
Home
Services
About us
Blog
Contacts
Logistics and Truck App Development: Driving the Future of Autonomous Semi Trucks
1. Logistics and Truck App Development: Why It Matters Today
2. From Fleet Management to Automated Trucking: The Evolution
3. Core Features of a Modern Truck & Logistics App
4. The Landscape of Automated Trucking Apps
5. Testing and Quality Assurance in Driverless Semi Truck Apps
6. The Future of Logistics and Truck App Development
7. Historical and Economic Timeline of Driverless Trucks

In the last decade, the logistics sector has shifted from manual dispatch boards and endless phone calls to digital platforms and real-time decision-making tools. At the very heart of this transformation lies logistics and truck app development—a field that is not just streamlining fleet operations but also laying the groundwork for self driving semi trucks and autonomous semi trucks.
At A-Bots.com, we specialize in creating custom, bespoke mobile apps for logistics and truck companies that want to stay ahead of this curve. Whether it’s building a fleet management app that integrates with IoT sensors or designing a control system for driverless semi trucks, our team delivers solutions that are tailored, scalable, and future-ready. Unlike off-the-shelf products, which often lack the precision and adaptability that logistics firms require, our approach focuses on developing digital ecosystems where every function—from route optimization to safety monitoring—is seamlessly connected.
This positioning matters more than ever because the race toward automated trucking is no longer speculative; it’s happening in real time. In the United States, companies like Aurora and TuSimple are running test fleets of self driving semi trucks across highways, moving commercial goods with reduced human input. In China, autonomous freight corridors are already under development, backed by government policy that aggressively promotes driverless semi trucks as part of its smart city initiatives. Meanwhile, in Europe, regulatory frameworks are evolving to allow trials of autonomous semi trucks that can reduce emissions, optimize cross-border freight, and tackle the continent’s chronic driver shortages. Each region is moving at a different pace, but the unifying factor is the critical role of logistics app development companies in enabling these breakthroughs.
For logistics providers, the implications are enormous. A tailored mobile app becomes the central nervous system of the operation: dispatchers gain a live map of fleets, predictive analytics cut downtime through maintenance alerts, and AI-driven modules gradually bridge the gap between human-driven and automated trucking fleets. When A-Bots.com develops a solution, it’s not just about coding; it’s about creating resilience and competitive advantage in a market where margins are tight and efficiency is king.
As companies across the U.S., China, and Europe test autonomous semi trucks, the question isn’t whether this technology will become mainstream—it’s how quickly, and how prepared businesses are to adopt it. A poorly tested or rigid platform can cost millions in lost contracts, accidents, or regulatory penalties. A bespoke solution designed and tested by an expert logistics app development company like A-Bots.com ensures compliance, security, and adaptability to changing market conditions.
What sets our approach apart is the full cycle we provide. We can step in at any stage:
- End-to-end logistics and truck app development for enterprises that need a digital foundation.
- Bespoke modules for companies piloting self driving semi trucks, ensuring integration with onboard sensors and V2X communication.
- Outsourced testing and QA for firms building their own platforms but needing rigorous validation before deployment.
In other words, A-Bots.com is not just building apps—we are shaping the connective tissue between today’s logistics operations and tomorrow’s world of driverless semi trucks. By combining technical expertise with a global outlook, we help our partners in the U.S., Europe, and Asia navigate the most disruptive transition trucking has seen since the invention of the diesel engine.
1. Logistics and Truck App Development: Why It Matters Today
The logistics sector is one of the most dynamic and essential components of the global economy. Trucks move nearly 70% of freight in the United States, while in Europe the figure is similar, with cross-border trucking forming the backbone of regional commerce. In China, freight corridors carry billions of tons annually, with technology adoption accelerating faster than in most markets. Against this backdrop, logistics and truck app development has become more than a convenience—it is now a strategic imperative for companies that want to remain competitive in a changing industry.
1.1 The Shifting Landscape of Logistics
Only a decade ago, fleet managers relied on spreadsheets, phone calls, and GPS devices that worked in isolation. Today, the rise of logistics app development companies has introduced a new paradigm where mobile apps serve as centralized platforms that unify dispatching, route optimization, fuel management, and safety compliance. This shift matters for several reasons:
- Global supply chain volatility. Recent disruptions—from pandemics to geopolitical conflicts—have forced logistics firms to embrace digital resilience. A custom app offers real-time adaptability.
- Driver shortages. Europe alone reports a deficit of more than 500,000 truck drivers, while the U.S. and China face similar gaps. Mobile apps help optimize fleets and act as transitional tools toward driverless semi trucks.
- Environmental pressures. With stricter emissions targets in the EU and California’s aggressive decarbonization laws, trucking companies must reduce inefficiencies, something automated trucking apps can address through intelligent routing and predictive maintenance.
This context explains why businesses no longer see mobile apps as optional add-ons. Instead, logistics and truck app development is the bridge to both immediate efficiency and long-term transformation toward autonomous semi trucks.
1.2 Beyond Tracking: Why Customization is Key
The rise of ready-made logistics platforms has created a misconception that every company can thrive with a plug-and-play solution. In practice, however, logistics operations vary drastically depending on region, fleet size, cargo type, and regulatory frameworks. A bespoke mobile app developed by a logistics app development company like A-Bots.com offers advantages that off-the-shelf platforms cannot match:
- Integration with local regulations. In Europe, tachograph compliance is mandatory, while in China, logistics platforms must meet cybersecurity requirements under national law. A custom-built app ensures compliance.
- Scalability. Fleets often expand from dozens to thousands of vehicles; only custom software can grow without major disruptions.
