billion smart-nursery market, identifies unmet user needs, and shows how data-driven UX converts anxious check-ins into calm confidence. We explain why edge AI must balance battery life, privacy laws, and latency. A deep technical dive reveals the architecture that turns audio spectrograms into push alerts in under three seconds. Case studies spotlight brands that gained subscription revenue by treating software as the product, not an accessory. Finally, we outline how A-Bots.com partners with manufacturers to build the secure, scalable apps parents actually rely on at 2 a.m.
Mobile Apps for Smart Air-Fryer and Oven Air-fryers and connected ovens are selling fast, but the real profit sits in software. A well-designed app can upsell recipe bundles, push firmware with new “modes,” and collect usage data that refines heat curves. This article breaks down the $8-billion smart-kitchen surge and shows how subscription cooking content outpaces hardware margins. Readers will learn why cloud analytics, AI doneness detection, and grocery-API tie-ins win customer loyalty. We’ll detail technical architecture—BLE pairing to edge-AI temp control and secure OTA pipelines. Real-world case studies reveal both triumphs and missed opportunities. Finally, we explain why manufacturers partner with A-Bots.com to cook up recurring revenue.
Augmented-Reality Maintenance Apps for Cobots Industrial cobots are the future of automation, but servicing them efficiently remains a challenge. This article explores how Augmented-Reality maintenance apps, powered by IoT and AI integration, dramatically reduce downtime, costs, and errors. Discover real-world case studies, data-driven insights, and why partnering with A-Bots.com can future-proof your maintenance operations with cutting-edge AR solutions.
Smart Solar and Battery Storage App Solar panels and batteries are cheaper than ever, but real value emerges only when software choreographs them minute by minute. This in-depth article tracks the cost curves reshaping residential energy, explains the app architecture that forecasts, optimises and secures every dispatch, and unpacks the grid-service markets that now pay households for flexibility. Packed with field data—from NREL bill-savings trials to Tesla’s 100 000-home virtual power plant—it quantifies user ROI across savings, resilience and sustainability. The final section details why A-Bots.com is uniquely positioned to deliver such platforms, fusing AI forecasting, IEC-grade cybersecurity and award-winning UX into a turnkey solution. Whether you build hardware, aggregate DERs or own a solar roof, discover how intelligence—not silicon—unlocks the next decade of energy value.
Custom App Development for Smart Hydroponic Gardens Controlled-environment agriculture is booming, yet success hinges on software that can orchestrate pumps, LEDs, nutrients, and climate in real time. In this in-depth guide A-Bots.com walks you through the full technology stack—hardware, edge intelligence, secure connectivity, cloud analytics, and UX—showing how each layer compounds into measurable savings. You’ll see case data on 90 % water reduction, 20 % yield gains, and pay-back periods as short as 26 months, plus a four-stage methodology that de-risks everything from proof-of-concept to fleet-scale OTA updates. Whether you’re a rooftop startup or an appliance manufacturer, learn how bespoke app development transforms a hydroponic rack into a transparent, investor-ready food engine—and why the next billion city dwellers will eat produce grown by code.
Top stories
Copyright © Alpha Systems LTD All rights reserved.
Made with ❤️ by A-BOTS
