
Home
Services
About us
Blog
Contacts
From Tamagotchi to AI Companions: The Evolution of Interactive Robots and the Future of Modular Companion Systems
A Comprehensive Analysis of Next-Generation Educational, Domestic, and Multi-Purpose Robotic Platforms
Executive Summary
The landscape of interactive toys and companion devices has undergone a remarkable transformation since the introduction of the Tamagotchi in 1996 and the Furby in 1998. What began as simple electronic pets with limited functionality has evolved into a sophisticated ecosystem of AI-powered robots capable of education, emotional support, household assistance, and collaborative problem-solving. This comprehensive analysis examines the historical trajectory of interactive toys, explores the technological foundations enabling modern companion robots, and presents a visionary concept for the next generation of modular, multi-functional robotic systems that can seamlessly transition between roles as educational tutors, household assistants, and collaborative partners.

The global smart toys market, valued at approximately USD 21.40 billion in 2025, is projected to reach USD 38.20 billion by 2030, representing a compound annual growth rate of 12.40 percent. Concurrently, the autonomous robot toys market is expected to grow from USD 8.27 billion in 2024 to USD 31.72 billion by 2032, driven by advances in artificial intelligence, computer vision, and modular robotics. These figures underscore the tremendous commercial potential and consumer demand for sophisticated interactive robotic systems.
This document outlines the technical requirements, functional specifications, and development considerations for a revolutionary modular companion robot platform that combines educational capabilities, domestic utility, and the potential for outdoor applications. The concept emphasizes modularity, swarm intelligence for multi-robot coordination, and advanced AI integration to create a truly versatile robotic ecosystem that transforms science fiction into reality.
Chapter 1: The Historical Foundation of Interactive Electronic Companions
1.1 The Dawn of Virtual Pets: Tamagotchi Revolution
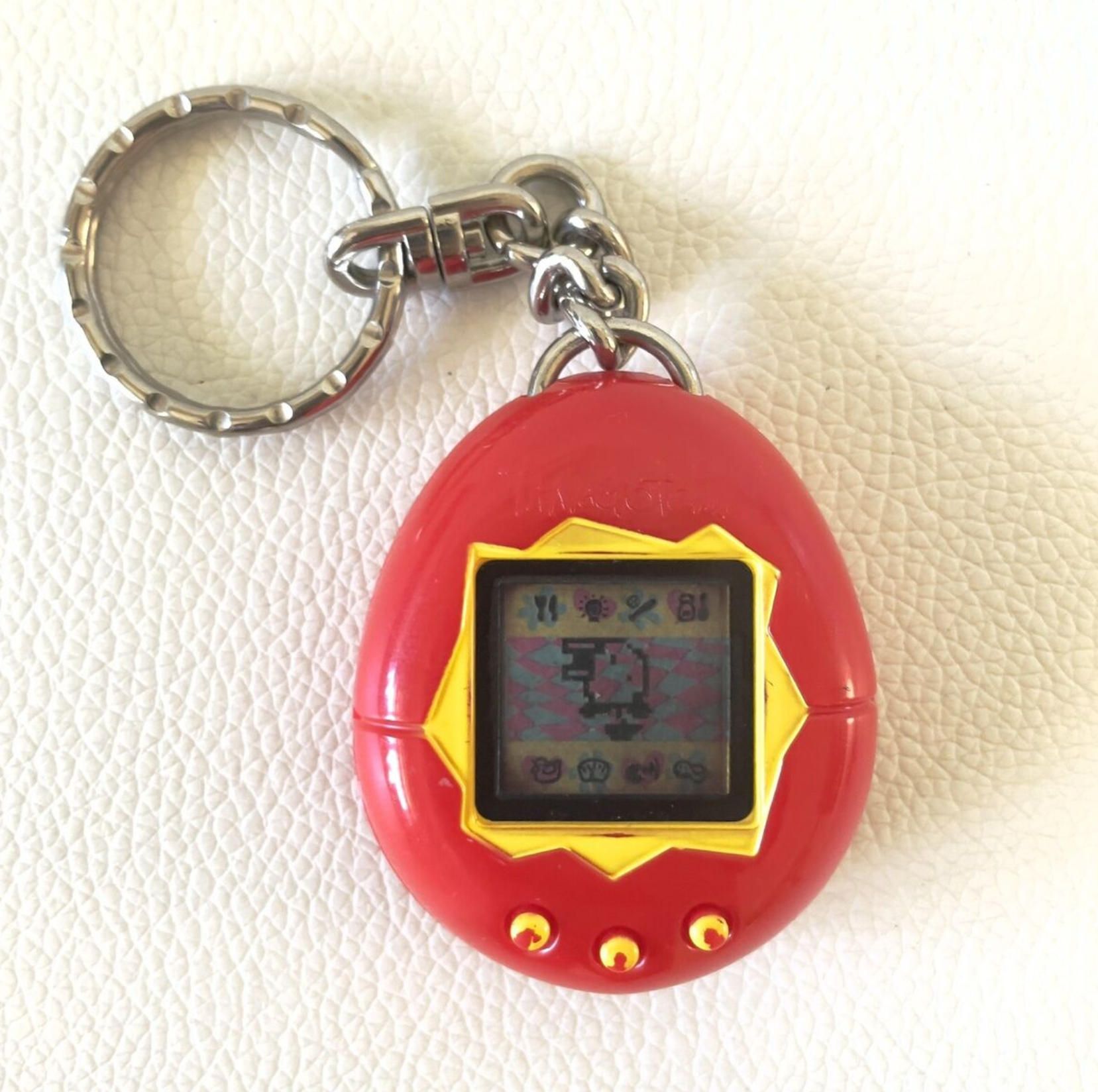
On November 23, 1996, Japanese toy manufacturer Bandai introduced a device that would fundamentally reshape the relationship between children and electronic toys. The Tamagotchi, conceived by Aki Maita and Akihiro Yokoi, emerged from an observation about a child who desperately wanted to bring his pet turtle to kindergarten. This simple desire sparked the concept of a portable virtual pet that could accompany its owner anywhere.
The name Tamagotchi derives from the Japanese words tamago (egg) and uotchi (watch), perfectly describing its egg-shaped design and wearable nature. The device featured a small LCD screen with basic 8-bit grayscale graphics, housed within a keychain-sized plastic shell with just three navigation buttons. Despite its technological simplicity, the Tamagotchi introduced revolutionary gameplay mechanics that demanded continuous emotional investment from users.

Players were responsible for feeding, cleaning, playing with, and nurturing their digital pets through multiple life stages. The consequence of neglect was stark and emotionally impactful: the virtual pet would become ill and eventually die, complete with a ghostly tombstone animation. This mechanic created an unprecedented emotional connection between users and their electronic companions, establishing what researchers later termed the Tamagotchi Effect, describing how humans develop genuine emotional attachments to artificial life forms.
The commercial success was immediate and overwhelming. Within its first year, approximately 20 million units sold in Japan alone, with another 20 million distributed globally. At the height of demand, Bandai reported selling 15 units every minute. The phenomenon spread across more than 50 countries, spawning countless imitations and establishing the virtual pet category as a legitimate market segment. By 2025, cumulative sales have exceeded 98 million units worldwide, with the brand continuing to release new iterations including the Tamagotchi Pix, featuring cameras and social features, and the Tamagotchi Uni, incorporating WiFi connectivity.
The psychological impact of Tamagotchi extended beyond mere entertainment. Schools in multiple countries banned the devices due to classroom disruptions caused by students attending to their virtual pets. Parents reported children experiencing genuine grief when their Tamagotchis died, leading Bandai to modify the American version to show pets transforming into angels rather than displaying gravestones. The Tamagotchi demonstrated that emotional engagement, rather than graphical sophistication, was the key to creating meaningful human-technology relationships.