- Autonomous compatibility. Businesses experimenting with self driving semi trucks need apps designed to communicate with AI systems, LiDAR, and V2X networks—something generic apps rarely support.
This distinction is critical because as the trucking industry edges closer to automated trucking, only tailored systems will be capable of handling the unique workflows of early adopters.
1.3 Technology as a Competitive Advantage
Adopting logistics and truck app development is no longer about catching up—it’s about gaining a lead. Companies in the U.S. that invested early in route optimization apps now report fuel savings of up to 15% annually. In China, firms piloting autonomous semi trucks across fixed freight corridors have reduced operational costs by double digits, largely thanks to integrated software platforms. In Europe, where sustainability is a competitive differentiator, companies that use AI-powered apps are better positioned to win green contracts.
The competitive advantages stem from four pillars:
- Efficiency. Reduced downtime through predictive maintenance and intelligent scheduling.
- Safety. Real-time monitoring systems that minimize accidents and insurance claims.
- Sustainability. Lower emissions through optimized driving and electrification support.
- Future-readiness. Compatibility with driverless semi trucks as regulations evolve.
These pillars reinforce the fact that logistics apps are not merely operational tools—they are business differentiators.
1.4 Preparing for the Autonomous Era
Perhaps the most compelling reason why logistics firms must embrace logistics and truck app development is the rise of automation. While the timeline varies by region, the trajectory is clear. The U.S. leads in highway testing of self driving semi trucks, China accelerates with government-backed autonomous freight zones, and Europe refines regulations to accommodate driverless semi trucks in mixed-traffic scenarios.
The future will not be a sudden replacement of human drivers with machines; it will be a hybrid period where fleets operate with both human-driven and autonomous vehicles. During this transitional phase, the role of mobile apps will be decisive. They will serve as:
- Bridges between human and autonomous operations. Dispatchers will manage fleets where some trucks operate independently while others still require manual driving.
- Data translators. Apps will connect autonomous truck sensors with enterprise systems, ensuring data is actionable for business decisions.
- Testing and compliance frameworks. Every update to autonomous semi trucks software requires rigorous validation, something integrated QA-ready platforms can facilitate.
In this sense, logistics apps are not just tools for managing fleets—they are the connective tissue that enables automated trucking to scale safely and profitably.

2. From Fleet Management to Automated Trucking: The Evolution
The story of logistics and truck app development is really the story of how a dispersed, analog industry learned to think—and act—in real time. In less than a decade, smartphones and cloud telemetry made the cab, the trailer, and the back office visible to each other. Then came mandated telematics like the U.S. Electronic Logging Device (ELD) rule in 2017, which forced digital record-keeping at scale and accelerated software adoption across fleets of every size. That single policy shift nudged operators toward integrated platforms where hours-of-service, routing, safety, and maintenance live in one stack—often inside a mobile app. fmcsa.dot.gov
2.1 The App Era: From Tracking Dots to Operational Nerve Centers
Early “dots on a map” tools did little more than show GPS pings. As logistics matured, mobile apps began orchestrating dispatch, digitizing proof-of-delivery, and synchronizing drivers with TMS, WMS, and billing. A capable logistics app development company designs this orchestration as a living system: the driver app becomes the edge device for data capture and safety prompts; the supervisor console turns into an operations cockpit; APIs broker truth across ELDs, fuel cards, reefers, and camera systems. In practice, that architecture reduces deadhead, improves on-time performance, and shortens cash cycles—outcomes that explain why custom solutions outcompete one-size-fits-all software in complex, multi-region fleets.
This is also where the groundwork for automated trucking begins. The same telemetry that powers ETA predictions becomes training data for hazard models; driver behavior scoring evolves into machine-readable policies for speed, lane changes, and following distances; maintenance logs feed predictive algorithms that matter even more when uptime is measured against a driverless duty cycle. In short, logistics and truck app development didn’t just digitize paperwork—it created the control plane that self driving semi trucks now plug into.
2.2 The Middle Step: ADAS, Platooning, and Hub-to-Hub Autonomy
Before autonomous semi trucks arrive everywhere, autonomy grows inside constrained envelopes. Think limited-access highways, fair-weather operations, fixed corridors between transfer hubs. Europe tested coordinated truck platooning years ago; Germany then built a legal pathway for Level 4 operations on public roads, culminating in permits that enabled real motorway runs in 2024–2025. Those permissions did not appear in a vacuum—they reflect a regulatory acceptance of supervised autonomy that can be proven and audited.
China followed a different path: city- and port-led pilots prioritized goods flow, not personal mobility. Trials in Shanghai’s port corridor demonstrated driver-out heavy-duty trucking on approved routes, with municipal support and industrial partners tightening the loop between infrastructure and vehicles. The policy-industrial alignment allowed rapid scaling in logistics zones—an approach that continues as Shanghai accelerates L4 deployments of unmanned heavy trucks. DHL
The U.S. path has been market-led and uneven by design. Some programs paused or re-scoped—Waymo shifted focus to robotaxis in 2023—while others crossed the driver-out threshold on commercial lanes in Texas. By mid-2025 Aurora began driverless freight between Dallas and Houston and outlined expansions to El Paso and Phoenix, while new capital and public listings signal continued momentum from players like Kodiak. The result is a patchwork of ODDs (operational design domains) expanding corridor by corridor, week by week.
For software leaders, these regional differences matter less than the common operating model: a transfer-hub network where human drivers handle the first/last miles and driverless semi trucks handle the long highway middle. In that topology, the app is the broker of truth—assignments, handoffs, inspections, and exception handling all flow through one pane of glass. (Analysts and trade sources now routinely describe this hub-to-hub phase as the first mass-market stage of autonomy.) SeaRates
What changed under the hood? Three things:
- Sensing to semantics. Cameras, radar, and LiDAR once produced raw pixels and points; now perception systems output drivable space and intent cues that an app can turn into policies and alerts for ops teams.
- Cloud to corridor. Instead of generic maps and blanket connectivity, autonomy stacks depend on corridor-specific HD maps, geofenced policies, and curated telemetry paths into enterprise systems.
- Human-in-the-loop to exception-in-the-loop. Apps no longer “supervise drivers”; they supervise autonomy—surfacing events that need human adjudication (weather re-routes, work zone anomalies, load integrity checks).

2.3 The New Control Plane: Mobile Apps for Autonomous Operations
As fleets step into autonomy, the mobile experience shifts from helping a person drive to helping a system operate. For a logistics app development company, the design brief now spans four layers:
- Operational Layer. Dispatch orchestration, slot booking at hubs, dynamic staging at yards, and geofenced SOPs for autonomous arrivals and departures.
- Safety & Compliance Layer. Live policy checks, incident timelines, audit trails tied to specific software releases, and automatic evidence packages aligned to regional rules in the U.S., EU, and China.
- Maintenance & Reliability Layer. Condition-based maintenance tied to perception/actuation health, firmware rollouts with staged canary cohorts, and MTBF dashboards that treat the autonomy stack like mission-critical avionics.
- Business Layer. Contract compliance, carbon reporting for tenders, and automated claims workflows that blend sensor forensics with carrier SLAs.
Crucially, each layer must speak the language of autonomy. The app needs to know the truck’s current ODD, its contingency plans, and the escalation paths to remote assistance. It needs to understand how a construction-zone downgrade affects ETA and which customer service scripts to trigger. It needs guardrails so that a human can never silently overrule a safe stop policy. That’s why logistics and truck app development for autonomy is not merely “add a module”—it is a re-platforming around real-time, safety-critical operations.
In China, this re-platforming leans into corridor permits and port timetables; in Europe, into cross-border documentation and sustainability reporting; in the U.S., into customer SLAs across sprawling line-haul networks. Yet the connective tissue is the same: a bespoke mobile control plane that can integrate with an autonomy provider today and another tomorrow. That supplier-agnostic stance is how shippers avoid vendor lock-in while still moving forward with automated trucking pilots. TU Braunschweig
2.4 Lessons From the Frontier—and What Comes Next
The last two years taught the market that self driving semi trucks are both closer and more operationally specific than many assumed. Some programs consolidated; others went driver-out on real freight; regulators learned by granting limited permissions and watching telemetry; investors learned to care about corridor economics, not just miles. The throughline is that autonomy rewards operational discipline—networks built around predictable lanes, strong yard processes, and clean data exhaust.
For shippers and carriers, three pragmatic takeaways stand out:
- Treat autonomy like a network product. Start with lanes where you already have schedule density and consistent assets. Build transfer hubs to spec, with standardized inspection flows your app can enforce. Your logistics and truck app development roadmap should mirror that network plan.
- Design for mixed fleets. For the next decade, human-driven, fallback-driver, and fully driverless semi trucks will coexist. Your app should visualize capability by VIN and software build, enforce lane eligibility, and automate handoffs between human and autonomous operations. Reuters
- Elevate testing to a first-class feature. As you integrate autonomous semi trucks, treat simulation coverage, release notes, and safety-case evidence as product surfaces within the app, not artifacts in a binder. Regulatory readiness in Germany differs from Texas; Shanghai differs from Rotterdam. Only a bespoke stack can keep those threads together. connectedautomateddriving.eu
Where does this go next? Expect denser driver-out coverage on U.S. and Chinese corridors, more L4 permits and type approvals in Europe, and an expanding procurement language that bakes autonomy into freight contracts. The competitive edge will sit with companies that fuse corridor economics with software maturity—firms that invest in logistics and truck app development not as an IT project but as the operating system for automated trucking. And that is precisely where a specialized logistics app development company can change the slope of the curve: by delivering a mobile control plane that is safety-literate, corridor-aware, supplier-agnostic, and ready for the realities of self driving semi trucks. kba.de
3. Core Features of a Modern Truck & Logistics App
The global shift toward logistics and truck app development is not just about digitizing dispatch boards or tracking trucks on a map. The modern logistics app is becoming the brain of the operation, capable of coordinating fleets, predicting failures before they occur, and even serving as the interface for self driving semi trucks and autonomous semi trucks. To stay competitive, logistics firms need to understand which features are now considered baseline and which ones provide a strategic advantage.
3.1 Real-Time Tracking and Intelligent Routing
No logistics app can survive in today’s market without robust tracking. But “real-time” in 2025 means more than dots on a map—it means predictive positioning, machine learning–based route recalculation, and dynamic adjustments tied to traffic, weather, and regulatory restrictions.
- In the U.S., major fleets use apps that integrate with DOT feeds, enabling trucks to avoid bottlenecks and toll-heavy routes automatically.
- In Europe, where cross-border movement adds complexity, apps must dynamically update based on customs wait times and emissions regulations in low-carbon zones.
- In China, predictive routing tied to freight corridors has become a core feature, particularly as automated trucking corridors expand.
For companies piloting driverless semi trucks, intelligent routing does more than save fuel—it dictates the operational design domain (ODD) within which autonomous trucks can safely operate. A custom app ensures ODD-specific parameters are baked into route choices, preventing unsafe detours.