1.2 Furby: The First Consumer Robot with Personality
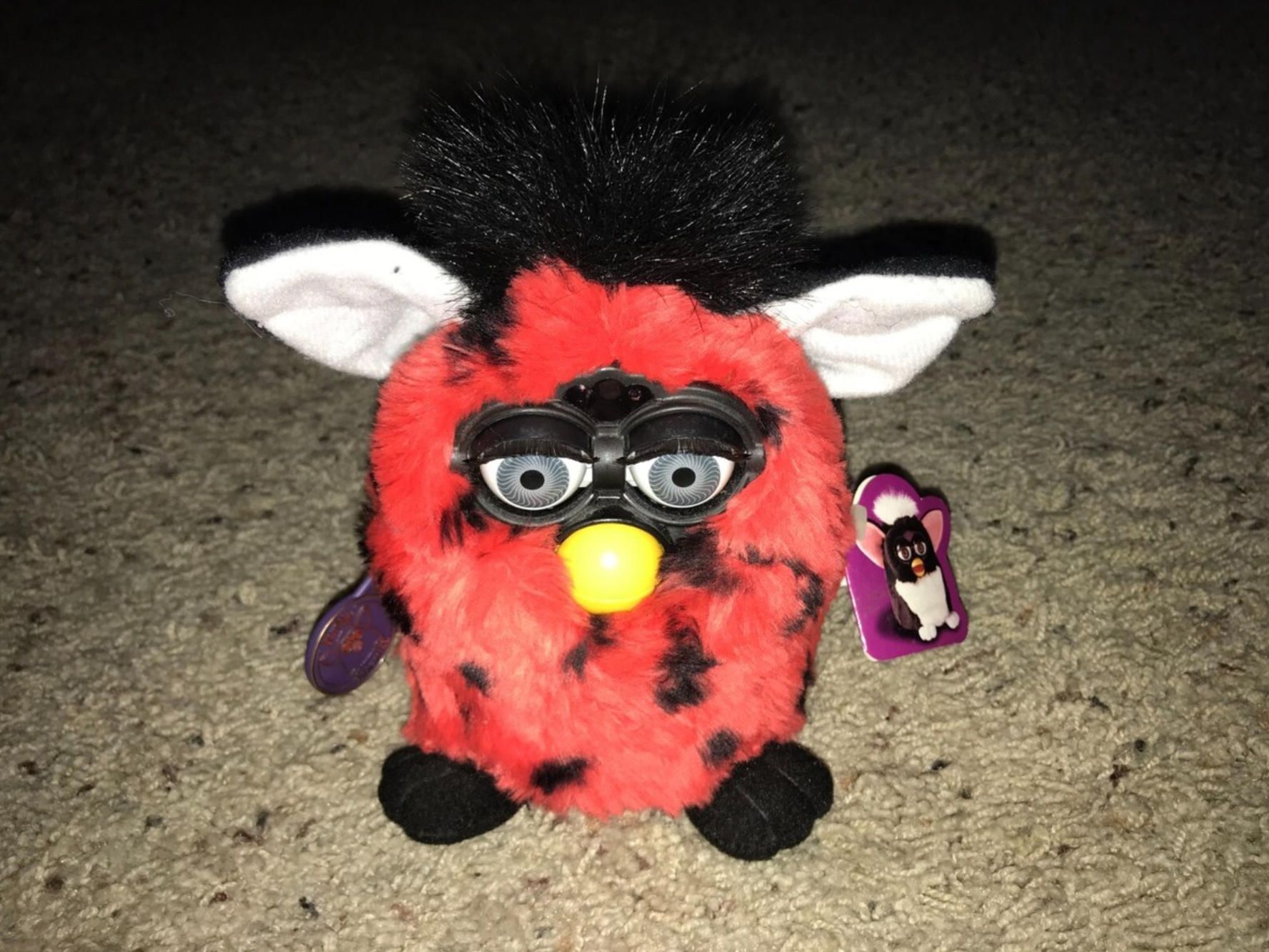
If Tamagotchi introduced emotional attachment to digital creatures, Furby brought that connection into the physical realm. Released on October 2, 1998, by Tiger Electronics (a Hasbro subsidiary), Furby represented the first widely successful attempt to create an affordable consumer robot with apparent intelligence and personality. The creation of inventors Dave Hampton and Caleb Chung, Furby required eighteen months of intensive development to transform from concept to production-ready product.
The technical achievement packed into Furby's compact form was remarkable for its era. The device utilized a Sunplus SPC81A microcontroller, a variant of the venerable 6502 processor architecture, combined with a Texas Instruments TSP50C04 voice synthesis chip. With only 80KB of ROM, engineers created a system capable of simulated language learning, environmental response, and autonomous movement. A single motor driving a sophisticated camshaft assembly enabled Furby to move its eyes, ears, mouth, and body, creating an illusion of lifelike behavior.
The most distinctive feature was Furbish, a proprietary language of 42 words that Furbies spoke exclusively when first activated. Through continued interaction, Furbies gradually incorporated English words into their vocabulary, creating the impression that owners were teaching their electronic pets to speak. This language learning was actually pre-programmed to unlock based on usage time rather than actual learning, but the illusion was sufficiently convincing to captivate millions of users.

Furby's sensory capabilities included light sensors for day-night awareness, touch sensors responding to petting and physical interaction, sound sensors for voice activation, and infrared communication ports enabling Furbies to interact with each other. When two Furbies detected each other via infrared, they would appear to have conversations, sing together, or play games, demonstrating an early form of robot-to-robot social interaction that foreshadowed modern swarm robotics concepts.
The commercial performance exceeded all projections. Tiger Electronics sold 1.8 million units during the 1998 holiday season alone, with demand so intense that resale prices reached USD 300 or more for toys with a USD 35 retail price. Over its initial three-year production run, more than 40 million Furbies were sold globally, with the product translated into 24 languages. The success prompted a memorable security concern when the National Security Agency reportedly banned Furbies from its facilities in January 1999, fearing the devices could record and repeat classified information. Despite Tiger Electronics clarifying that Furbies lacked any recording capability, the incident illustrated how convincingly the illusion of intelligence had been crafted.
Furby's legacy extends beyond commercial success to represent a pivotal moment in consumer robotics. It demonstrated that mass-market consumers would embrace interactive robotic companions at accessible price points, that the appearance of intelligence was more important than actual artificial intelligence for creating emotional bonds, and that physical embodiment significantly enhanced engagement compared to purely screen-based interactions. These principles continue to guide companion robot development today.
1.3 The Evolutionary Path: From Electronic Pets to Social Robots
The period following Tamagotchi and Furby witnessed continuous innovation in the interactive toy and companion robot space. Bandai introduced Digimon in 1997, explicitly targeting boys with battle-capable virtual pets that could connect and fight. Nintendo revolutionized the genre with Nintendogs in 2005, leveraging the DS handheld system's touchscreen and microphone to create remarkably realistic virtual puppies that responded to voice commands and stylus petting.
Sony's AIBO, first released in 1999, represented the premium end of the companion robot market. Priced initially at USD 2,500, AIBO demonstrated that consumers would invest substantially in sophisticated robotic companions. The robot dog featured actual walking capability, visual recognition, and genuine machine learning that allowed personality development over time. When Sony discontinued AIBO support in 2006, devoted owners organized funeral ceremonies for their robotic pets, demonstrating the depth of emotional attachment possible with well-designed companion robots.
The 2010s brought the integration of smartphone connectivity and application ecosystems to interactive toys. Furby returned in 2012 with LCD eyes enabling thousands of expressions and an accompanying mobile app. Sphero introduced programmable robotic balls that taught coding concepts through play. Anki's Cozmo, launched in 2016, combined computer vision, facial recognition, and personality algorithms to create what many considered the most emotionally engaging consumer robot yet produced.
More recently, Moxie from Embodied, Inc. has demonstrated the potential for AI-powered robots focused specifically on child development. Utilizing generative AI, natural language processing, and computer vision, Moxie engages children in play-based learning activities designed by child development experts. Clinical studies have shown measurable improvements in social skills, emotional regulation, and communication abilities among children using the robot regularly. The device represents the convergence of entertainment, education, and therapeutic applications in a single platform.
The Luka reading companion robot, deployed in studies beginning in 2021, demonstrated remarkable longevity of human-robot relationships. Follow-up research in 2025 found that 18 of 19 families retained their reading robots years after the educational intervention ended, even though children had aged beyond the target demographic. Families reported emotional attachments, role transitions where children became teachers to their robots, and repurposing for new functions like music playback. This persistence suggests that well-designed companion robots can become permanent household members rather than temporary novelties.

Chapter 2: Contemporary Market Landscape and Growth Projections
2.1 Global Smart Toys Market Analysis
The smart toys market has emerged as one of the most dynamic segments within the broader toy industry, driven by technological advancement, changing consumer expectations, and growing recognition of educational benefits. According to market research, the global smart toys market size was estimated at USD 21.40 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 38.20 billion by 2030, representing a compound annual growth rate of 12.40 percent during the forecast period.
This growth trajectory is underpinned by several converging factors. Advances in kid-safe large language models have enabled conversational play experiences that adapt in real-time, transforming toys from pre-scripted devices to genuinely interactive companions. Rising parental demand for screen-free learning alternatives has created market space for physical robots that deliver educational content without the concerns associated with tablet and smartphone usage. Regulatory clarity regarding children's data protection has given manufacturers confidence to develop connected products without fear of compliance complications.
Market segmentation reveals interesting patterns. Educational robots represent the fastest-growing category, with projected compound annual growth rates exceeding 14.5 percent through 2030. Interactive games account for approximately 75 percent of market revenue but are growing more slowly as consumers shift toward physical robotic platforms. Smartphone-connected toys captured 45 percent of market share in 2024, leveraging existing mobile hardware for control and display functions while focusing hardware investment on sensors and actuators.
Geographically, North America leads with approximately 34 percent of 2024 global revenue, supported by high disposable incomes and established ed-tech adoption patterns. However, Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region with projected compound annual growth rates of 14.7 percent through 2030, driven by government mandates embedding robotics in educational curricula. China's humanoid robot guidelines and India's USD 3 billion domestic toy manufacturing program are accelerating regional supply ecosystem development.
2.2 Autonomous Robot Toys and AI Companions
The autonomous robot toys market specifically was valued at USD 8.27 billion in 2024 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 18.3 percent to reach USD 31.72 billion by 2032. This segment encompasses self-operating, AI-powered toys that interact with users and environments using sensors and programmable features, serving both educational and entertainment purposes.