3.2 Predictive Maintenance and Fleet Health Monitoring
Downtime is the silent killer of profitability. Modern logistics and truck app development integrates predictive analytics, turning raw sensor data into actionable insights.
- Apps pull diagnostics from engines, tires, brakes, and refrigeration units, predicting failures before they happen.
- AI-driven algorithms calculate the probability of breakdowns under specific loads, terrains, or weather conditions.
- For autonomous semi trucks, predictive maintenance is mission-critical—any unscheduled stop without a human driver on board can paralyze operations and trigger safety audits.
When tailored by a logistics app development company, predictive maintenance modules connect directly to ERP systems, ensuring that service scheduling aligns with cargo delivery commitments. This prevents costly disruptions and ensures uptime across mixed fleets of human-driven and driverless semi trucks.
3.3 Driver Assistance and Transition to Autonomy
Even as the industry moves toward automated trucking, human drivers remain essential in the transition period. That is why apps must simultaneously support human operators and prepare for autonomous integration.
Driver-focused features include:
- Fatigue detection alerts based on driving patterns and wearable data.
- AI coaching for eco-driving, reducing fuel burn by up to 12%.
- Gamification tools that improve compliance and reduce turnover.
Autonomy-focused features, on the other hand, involve:
- Interfaces for monitoring self driving semi trucks on highway corridors.
- Alerts when a vehicle hands off control at a transfer hub.
- Remote override and incident escalation workflows compliant with U.S., EU, and Chinese regulations.
A bespoke app allows seamless blending of both worlds, acting as the control panel for mixed fleets where human and machine coexist.
3.4 Integration with IoT, V2X, and AI Systems
The true frontier of logistics and truck app development lies in connectivity. Modern apps are no longer standalone products; they are hubs that bring together IoT sensors, Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communication, and AI-driven decision-making.
- IoT integration. Cargo sensors monitor temperature, humidity, and shock exposure in real time, especially critical for pharmaceuticals and perishables.
- V2X communication. Trucks exchange data with traffic lights, toll stations, and other vehicles, making driverless semi trucks safer in mixed-traffic scenarios.
- AI systems. Algorithms analyze billions of data points to recommend the safest and most efficient operational choices.
For autonomous semi trucks, these integrations are not optional—they are the lifeblood of reliable operations. Without them, automated systems cannot adapt to unpredictable real-world conditions. A logistics app development company like A-Bots.com designs apps that not only connect to these systems but also translate raw machine data into dashboards, insights, and alerts accessible to human decision-makers.
3.5 Security, Compliance, and Trust
In the race toward automated trucking, security is often the hidden variable. A hacked truck is not just a lost shipment—it can be a moving hazard. That is why modern apps must integrate:
- End-to-end encryption for all telemetry.
- Multi-factor authentication for fleet operators.
- Compliance modules tailored to region-specific rules, whether it’s GDPR in Europe, FMCSA in the U.S., or cybersecurity requirements in China.
Trust is also about transparency. A properly designed logistics app generates auditable logs for regulators, insurers, and clients—an absolute requirement once fleets incorporate autonomous semi trucks and driverless semi trucks into commercial service.
The features that define today’s logistics apps—real-time tracking, predictive maintenance, driver assistance, IoT/V2X integration, and robust compliance—are not just technological add-ons. They are the foundation upon which self driving semi trucks and fully automated trucking will scale safely. Businesses that invest now in bespoke logistics and truck app development position themselves not only for efficiency but for future dominance in an industry that is shifting from human-driven freight to digital-first ecosystems.

4. The Landscape of Automated Trucking Apps
The rapid rise of automated trucking is not only about vehicles equipped with LiDAR, radar, and AI stacks—it is equally about the software ecosystems that make these vehicles practical in real-world operations. A new class of mobile apps and control platforms has emerged, designed to monitor, manage, and scale fleets of self driving semi trucks. By examining the most popular solutions on the market, we can see how technology leaders are shaping the industry—and where custom logistics and truck app development still has space to innovate.
4.1 Key Players in Automated Trucking Apps
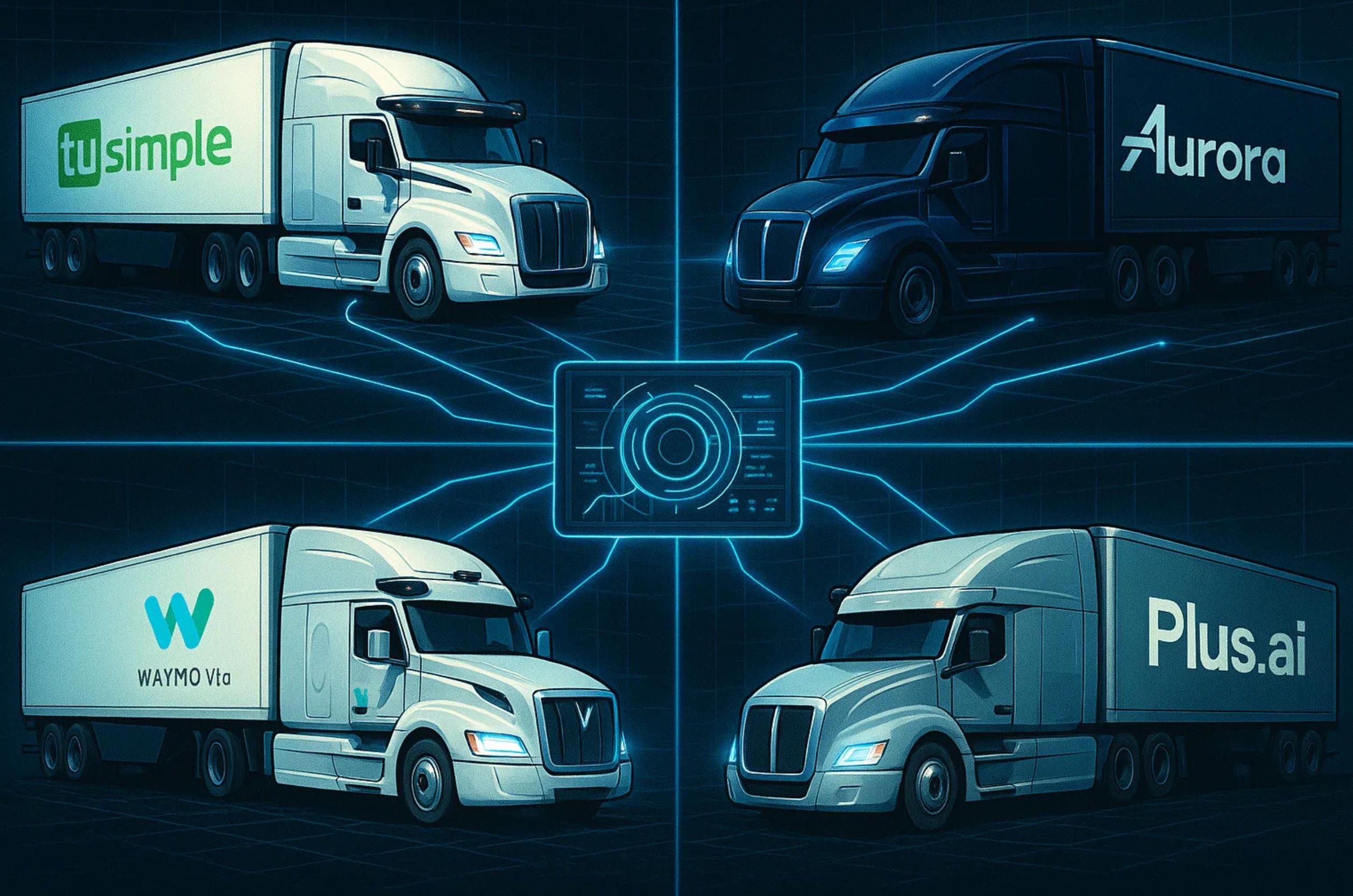
Several companies dominate the global discussion around autonomous semi trucks and their software layers. Each has developed proprietary apps or platforms that serve as nerve centers for their fleets:
- TuSimple (U.S. & China). One of the earliest companies to deploy driverless semi trucks on long-haul routes, TuSimple’s app emphasizes real-time visibility into autonomous operations. Dispatchers can monitor autonomous trucks on fixed corridors, receive incident alerts, and access detailed safety reports. The system is built for hub-to-hub freight and integrates predictive analytics that estimate arrival times down to the minute.
- Aurora Driver (U.S.). Aurora’s platform powers both passenger and freight vehicles, but its trucking division is focused on line-haul autonomy. The Aurora Beacon app acts as a mission control interface, giving logistics companies the ability to assign loads, track driver-out trucks, and receive updates on operational design domain (ODD) limitations. Aurora highlights safety transparency, allowing customers to see logs of every autonomous decision made during a trip.
- Waymo Via (U.S.). Originally a division of Google’s Waymo, Waymo Via’s app platform integrates tightly with existing TMS (transportation management systems). It emphasizes seamless integration into enterprise workflows, with APIs that allow shippers to treat self driving semi trucks like any other carrier asset. Waymo’s key innovation lies in its route optimization and mixed-fleet support, ensuring that human-driven and autonomous semi trucks can share operations.
- Embark (U.S.). Embark’s Driver software is less of a public-facing app and more of a back-end system, but logistics partners interact with its fleet management modules. The Embark Guardian platform enables real-time tele-operations—remote supervisors can intervene in rare edge cases, making it a critical step in ensuring safety for early deployments.
- Plus.ai (China & U.S.). Plus.ai has positioned itself as a scalable autonomy provider. Its PlusDrive platform is accessible through mobile and web apps, offering features like real-time alerts, over-the-air updates, and compliance dashboards. Designed to retrofit existing fleets, Plus.ai emphasizes modularity and integration, appealing to carriers that cannot replace their entire fleet at once.
4.2 What These Apps Have in Common
Despite differences in branding and regional focus, most of the above platforms share several core attributes:
- Real-time fleet visibility. Every app provides live maps, performance metrics, and safety alerts for driverless semi trucks.
- Integration with logistics systems. APIs allow apps to connect with enterprise TMS and ERP platforms, making autonomy fit into established workflows.
- Safety-first design. From predictive alerts to incident replay functions, each app emphasizes transparent decision-making to satisfy regulators, insurers, and customers.
These commonalities show that the industry has converged on certain must-have features. Yet, many of these apps are built for specific providers and lack the flexibility needed by carriers who operate mixed fleets or want supplier-agnostic solutions.
4.3 Opportunities for Custom App Development
While major players lead with proprietary systems, gaps remain where a logistics app development company like A-Bots.com can deliver value:
- Mixed-fleet orchestration. Most existing apps only work with a single autonomy provider. A bespoke app could unify operations across TuSimple, Aurora, and human-driven fleets under one dashboard.
- Regional compliance. Regulations differ drastically between Texas, Shanghai, and Germany. Custom logistics and truck app development ensures compliance with each region’s rules.