The AI robot toy market, focused specifically on artificial intelligence integration, was estimated at USD 2.6 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 9.7 billion by 2035, with a compound annual growth rate of 14.2 percent. The 3-8 years age segment holds approximately 38.2 percent of market revenue, reflecting high demand for early childhood development products featuring AI capabilities that enhance learning, problem-solving, and creativity.
Entertainment robotics presents a broader category including animatronics, companion robots, and interactive devices for theme parks and retail environments. This market is expected to grow from USD 7.127 billion in 2025 to USD 20.190 billion by 2030, representing a compound annual growth rate of 23.17 percent. The growth reflects increasing adoption of humanoid and companion robots in public spaces, advances in AI and motion programming enabling more realistic interactions, and convergence of engineering design with narrative storytelling.
Key market players include established toy manufacturers like Mattel, Hasbro, LEGO, and Spin Master alongside technology-focused entrants like Sphero, UBTECH Robotics, and WowWee. Notably, Mattel, LEGO, Hasbro, Spin Master, and WhalesBot collectively controlled 54 percent of 2024 global revenue, indicating a moderately concentrated competitive landscape with significant room for specialized entrants targeting specific applications or demographics.

2.3 Enabling Technologies: Computer Vision and AI Market Growth
The technological foundation enabling advanced companion robots rests substantially on computer vision and artificial intelligence capabilities. The global AI in computer vision market size was USD 22.93 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 330.42 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 30.58 percent. This dramatic expansion reflects the pervasive integration of visual AI across industries from automotive to healthcare to consumer robotics.
Edge computing advancement has been crucial for consumer robotics applications, enabling real-time visual processing without cloud latency. The global edge computing market is projected to grow from USD 60.0 billion in 2024 to USD 110.6 billion by 2029 at a compound annual growth rate of 13.0 percent. This shift toward local processing reduces latency, conserves bandwidth, and addresses privacy concerns by keeping sensitive visual data on-device rather than transmitting to remote servers.
Self-supervised learning has emerged as a transformative approach for training vision systems without requiring expensive labeled datasets. The technology can reduce labeled data requirements by up to 80 percent while improving model generalization. Market projections suggest self-supervised learning will grow from USD 7.5 billion in 2021 to USD 126.8 billion by 2031, with a compound annual growth rate of 33.1 percent. For consumer robotics manufacturers, this means more capable vision systems at lower development costs.
Vision Transformers have largely supplanted traditional convolutional neural networks for many computer vision applications, processing entire images holistically rather than through sequential convolution operations. Combined with advances in 3D reconstruction and depth sensing, these technologies enable robots to understand spatial relationships, navigate physical environments, and interact with objects in ways previously impossible at consumer price points.
Chapter 3: The Vision: Next-Generation Modular Companion Robots
3.1 Conceptual Framework
The convergence of mature artificial intelligence, affordable sensor technology, advanced robotics, and modular design principles creates an unprecedented opportunity to develop companion robots that transcend the limitations of previous generations. Rather than single-purpose devices that quickly become obsolete or boring, the next generation of companion robots should function as adaptable platforms capable of growing with their users and serving multiple roles within the household ecosystem.
The conceptual foundation rests on three pillars. First, deep artificial intelligence integration enabling genuine understanding, personalization, and natural interaction. Second, modular hardware architecture allowing functional expansion through attachable accessories and peripherals. Third, swarm capability enabling multiple robots to collaborate, communicate, and coordinate activities for enhanced utility and engagement.
This vision transforms what was once science fiction into achievable engineering goals. A child's educational companion can also assist with household chores, patrol for security threats, monitor environmental conditions, and coordinate with sibling robots to accomplish tasks beyond individual capability. The same platform that teaches mathematics through interactive games can attach a vacuum module for floor cleaning, a camera module for home monitoring, or specialized sensors for outdoor exploration.

3.2 Core Artificial Intelligence Capabilities
The central intelligence system must incorporate multiple AI subsystems working in concert. Natural language processing enables conversational interaction in multiple languages with contextual understanding, appropriate responses, and personality consistency. Unlike early Furbies with pre-programmed vocabulary progression, modern companion robots can engage in genuine dialogue, answer questions, tell stories, and adapt communication style to user age and preference.
Computer vision provides environmental awareness through object recognition, facial identification, spatial mapping, and activity understanding. The robot should recognize individual family members, remember their preferences, track their locations within the home, and understand what activities they are engaged in. This visual intelligence enables appropriate responses, whether offering homework help to a child at a desk or avoiding disruption when adults are in a meeting.
Emotional intelligence allows the robot to recognize human emotional states through facial expressions, voice tone, body language, and behavioral patterns. Research has demonstrated that robots providing empathic responses can significantly improve outcomes for children with autism spectrum conditions, extend engagement duration for educational activities, and provide genuine comfort during emotional distress. The system should respond appropriately to detected emotions, offering encouragement during frustration, celebration during achievement, and calm presence during anxiety.
Personalization engines track individual user characteristics, learning progress, preferences, and interaction history to deliver customized experiences. An educational module should adapt difficulty levels based on demonstrated competency, introduce topics aligned with expressed interests, and vary teaching approaches based on what methods prove most effective for each user. A child struggling with multiplication might receive more visual explanations and additional practice problems while an advanced learner receives challenges extending beyond grade level.
Safety systems provide critical guardrails for AI interaction with children. Content filtering ensures all generated responses, stories, and educational materials remain age-appropriate and aligned with parental preferences. Activity monitoring alerts parents to concerning patterns while respecting reasonable privacy. Physical safety algorithms prevent dangerous movements, collisions, or behaviors that could harm children or damage property.
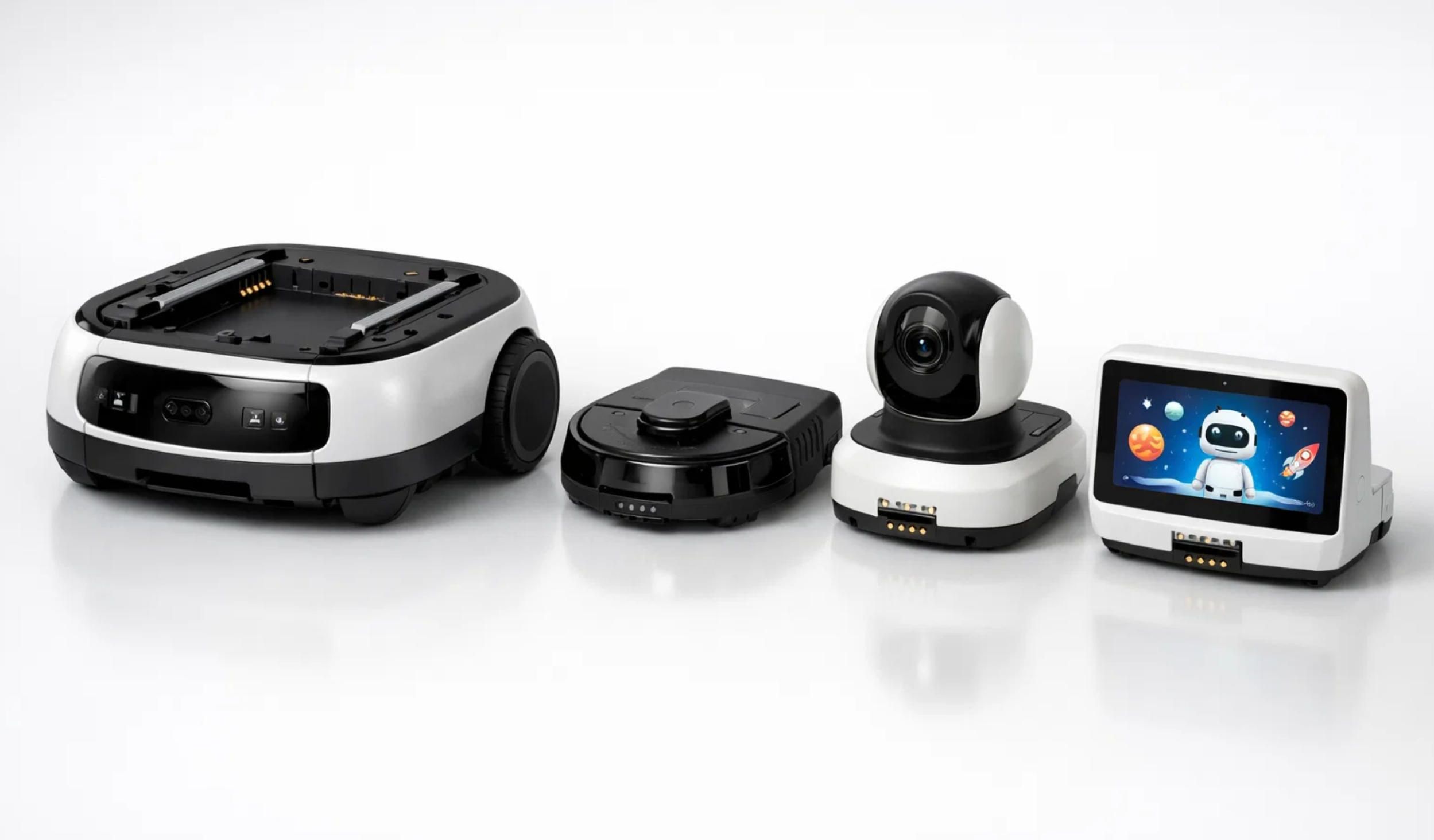
3.3 Modular Hardware Architecture
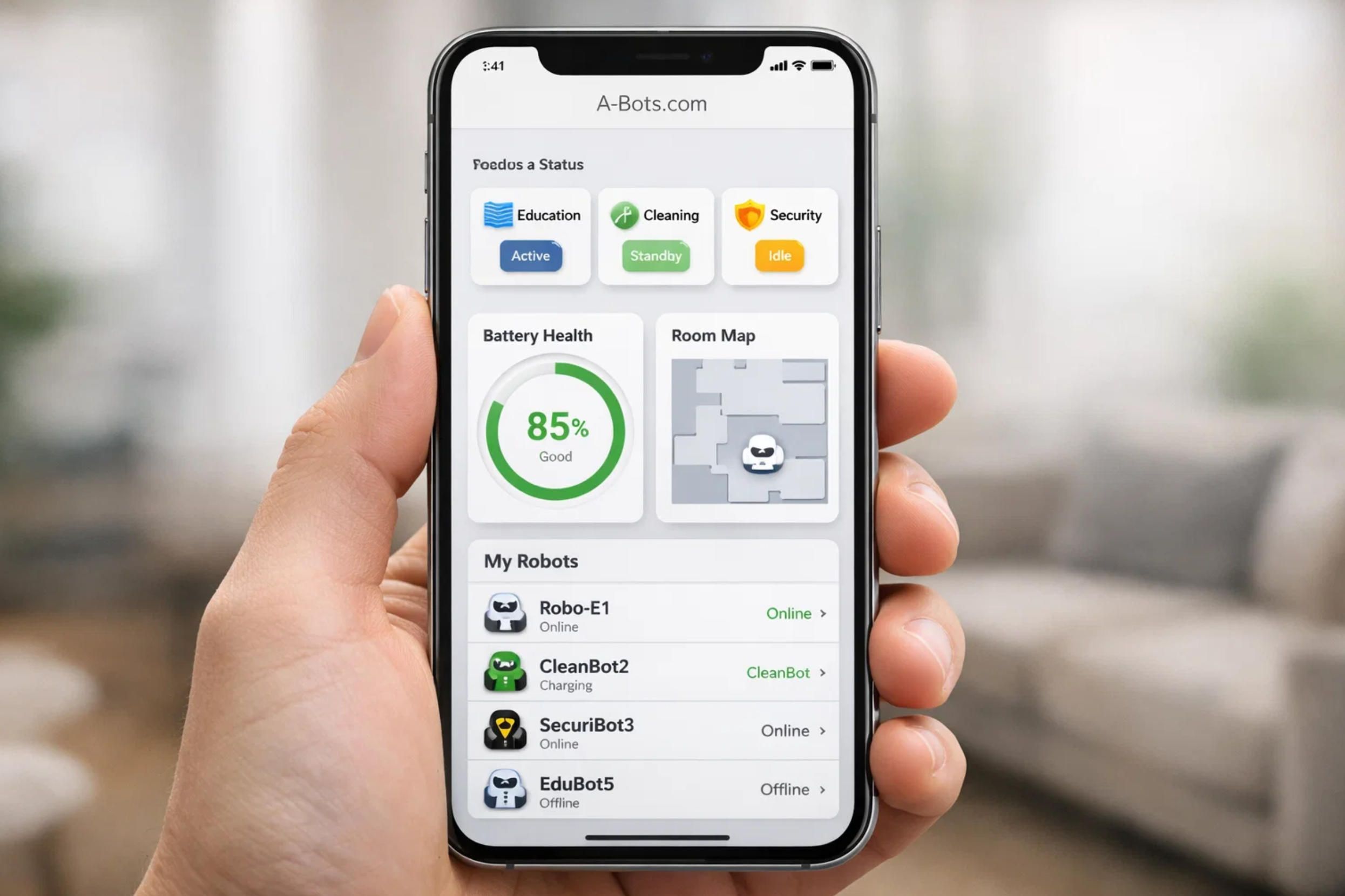
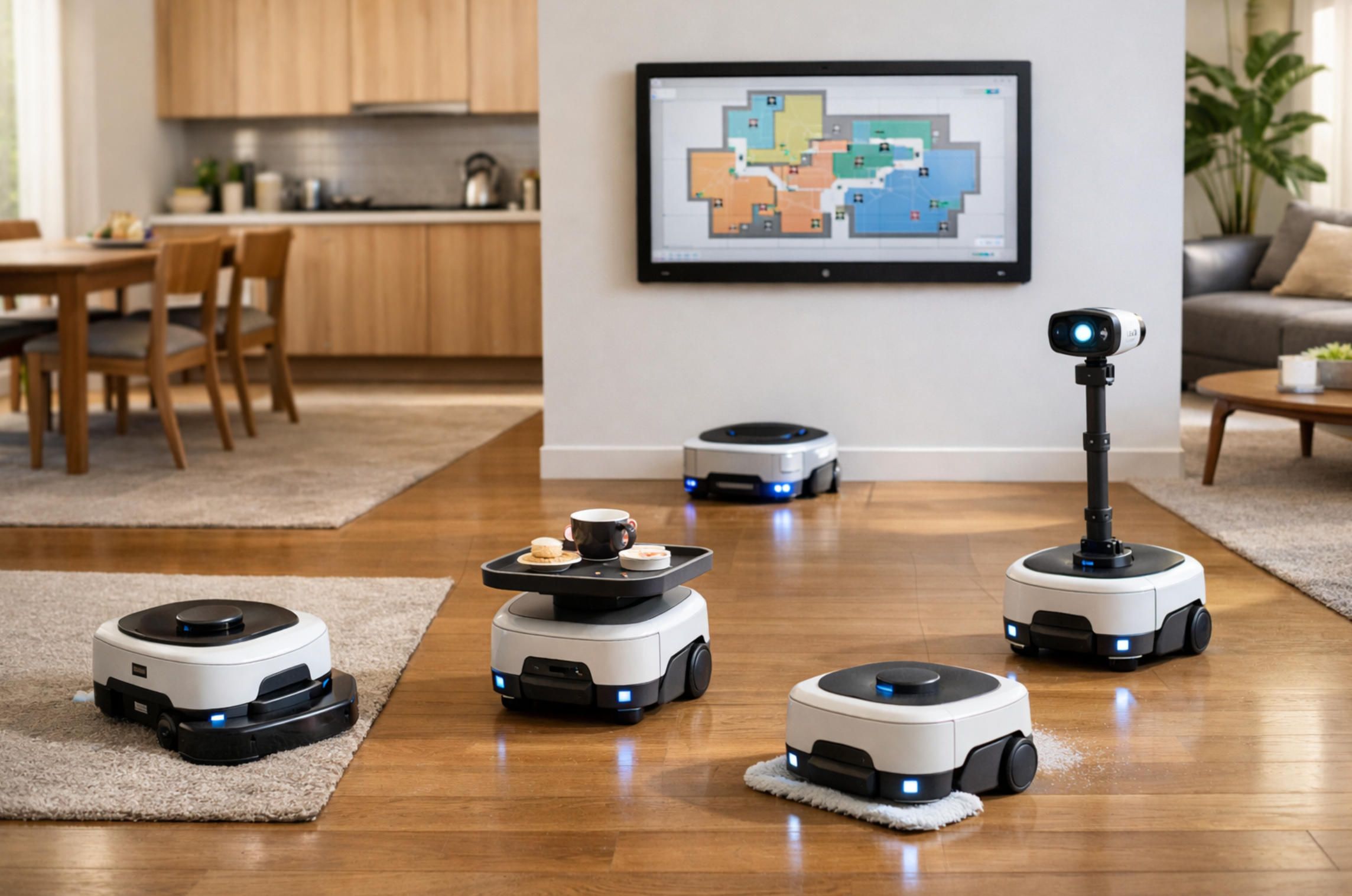
The modular design philosophy draws inspiration from successful implementations like the SwitchBot K20+ Pro, which demonstrated consumer acceptance of robots with interchangeable functionality. The base unit should contain core systems including primary processing, battery power, locomotion, primary sensors, and communication infrastructure. This base provides consistent capability across all configurations while specialized modules extend functionality for specific applications.
The FusionPlatform approach pioneered by SwitchBot provides a template for modular attachment systems. A standardized mounting surface with power connections, data interfaces, and mechanical attachment points allows users to swap between modules based on current needs. The robot configured for educational activities in the morning can transform into a floor cleaning assistant in the afternoon, then reconfigure as a security patrol unit at night.
Potential attachment modules span numerous categories:
Cleaning Modules: Vacuum units for floor debris collection, mopping systems for hard surface cleaning, and air purification units that can move between rooms to address air quality throughout the home.