- Extended modules. Shippers increasingly demand carbon reporting, blockchain-based freight contracts, and AI-driven customer service—functions rarely found in provider apps.
- Independent testing platforms. Businesses need QA and validation tools that aren’t tied to one vendor’s ecosystem, especially when evaluating autonomous semi trucks from multiple providers.
In other words, while TuSimple, Aurora, and Waymo have defined the cutting edge of automated trucking, the broader market is wide open for tailor-made, supplier-agnostic platforms. This is where A-Bots.com, as a specialized logistics app development company, steps in to design apps that not only match but exceed the current benchmarks.

5. Testing and Quality Assurance in Driverless Semi Truck Apps
The shift from traditional fleet management to automated trucking introduces not only new opportunities but also unprecedented risks. Unlike conventional logistics apps, where a minor software glitch might delay shipments or frustrate drivers, failures in driverless semi truck applications can have severe safety, financial, and regulatory consequences. This is why testing and quality assurance (QA) are no longer peripheral steps—they are central pillars of every project in logistics and truck app development.
5.1 Why QA is Critical in Automated Trucking
When designing apps for self driving semi trucks or autonomous semi trucks, the stakes are higher than in nearly any other industry. A small error in an algorithm could cause a lane departure, misinterpretation of a traffic signal, or even a collision. For this reason, quality assurance in logistics software requires a deeper scope than traditional mobile app testing.
- Safety validation. Every feature must be evaluated in simulated and real-world environments to ensure the truck responds appropriately to unexpected scenarios.
- Regulatory compliance. Governments in the U.S., EU, and China are building frameworks that demand detailed evidence of software reliability before granting driver-out permissions.
- Business continuity. Any unscheduled downtime in an autonomous fleet creates ripple effects across supply chains. Testing prevents breakdowns that could halt critical operations.
A poorly tested app is more than a technical liability—it’s a business risk. Logistics firms adopting automated trucking need QA strategies that protect their reputation, contracts, and compliance standing.
5.2 Simulation Environments and Edge-Case Testing
One of the most powerful tools in QA is simulation. Since driverless semi trucks encounter countless scenarios that cannot be physically tested on every road, simulation environments allow developers to recreate complex edge cases at scale:
- Sudden lane closures, construction zones, or detours.
- Rare weather conditions such as snowstorms in Texas or sandstorms in northern China.
- Human driver unpredictability—cutting off trucks, tailgating, or sudden braking.
By integrating these scenarios into testing platforms, a logistics app development company ensures that every app is resilient, not just in ideal conditions but also in the most challenging ones. At A-Bots.com, for example, QA processes include building virtual twins of freight corridors so that autonomous semi trucks can be tested in simulation before deployment. This prevents costly and dangerous failures during live runs.
5.3 Outsourced Testing as a Strategic Advantage
Not every logistics firm or OEM has the in-house capacity to run such advanced QA programs. This is where outsourcing to specialists like A-Bots.com creates measurable value. By acting as an external partner, A-Bots.com can:
- Conduct end-to-end QA. From unit testing and integration checks to full-scale operational stress tests.
- Validate multi-vendor systems. Fleets often combine hardware and autonomy stacks from different providers. A neutral QA partner ensures interoperability across platforms.
- Document compliance. Outsourced QA generates evidence logs, audit trails, and safety-case reports tailored to regulators in different regions.
For businesses considering self driving semi trucks, outsourcing QA is not a cost—it is an investment in risk reduction. It provides peace of mind that every update, patch, or integration is vetted before it hits the highway.
5.4 Building QA into the Development Cycle
Too often, QA is treated as a final checkpoint. In reality, testing must be continuous throughout logistics and truck app development. Modern agile frameworks emphasize “shift-left” testing, where QA begins in the earliest design phases and continues long after launch.
Best practices include:
- Embedding automated test suites into CI/CD pipelines, ensuring that every new build is validated before release.
- Running regression tests whenever new integrations (IoT, V2X, AI modules) are introduced.
- Monitoring live deployments and feeding operational data back into QA systems for iterative improvement.
When QA is built into the lifecycle, apps evolve with fewer disruptions, remain secure against cyber threats, and maintain the reliability required for driverless semi trucks operating in mixed traffic.
Testing and quality assurance are not optional extras in the age of automated trucking—they are the foundation of trust. From simulation-driven edge-case analysis to outsourced validation, the success of self driving semi trucks depends on rigorous QA pipelines. Companies that partner with an experienced logistics app development company like A-Bots.com gain a crucial advantage: not only do they get custom-built solutions, but they also ensure that every feature is safe, compliant, and ready for the unpredictable world of real logistics.
In this sense, testing is not the last step of development; it is the insurance policy and competitive differentiator that separates leaders from laggards in the race toward autonomous semi trucks.