Educational Modules: Additional screens for enhanced visual content, manipulation arms for physical learning activities, or science experiment accessories for hands-on STEM education.
Utility Modules: Cargo platforms for item delivery between rooms, tool holders for DIY assistance, or plant care systems with watering and monitoring capabilities.
Entertainment Modules: Projection systems for movies and games, enhanced audio systems for music playback, or gaming controllers for interactive play experiences.
Security and Monitoring Modules: Enhanced surveillance through additional cameras with night vision, motion sensors with broader coverage, or environmental sensors detecting smoke, gas leaks, or water damage.
Communication Modules: Video calling capabilities for remote family connection or integration with smart home systems for unified control.
For outdoor applications, ruggedized modules would provide weather resistance, terrain-appropriate locomotion attachments, solar charging capability, and sensors optimized for outdoor environments. A gardening module might include soil moisture sensors, plant identification cameras, and controlled watering systems. A security patrol module could incorporate perimeter monitoring, motion detection, and integration with outdoor lighting and alarm systems.
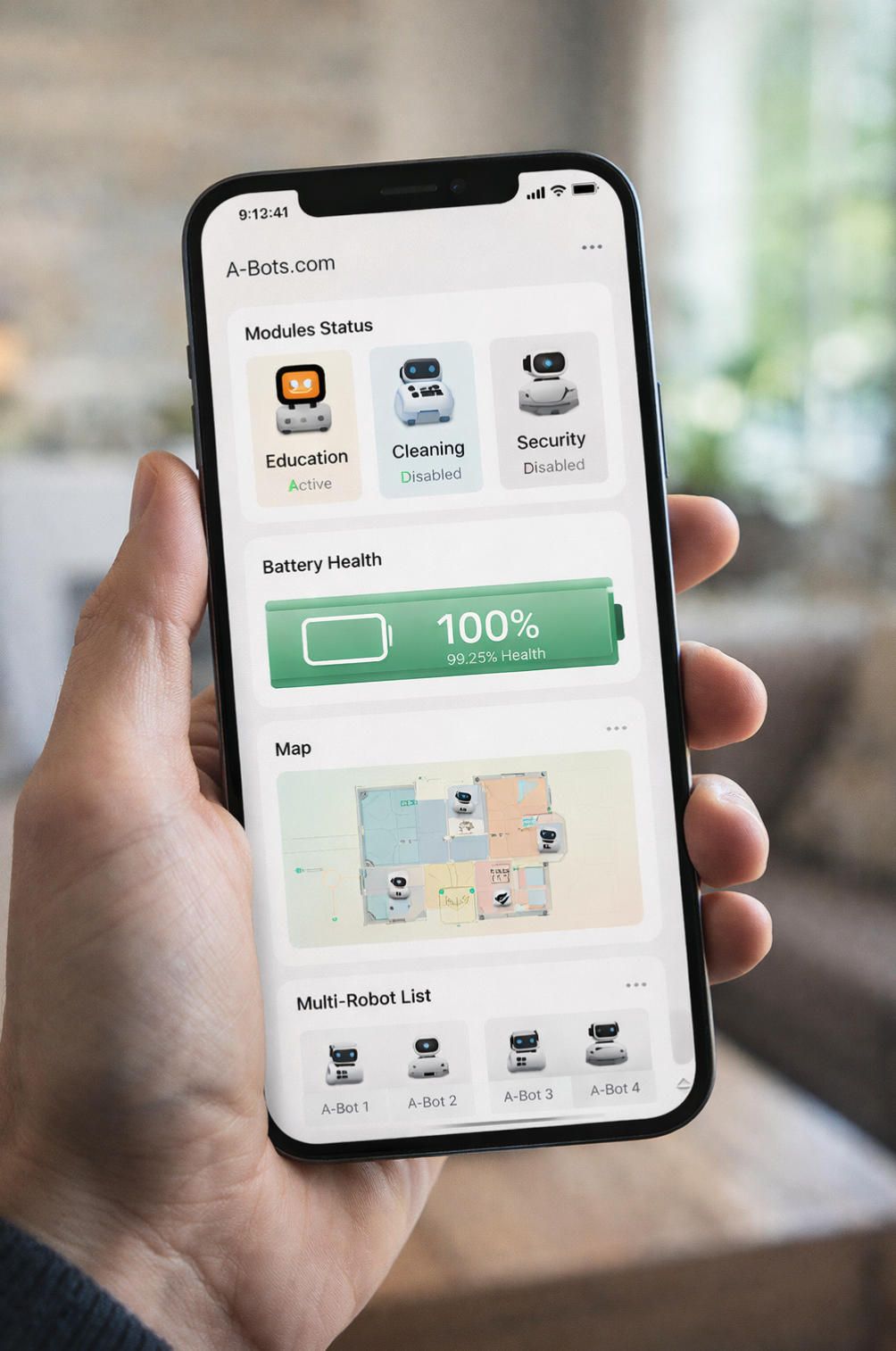
3.4 Multi-Robot Collaboration and Swarm Intelligence
The power of modular companion robots multiplies dramatically when multiple units work together. Swarm robotics research has demonstrated that groups of simple robots coordinating through local communication can accomplish tasks impossible for individual units while providing resilience through redundancy. The global swarm robotics market, projected to grow from USD 1.30 billion in 2025 to USD 9.44 billion by 2033 at a compound annual growth rate of 28.1 percent, reflects increasing recognition of collaborative robot potential.
Research indicates that swarm robotic algorithms inspired by biological self-organization can enable systems with up to 1,000 robots operating without centralized control. More practically for household applications, swarm intelligence algorithms improved coordination efficiency by 35 percent in systems with hundreds of robots while reducing communication delays significantly. Even modest multi-robot households with two to five units can benefit from coordinated behavior patterns.
Collaborative capabilities enable numerous enhanced applications:
Coordinated Cleaning: Multiple robots can divide floor space efficiently, with one unit vacuuming while another mops, or units working different rooms simultaneously to reduce total cleaning time. Warehouse studies showed swarm robots reducing task completion time by 45 percent compared to single-robot operations, processing 800 packages per hour versus 450 for individual systems.
Search and Monitoring: If a child's toy goes missing, multiple robots can systematically search different areas while communicating findings. Home security improves when multiple units can patrol different zones while maintaining communication about detected anomalies. Environmental monitoring achieves broader coverage when robots distribute themselves throughout the home to track temperature, humidity, air quality, and other conditions.
Educational Applications: Children can observe and direct cooperative robot behavior, learning principles of coordination, communication, and systems thinking. Robots can demonstrate concepts like division of labor, specialization, and emergent behavior through their collaborative activities. Competitive games between robot teams add engagement while teaching strategy and resource allocation.
Social Interaction: Like original Furbies that appeared to converse via infrared communication, modern companion robots can engage in visible interactions that entertain users while modeling social behaviors. Robots can play games together, have apparent conversations, or collaborate on tasks in ways that delight children while demonstrating positive social dynamics.
Chapter 4: Educational Applications and Child Development
4.1 Social-Emotional Learning Support
Social robots have demonstrated remarkable potential for supporting children's cognitive, emotional, and social development. Research published in leading journals confirms that robots functioning as companions, assistants, or tutors can provide emotional support, academic learning assistance, and behavioral guidance with measurable positive outcomes. Studies at Yale University found children with autism using robots for 30 minutes daily showed noticeable improvements in eye contact and communication initiation.
The CARE (Customized Assistive Robot-based Education) approach combines cognitive and emotional assessment to deliver tailored educational experiences. Through real-time facial expression analysis, subjective feedback collection, and performance metrics, the system classifies students into proficiency categories and adapts instruction accordingly. Students working with tutor robots demonstrated increased motivation, engagement, and academic performance compared to traditional instruction methods.
Field studies with family companion robots in Korea found 92 percent of children and 80 percent of parents satisfied with robot-delivered activity services designed to cultivate social emotions. Importantly, the robots improved relationships between children and families by functioning as communication facilitators. Children shared experiences with their robots that they discussed with parents, creating new conversation opportunities and family bonding moments.
Personalization emerges as critical for sustained engagement. Empathic robots that act as companions can extend play duration significantly compared to neutral interactions. Robots that remember previous dialogues and reference past conversations maintain children's interest over longer periods. The key insight is that personalization addresses symptoms of disengagement while understanding child development psychology addresses underlying causes.
4.2 Academic Tutoring and STEM Education
Educational robots have proven particularly effective for STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) instruction. Government investments totaling USD 2.8 billion globally in robotics curricula reflect recognition of this potential. Schools now drive approximately 40 percent of sales for programmable educational robots as institutions embed hands-on robotics experiences into formal instruction.
Language learning applications have demonstrated strong results. Meta-analysis of robots in language classrooms found they can function as peers, learning companions, social partners, or teaching assistants depending on configuration and curriculum design. Integration of AI-powered social robots into Chinese language classrooms showed students gained both linguistic skills and technological literacy through interactive sessions.