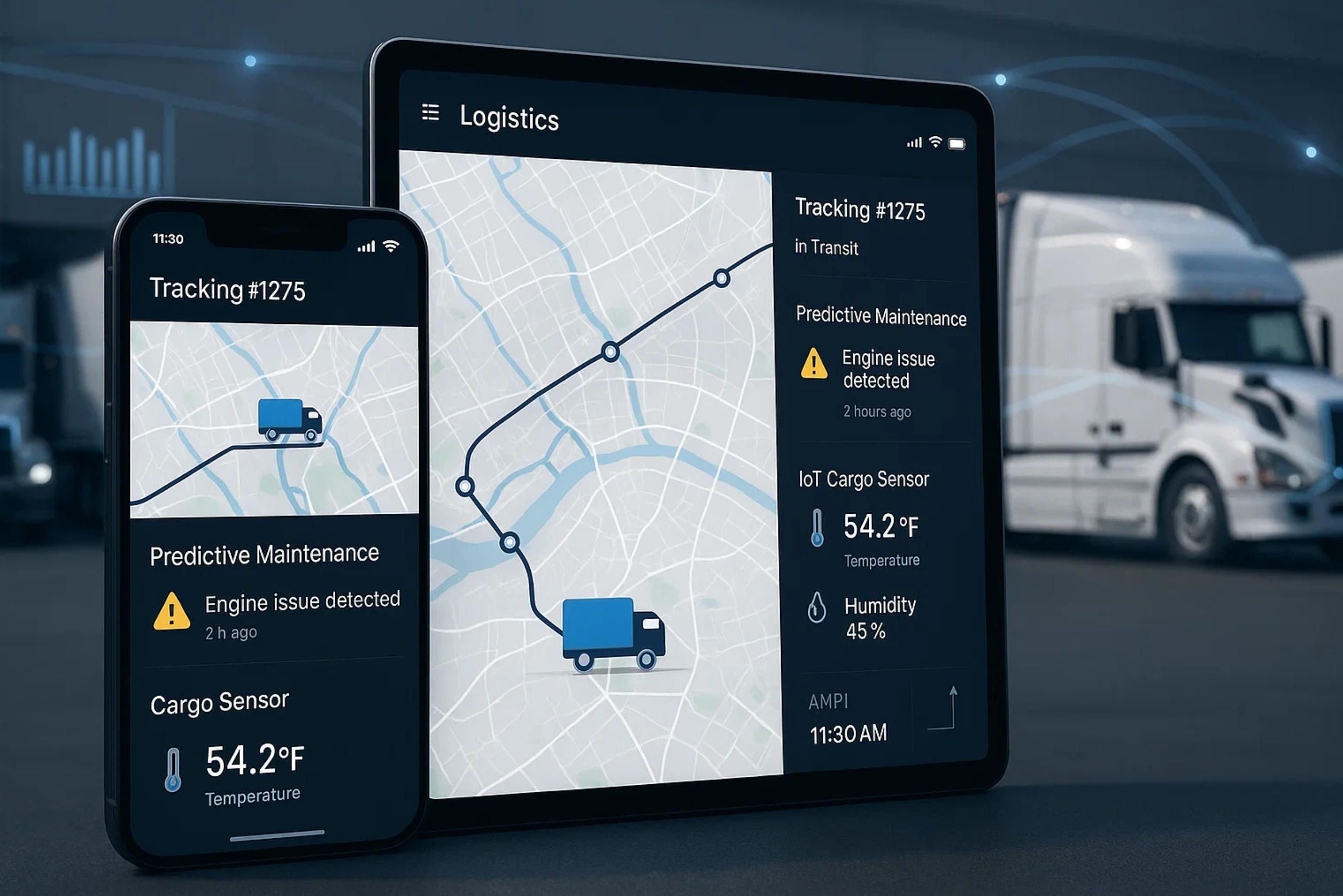
6. The Future of Logistics and Truck App Development
The trajectory of the logistics industry is inseparable from its embrace of digital ecosystems. Logistics and truck app development is no longer a supportive layer—it is the strategic backbone that defines how fleets operate, scale, and prepare for disruption. As technologies like AI, blockchain, and 5G/6G connectivity mature, the mobile app becomes the decisive interface where all these innovations converge. In practice, this means that the next decade will see logistics apps evolving from operational tools into full-fledged command centers capable of orchestrating human and machine collaboration across continents.
One of the most significant accelerators will be the rollout of high-speed connectivity. With 5G already deployed in the U.S., Europe, and China, and 6G research underway, the latency barrier that once limited real-time decision-making is rapidly disappearing. For self driving semi trucks, this evolution is critical: faster networks allow autonomous systems to communicate seamlessly with traffic infrastructure, freight hubs, and cloud-based safety monitors. The app is the translator in this chain, turning high-bandwidth data streams into actionable insights for both machines and human supervisors.
Equally transformative is the integration of blockchain-based freight contracts and carbon tracking. As governments and clients push for transparent, sustainable supply chains, logistics firms will be required to prove both compliance and environmental impact. A bespoke app built by a logistics app development company like A-Bots.com can embed blockchain smart contracts directly into workflows, automating payments and dispute resolution while generating immutable carbon reports. This shift not only reduces administrative overhead but also redefines trust in an industry historically burdened by paperwork and disputes.
Artificial intelligence will be the invisible co-pilot of tomorrow’s logistics systems. From predicting cargo demand surges to managing maintenance across fleets of driverless semi trucks, AI-powered modules will ensure that logistics providers can operate with unprecedented efficiency. These capabilities will not be plug-ins; they must be deeply embedded in the DNA of logistics apps, designed to learn continuously from real-world operations. A-Bots.com positions itself at the forefront of this integration, ensuring that AI-driven insights are not abstract models but practical, business-shaping tools.
The global dimension of this future cannot be overlooked. In the U.S., policy debates about safety and liability will shape adoption curves, while in Europe, carbon neutrality and regulatory compliance will dominate priorities. In China, state-backed corridors for autonomous semi trucks will accelerate mass deployment faster than anywhere else. Each market requires not just technological expertise but cultural and regulatory awareness, which makes bespoke, region-specific app development more important than standardized solutions.