The companion robot concept enables academic tutoring that combines the patience and consistency of computerized instruction with the physical presence and emotional engagement of human interaction. Unlike screen-based tutoring applications, robotic tutors occupy physical space, maintain eye contact, use gesture and movement to emphasize concepts, and respond to student physical cues of confusion or understanding.
Coding education benefits particularly from robotic platforms. Children can write programs that produce visible, physical results as robots execute their instructions. The immediate feedback of seeing a robot respond to code creates powerful learning loops that abstract programming exercises cannot match. Platforms like VinciBot integrate programming education with computational thinking, creativity development, and problem-solving skills through construction and control activities.

4.3 Therapeutic Applications
Beyond general education, companion robots show significant promise for therapeutic applications supporting children with special needs. Robots provide consistent, nonjudgmental interactions that help children with autism spectrum disorder improve communication, social skills, and emotional regulation. The predictable behavior of robots reduces anxiety that can accompany human interaction while still developing skills transferable to human relationships.
Social robots have demonstrated feasibility in pediatric clinical settings. Pilot studies at children's hospitals found robots useful for encouraging positive behaviors, helping children stay on track with activities and goals, and providing emotional support during stressful medical experiences. The robots could gently redirect children while encouraging them to practice skills in real-world contexts beyond robot interaction.
For families facing geographic barriers, cost constraints, or clinician availability shortages, companion robots can supplement professional therapy by providing consistent practice opportunities between clinical sessions. While robots cannot replace human therapists, they can extend therapeutic benefit by ensuring children continue practicing skills, maintaining routines, and receiving supportive interaction even when professional care is not immediately available.
The APO social robot demonstrated success helping hearing-impaired individuals improve lip-reading skills through educational games, suggesting potential for companion robots to support children with diverse sensory processing differences. Inclusive education applications focus on providing equal access to quality educational experiences for all students, including those with varied abilities, through adaptive robotic assistance.
Chapter 5: Domestic Utility Applications
5.1 Household Cleaning and Maintenance
The robot vacuum market has established strong consumer acceptance for autonomous household cleaning. Products like the Shark Clean robot vacuum, with mobile applications enabling scheduling, mode selection, and status monitoring, demonstrate mature ecosystems for automated floor care. A-Bots.com has contributed to this space through development of IoT mobile applications for controlling robotic vacuum cleaners, providing relevant experience for expanded household robotics applications.
Modular companion robots extend beyond dedicated vacuum appliances by integrating cleaning capability as one function among many. The SwitchBot K20+ Pro exemplifies this approach with its FusionPlatform supporting interchangeable modules including cordless vacuum attachments, mopping systems, and air purification units. This modularity allows a single robot platform to address multiple household maintenance needs while serving additional roles in education, entertainment, and monitoring.
Air purification benefits significantly from mobile deployment. Fixed air purifiers treat only their immediate vicinity while mobile units can systematically address air quality throughout the home. The K20+ Pro's air purifier module moves room to room, measuring air quality, operating purification systems, and reporting results through the companion application. This approach proves particularly valuable for allergy management in multi-room residences.
Floor mopping represents another modular attachment opportunity. Hard surface cleaning requires different mechanisms than carpet vacuuming, making specialized mopping modules appropriate. Combined with navigation intelligence that recognizes floor surface types, a modular robot can transition between vacuuming carpeted areas and mopping hard floors within a single cleaning session without human intervention.
5.2 Delivery and Item Transport
Within-home delivery capability transforms companion robots into practical household assistants. The ability to transport items between rooms addresses genuine needs for elderly residents, people with mobility limitations, or simply busy families juggling multiple activities. Modular cargo platforms can carry items weighing up to 16 pounds safely, handling medications, snacks, drinks, packages, or other items requiring transport.
Warehouse robotics research demonstrates the efficiency gains possible with coordinated delivery systems. Multi-robot approaches in logistics improved delivery throughput by 40 percent while maintaining 98 percent delivery success rates. Scaled appropriately for household applications, similar principles enable efficient item movement even in complex residential environments with multiple floors, narrow passages, and dynamic obstacles.
Integration with smart home systems enhances delivery utility. Voice commands through assistants like Alexa or Google Assistant can dispatch robots to retrieve items, deliver messages between family members in different rooms, or transport items to specific locations at scheduled times. Automation routines might include bringing morning medications to a bedside table, delivering mail from an entry point to a home office, or transporting laundry between rooms.
5.3 Security and Environmental Monitoring
Mobile security robots offer advantages over fixed camera systems through dynamic coverage and adaptive response. Rather than relying on camera positioning to cover potential intrusion points, mobile robots can patrol throughout the home, investigate detected anomalies, and provide real-time video feeds from any location. Integration with smart home security systems enables coordinated response including lighting activation, alarm triggering, and emergency notification.
Environmental monitoring extends security concepts to household safety hazards. Sensors detecting smoke, carbon monoxide, natural gas leaks, or water damage can be integrated into patrol routines. Mobile deployment enables more comprehensive coverage than fixed sensor networks while allowing robots to investigate potential hazards and provide visual confirmation before triggering false alarms.
Pet monitoring represents another application bridging security and care functions. Robots can check on pets while owners are away, provide status updates through video feeds, dispense treats or food at scheduled times, and alert owners to unusual pet behavior that might indicate health concerns. The emotional appeal of maintaining connection with pets during absence enhances robot value proposition for pet-owning households.
Chapter 6: Outdoor and Extended Environment Applications
6.1 Garden and Landscape Assistance
Outdoor-capable companion robots open extensive application possibilities in garden care, property monitoring, and exterior maintenance. Agricultural robotics research demonstrates significant potential for automated plant care, with swarm systems improving crop monitoring by 35 percent while covering 1,200 hectares daily with 99 percent accuracy compared to manual methods. Scaled for residential properties, similar approaches enable automated lawn care, garden monitoring, and landscape maintenance.
Soil moisture monitoring, plant health assessment through visual analysis, automated watering, and pest detection represent garden care functions achievable with appropriately equipped outdoor robots. Integration with weather forecasting enables intelligent scheduling that avoids watering before rain, adjusts irrigation based on temperature forecasts, and accounts for seasonal variation in plant needs.
Robotic lawn mowers have achieved significant market penetration, demonstrating consumer acceptance of autonomous outdoor equipment. Products like the Gardena Sileno integrate with smart home systems including Home Assistant for scheduling, monitoring, and control. A modular companion robot could incorporate lawn mowing capability as one outdoor function among many, transitioning between lawn care, garden monitoring, perimeter patrol, and outdoor entertainment assistance.
6.2 Property Security and Perimeter Monitoring
Outdoor security applications leverage the same mobile surveillance advantages as indoor security with additional considerations for weather resistance, terrain navigation, and extended operating range. Perimeter patrol routines can supplement or replace fixed camera installations, providing coverage of areas difficult to monitor with static equipment while responding dynamically to detected intrusions.
Integration with outdoor lighting, gate systems, and alarm infrastructure creates comprehensive security ecosystems. A robot detecting unusual activity can activate lights to deter intruders, capture video evidence, trigger alarms, and notify owners or security services. The visible presence of a patrol robot may itself provide deterrent value beyond detection capabilities.
Wildlife monitoring offers a gentler outdoor application for nature-interested households. Robots equipped with quiet operation modes, appropriate cameras, and species recognition capabilities can document wildlife visiting properties, track animal behavior patterns, and provide educational content about observed species. This application connects outdoor utility with the educational mission central to companion robot design.
6.3 Outdoor Recreation and Exploration
Companion robots extend entertainment value to outdoor environments through interactive play, exploration assistance, and activity documentation. Robots can participate in outdoor games, lead nature exploration activities, document adventures through photography and video, and provide educational commentary about observed environments.
For children, outdoor robot companions combine supervision benefits with engagement appeal. Parents gain confidence knowing robots can monitor children's outdoor activities, alert to potential dangers, and maintain communication links. Children enjoy robotic playmates that suggest activities, teach nature facts, capture memories, and add technological novelty to traditional outdoor play.
Fitness and activity tracking integration transforms companion robots into exercise partners. Robots can accompany jogging routines, lead outdoor workout sessions, track activity metrics, provide encouragement, and adjust difficulty based on performance. The social presence of a robot companion may increase exercise adherence compared to purely digital tracking applications.
Chapter 7: Technical Implementation Considerations
7.1 Hardware Architecture Requirements
Successful modular companion robot implementation requires careful hardware architecture design balancing capability, cost, power efficiency, and durability. The base unit must incorporate sufficient processing power for real-time AI inference, adequate sensor arrays for environmental awareness, reliable locomotion systems for diverse surfaces, robust communication infrastructure for connectivity, and expandable interfaces for modular attachments.
Processing requirements have become more achievable through edge AI hardware advances. Application-specific integrated circuits optimized for neural network inference provide substantial computational capability within power and thermal envelopes appropriate for battery-powered mobile robots. Continuous improvement in neural processing units enables increasingly sophisticated AI capabilities without requiring cloud connectivity for every operation.
Sensor arrays typically include multiple camera types for visual perception, depth sensors for spatial awareness, microphones for voice interaction and environmental sound detection, touch sensors for physical interaction recognition, and inertial measurement units for motion tracking. Additional sensors for specific applications might include gas detectors for safety monitoring, soil moisture sensors for gardening, or specialized cameras for thermal imaging.
Power systems balance capacity against weight and charging convenience. Lithium polymer battery technology provides favorable energy density while supporting rapid charging. Modular designs might incorporate hot-swappable battery packs enabling continuous operation through battery rotation, or docking stations that automatically recharge robots when not actively deployed. Outdoor units might incorporate solar charging capability for extended autonomous operation.

7.2 Software Platform Architecture
Software architecture must support modular functionality mirroring hardware modularity. A robust operating system layer provides hardware abstraction, resource management, and security enforcement. Middleware services handle communication, data management, AI inference orchestration, and module integration. Application layers deliver specific functionality from educational content to cleaning routines to security monitoring.
The Robot Operating System (ROS) provides a proven foundation for mobile robot software development. The global robot operating system market is projected to reach USD 1.2 billion by 2033, reflecting widespread adoption. ROS provides communication infrastructure, hardware drivers, algorithm libraries, and development tools that accelerate custom robot application development while ensuring interoperability with broader robotics ecosystems.
AI subsystems require specialized frameworks for natural language processing, computer vision, and emotional intelligence. Large language models tuned for child-safe interaction provide conversational capability while content filtering ensures appropriate output. Vision models combining object detection, facial recognition, and activity understanding enable environmental awareness. Emotion recognition models analyzing facial expressions, voice characteristics, and behavioral patterns inform appropriate response generation.
Cloud connectivity extends on-device capabilities for computationally intensive operations, software updates, content delivery, and data synchronization across multiple robots or devices. Hybrid architectures maintain core functionality during connectivity interruptions while leveraging cloud resources when available for enhanced capabilities and continuous improvement through machine learning.
7.3 Safety and Privacy Considerations
Products designed for child interaction require rigorous attention to safety across physical, digital, and psychological dimensions. Physical safety encompasses stable locomotion preventing tip-overs, appropriate materials free of hazardous substances, secure attachment points for modular components, and emergency stop capabilities accessible to children and adults alike.
Digital safety addresses data protection, content filtering, and cybersecurity. Compliance with children's privacy regulations like COPPA (Children's Online Privacy Protection Act) requires explicit consideration of data collection, storage, and usage. Moxie Robot's COPPA Safe Harbor certification demonstrates achievable compliance through appropriate technical and procedural controls. Content filtering must prevent inappropriate material generation while avoiding over-restriction that limits educational value.
Psychological safety considerations include appropriate attachment relationships, realistic expectation setting, and support for healthy development. While robots can provide valuable companionship and educational support, they should not displace human relationships or create unhealthy dependencies. Clear communication about robot capabilities and limitations helps children understand the nature of their robotic companions.
Parental controls enable appropriate oversight without undermining trust. Dashboards tracking interaction patterns, content accessed, and development progress keep parents informed. Configurable restrictions allow families to customize robot behavior according to their values and preferences. Alert systems notify parents of concerning patterns while respecting appropriate privacy boundaries for developing children.
Chapter 8: A-Bots.com Development Capabilities
8.1 Relevant Experience and Expertise
A-Bots.com brings directly relevant experience to modular companion robot development through its portfolio of IoT, mobile application, and robotics projects. The Shark Clean mobile application for controlling robotic vacuum cleaners demonstrates expertise in human-robot interface design, device state monitoring, mode configuration, and seamless user experience for consumer robotics products. This foundation translates directly to companion robot control applications.
With over 70 completed projects across mobile development, web development, IoT solutions, chatbots, blockchain, and testing services, A-Bots.com possesses the breadth of technical capability required for comprehensive companion robot software development. The technology stack including React Native, Java, Kotlin, Swift for mobile platforms; Node.js, Django, React JS for backend services; and Python for AI and automation provides the tools necessary for robot software implementation.
Chatbot development experience directly informs conversational AI implementation for companion robots. Creating engaging, responsive dialogue systems that maintain context, adapt to user preferences, and deliver appropriate content represents core competency applicable to robot personality development. Integration experience with multiple platforms ensures companion robot applications can connect with existing smart home ecosystems.
Long-term client relationships, with many spanning 1.5 to 5+ years, demonstrate the sustained partnership approach necessary for complex robotics projects requiring iterative development, continuous refinement, and ongoing support. The 98 percent client satisfaction rate reflects commitment to quality and responsiveness that robotics development demands.
8.2 Development Service Offerings
A-Bots.com can support companion robot development across multiple engagement models. Custom software development creates bespoke applications tailored to specific robot hardware platforms, target markets, and functional requirements. From initial concept validation through production deployment and ongoing maintenance, the full-cycle development approach ensures comprehensive support throughout product lifecycle.
Mobile application development delivers the companion apps essential for robot configuration, monitoring, and control. Cross-platform development using React Native enables efficient creation of applications serving both iOS and Android users from shared codebases. Native development in Java, Kotlin, and Swift addresses performance-critical or platform-specific requirements.
Backend services development creates the cloud infrastructure supporting robot connectivity, data management, content delivery, and multi-robot coordination. Scalable architectures handle growing user bases while maintaining performance and reliability. Security-focused design protects sensitive user data, particularly important for products serving children.
Quality assurance and testing services ensure robot software meets functional requirements, performance standards, and safety criteria. Experience testing IoT applications translates directly to robot software validation. Comprehensive testing approaches including functional testing, performance testing, security testing, and user acceptance testing provide confidence in product quality before market release.
8.3 Quality Assurance for Existing Systems
Beyond new development, A-Bots.com provides testing and quality assurance services for existing companion robot products. Independent evaluation identifies software defects, security vulnerabilities, performance issues, and usability problems that internal development teams may overlook. Fresh perspective combined with testing expertise reveals improvement opportunities.
Specialized testing for children's products addresses unique requirements including age-appropriateness of content, safety of interaction patterns, privacy compliance verification, and parental control effectiveness. Testing methodologies adapted for child users ensure products perform appropriately across target age ranges and developmental stages.
Multi-robot coordination testing validates swarm behavior, communication reliability, collaborative task execution, and failure recovery. Systematic testing of robot-to-robot interactions ensures consistent behavior across varying robot counts, configurations, and operating conditions. Edge case identification reveals potential issues before they impact end users.
Chapter 9: Future Outlook and Development Roadmap
9.1 Technology Evolution Trajectory
The companion robot category will continue evolving as enabling technologies mature and costs decline. Large language models specifically trained for child interaction will become more sophisticated, enabling increasingly natural conversation while maintaining safety guardrails. Computer vision systems will achieve better object recognition, activity understanding, and emotional perception at lower computational cost.
Hardware miniaturization and efficiency improvements will enable more capable robots in smaller, lighter form factors. Battery technology advances will extend operating duration while reducing recharge time. Manufacturing cost reductions driven by scale and automation will bring premium features to mainstream price points.
Standardization efforts will improve interoperability between robots, smart home systems, and service ecosystems. Matter protocol adoption for smart home connectivity provides a template for robotics interoperability standards. Common interfaces for modular attachments could enable accessory ecosystems spanning multiple robot platforms.
Regulatory frameworks will mature to provide clearer guidance on children's robotics products while protecting innovation potential. Privacy regulations specific to AI-powered children's devices will establish baseline requirements. Safety standards will address physical, digital, and psychological dimensions of companion robot interaction.
9.2 Market Development Expectations
Market projections consistently indicate strong growth across smart toys, educational robots, and companion robotics categories through 2030 and beyond. The convergence of these categories into unified modular platforms represents a significant market opportunity for companies capable of delivering comprehensive solutions.
Consumer expectations will evolve from novelty appreciation toward utility demands. Early adopters accept limitations in exchange for innovation experience, but mainstream consumers require reliable functionality delivering genuine value. Products must transition from impressive technology demonstrations to trusted household tools.
Subscription and service revenue models will supplement hardware sales as robots require ongoing content, software updates, and cloud services. This transition from product to service relationships creates recurring revenue opportunities while aligning business incentives with customer success. Robots that continue improving through updates maintain relevance and reduce replacement pressure.
Geographic expansion will accelerate as manufacturing capabilities distribute globally and regulatory harmonization simplifies multi-market deployment. Asia-Pacific growth rates exceeding North American and European markets reflect untapped demand that will increasingly attract competitor attention and investment.
9.3 Societal Impact Considerations
Widespread adoption of companion robots will generate societal impacts requiring thoughtful consideration. Educational benefits for children with diverse learning needs could significantly improve developmental outcomes if accessibility is prioritized. Therapeutic applications could extend mental health support to underserved populations lacking access to human specialists.
Household assistance applications could support aging populations remaining in their homes longer, reducing institutional care requirements while maintaining quality of life. For families with demanding schedules, robot assistance could reduce stress while creating more time for meaningful human interaction.
Questions about appropriate robot roles in children's lives will require ongoing societal dialogue. Robots should supplement rather than replace human relationships, support development rather than create dependencies, and enhance rather than diminish real-world engagement. Industry responsibility includes designing products that encourage healthy usage patterns.
Environmental considerations include manufacturing sustainability, product longevity, repairability, and end-of-life recycling. Modular designs that extend useful life through upgrades and attachments inherently reduce environmental impact compared to disposable electronics. Sustainable materials and responsible manufacturing practices should guide product development.
Chapter 10: Conclusion
The journey from Tamagotchi and Furby to AI-powered modular companion robots represents one of the most remarkable evolutionary paths in consumer technology. What began as simple electronic toys with limited interactivity has transformed into sophisticated robotic platforms capable of genuine conversation, emotional understanding, household assistance, and collaborative behavior with other robots.
The foundational lessons from early interactive toys remain relevant. Emotional connection trumps technical sophistication for creating meaningful user relationships. Physical embodiment enhances engagement beyond what screen-based interfaces can achieve. Perceived intelligence and personality matter more than actual computational capability for user satisfaction.
Modern technology enables realizing the science fiction vision of robot companions that grow with us, assist with daily tasks, educate our children, protect our homes, and collaborate to accomplish what individual robots cannot. The modular approach extends robot utility across multiple domains while the swarm concept multiplies capability through coordination.
Market conditions strongly favor companion robot development. Projected growth rates across smart toys, educational robots, and companion robotics categories confirm substantial consumer demand. Technology cost curves continue declining while capability curves rise. The intersection creates opportunities for products that would have been impossible or unaffordable just years ago.
A-Bots.com stands positioned to contribute meaningfully to this technological transformation. Experience with robotic vacuum control applications, IoT systems, mobile development, and chatbot creation provides directly relevant expertise. Full-cycle development capability supports projects from concept through production. Quality assurance services help ensure product excellence.
The future of interactive companions combines the emotional warmth that made Tamagotchi and Furby beloved with technological capabilities their creators could only imagine. Robots that teach, assist, protect, and collaborate are no longer science fiction but engineering challenges awaiting solution. The companies that successfully develop these products will shape how the next generation relates to technology while creating substantial commercial value.
For organizations interested in developing modular companion robot software, mobile control applications, AI-powered interaction systems, or quality assurance for existing robotics products, A-Bots.com welcomes discussion of how our capabilities can support your vision. Together, we can transform the promise of intelligent robot companions into products that enhance lives, support development, and bring science fiction into everyday reality.
Contact A-Bots.com to discuss your companion robot development needs and explore how our expertise can accelerate your path from concept to market.
References and Sources
- Grand View Research. Smart Toys Market Size, Share and Growth Report, 2030.
- Market Research Future. Smart Toys Market Size, Growth Analysis, 2030.
- Mordor Intelligence. Smart Toys Market Size and Share Analysis, Industry Growth and Forecast 2030.
- Future Market Insights. Smart/AI Toy Market Global Analysis Report, 2035.
- Maximize Market Research. Autonomous Robot Toys Market Size Analysis, 2025-2032.
- Knowledge Sourcing. Entertainment Robotics Market Size and Trends Forecast 2025-2030.
- Precedence Research. AI in Computer Vision Market Size 2025 to 2034.
- Frontiers in Robotics and AI. Child-centered home service design for a family robot companion, 2024.
- Nature Humanities and Social Sciences Communications. Social robots for child development: research hotspots, topic modeling, and collaborations, 2025.
- Springer International Journal of Social Robotics. The Child Factor in Child-Robot Interaction, 2024.
- Wikipedia. Furby - History and Technical Specifications.
- Wikipedia. Tamagotchi - History and Cultural Impact.
- Official Furby Wiki. Furby 1998 Technical Documentation.
- Tamagotchi Wiki. Original Tamagotchi 1996 Pet Documentation.
- Behavioral Health News. The Benefits of Robotics and AI for Children and Behavioral Health, 2024.
- Moxie Robot. Official Product Documentation and Research.
- SwitchBot. K20+ Pro Modular Robot Technical Specifications.
- RoboticsTomorrow. Swarm Robotics Industry worth $3.0 billion by 2028, 2024.
- MDPI Applied Sciences. Swarm Intelligence-Based Multi-Robotics: A Comprehensive Review, 2024.
- AZoRobotics. Applications of Robot Swarms, 2025.
- ImageVision.ai. Key Trends in Computer Vision for 2025.
- DigitalOcean. 10 Computer Vision Applications for 2025.
- Tokyo Weekender. Tamagotchi's Evolution: How a Handheld Digital Pet Conquered the World, 2024.
- Frontiers in Robotics and AI. The robot that stayed: understanding how children and families engage with a retired social robot, 2025.
- A-Bots.com. Company Portfolio and Technical Capabilities.
✅ Hashtags
#RobotCompanion
#SmartToysMarket
#EducationalRobotics
#AIForKids
#ModularRobotDesign
#InteractiveEducation
#HomeRobotics
#SwarmIntelligence
#FurbyHistory
#TamagotchiEvolution
#ChildRobotInteraction
#IoTDevelopment
#RobotSoftware
#CustomAppDevelopment
Other articles
Hyodol. Aging Nations, Smarter Senior Care Aging isn’t a niche—it’s the new baseline across advanced economies. This article maps the real landscape: what an effective elder care app looks like today, why apps for senior caregivers must orchestrate TV-first and voice-first UX with fall-detection wearables and low-friction home signals, and where companion devices (from Hyodol to ElliQ) genuinely move the needle. We detail the system patterns that cut false alarms and speed response—care-circle routing, explain-why alerts, medication adherence 2.0, and privacy-by-design. Finally, we show how A-Bots.com—an IoT app development company—builds custom, interoperable platforms (FHIR-ready APIs, offline-first mobile, TV apps, guardrailed conversational agents) so your aged care app and elderly app scale from pilot to policy.
Custom CAD, 3D Modeling, BIM and Digital Twins Australia’s engineering and manufacturing sectors are accelerating digital transformation, but the country’s scale, remoteness, and resource-intensive operations often expose the limits of off-the-shelf software. This guide explains where custom engineering software delivers measurable advantage - from CAD and 3D modeling tools to BIM collaboration platforms and full-site digital twins for mining, construction, and advanced manufacturing. You will learn what Australian teams typically need: real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, regulatory-aligned BIM workflows, and deep integrations with existing operational systems. A-Bots.com builds tailored engineering applications that match sector-specific requirements and production realities.
Hair Salon App Development: AR Try-On, Booking and CRM Platform This comprehensive guide explores hair salon app development for modern beauty businesses seeking digital transformation. The article covers AR-powered virtual hairstyle try-on technology that allows clients to preview cuts and colors before booking. It details three-sided platform architecture serving clients, stylists, and administrators with integrated booking, CRM, and management tools. Key market statistics reveal the $247 billion global salon industry opportunity and compare USA versus European markets. The guide addresses no-show reduction through automated reminders, multi-location scalability, security compliance, and MVP development strategies. A-Bots.com demonstrates expertise in building custom salon applications with AR integration, appointment scheduling, and comprehensive business management features.
Custom IoT App Development Service: Complete Guide 2025 This comprehensive guide explores custom IoT app development service from concept to deployment. Learn how businesses leverage connected devices across healthcare, manufacturing, retail, and agriculture sectors. Discover technical requirements including security protocols, scalability considerations, and integration capabilities. Understand development methodologies, quality assurance processes, and realistic cost expectations ranging from $30,000 for basic applications to $200,000+ for enterprise solutions. Explore market dynamics with projections showing the IoT Application Development Services Market reaching $66.1 billion by 2032. Review emerging trends including edge computing, AI integration, and LPWAN technologies. Find practical guidance for selecting development partners, evaluating technical expertise, and ensuring project success. Includes authoritative sources, industry statistics, and actionable recommendations for organizations entering the IoT ecosystem.
Custom Mobile App Development for Startups 2025 Guide This detailed guide explores custom mobile app development for startups, covering every stage from initial concept to post-launch optimization. Learn practical strategies for building MVPs, managing development costs between $30,000-$150,000, and implementing comprehensive testing protocols. Discover why 88% of users abandon apps after poor experiences and how to prevent this through quality development. The article examines current market trends, with app revenue projected at $935 billion in 2025, and provides actionable insights on choosing development partners, securing funding, and scaling applications. A-Bots.com brings 70+ projects of experience in custom mobile app development for startups, offering both full-cycle development and specialized testing services to ensure your application succeeds in competitive markets.
App Development Companies for Startups: USA, EU and Nordics Guide This guide examines app development companies for startups across USA, European, and Scandinavian markets. American developers excel in rapid scaling and real-time architecture, with projects ranging from $30,000 to $250,000+. European partners specialize in GDPR compliance, fintech solutions, and multi-language applications. Nordic companies lead in impact-driven development, deep tech expertise, and sustainable technology practices. The article analyzes market-specific expectations, development methodologies, and emerging trends including AI integration, low-code platforms, and 5G capabilities. Features expert quotes from industry leaders, authoritative market data, and practical frameworks for evaluating technical expertise, cultural alignment, and post-launch support when selecting development partners.
Top stories
Copyright © Alpha Systems LTD All rights reserved.
Made with ❤️ by A-BOTS