As industry veteran Marc Andreessen once said, “In a startup, absolutely nothing happens unless you make it happen.” The same logic applies to logistics firms facing the leap into autonomy. The transition will not be a passive process dictated by regulators or OEMs; it will be driven by companies that actively invest in future-ready mobile ecosystems.
The conclusion is clear: the future of automated trucking is not only about trucks but also about the software that governs them. Logistics and truck app development will continue to evolve as the control plane for fleets, shaping how humans, machines, and markets interact. For companies ready to embrace this transformation, partnering with an experienced, innovative logistics app development company like A-Bots.com will be the key to thriving in a world where driverless semi trucks move goods faster, safer, and more intelligently than ever before.
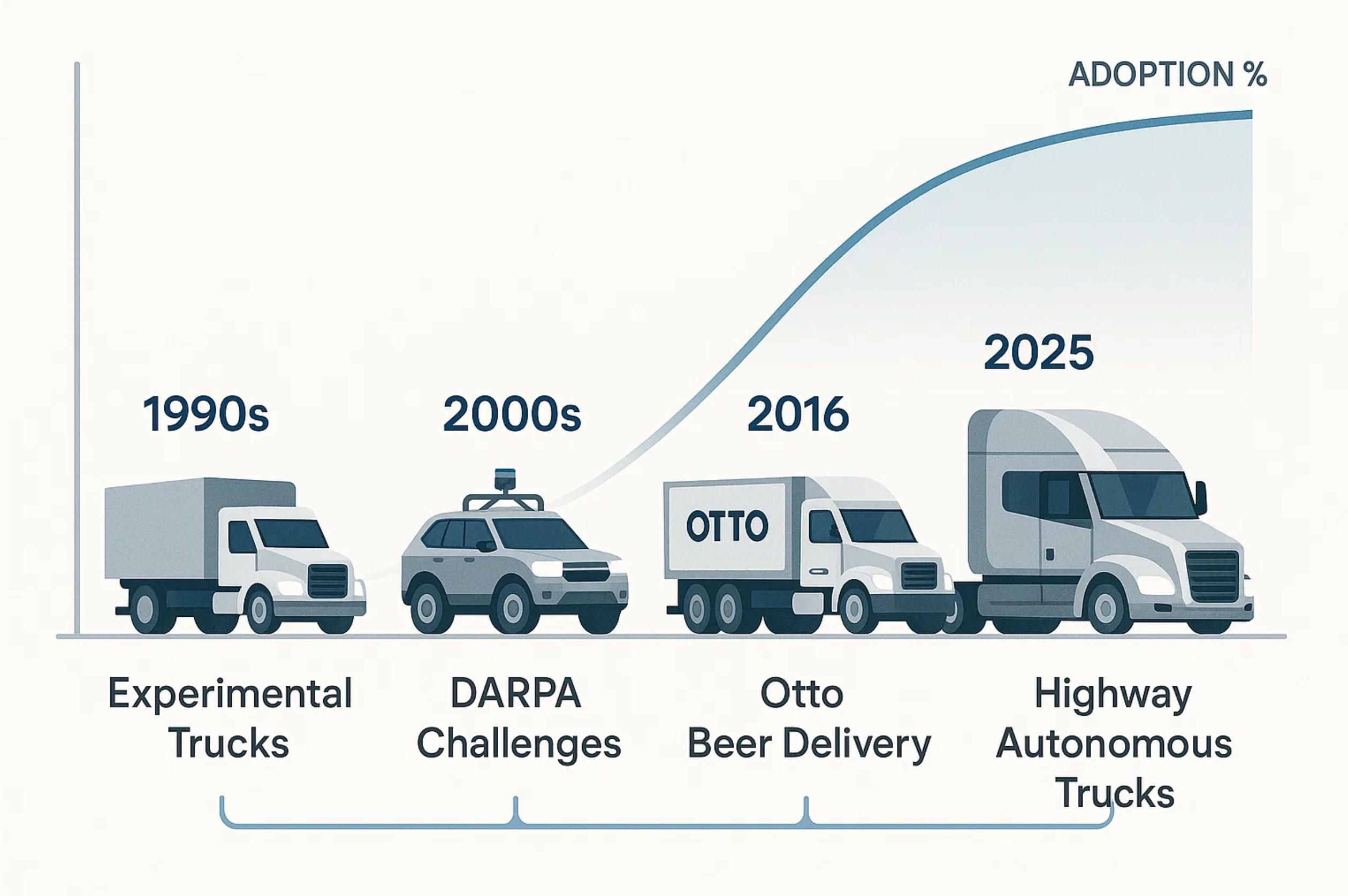
7. Historical and Economic Timeline of Driverless Trucks
The concept of driverless semi trucks did not emerge overnight. It is the product of decades of research, experimentation, and gradual technological adoption across multiple regions. Understanding this timeline helps explain both the progress already made and the challenges that remain for the future of automated trucking.
The first seeds of autonomy in trucking were planted in the late 1980s and early 1990s, when research projects in Europe and the U.S. began exploring advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS). Early demonstrations, such as Daimler’s Prometheus Project in Germany, showcased trucks following each other in controlled convoys using sensors and rudimentary computer vision. These were not fully self driving semi trucks, but they marked the beginning of the idea that trucks could someday move freight without continuous human intervention.
By the early 2000s, momentum grew as governments and private companies invested in large-scale challenges. The U.S. Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) Grand Challenge of 2004 and 2005 produced some of the earliest autonomous vehicles capable of navigating desert terrain. Although these were not freight trucks, they validated key technologies like LiDAR and machine learning that would later underpin logistics and truck app development for commercial fleets.
The 2010s marked a turning point. In 2016, Otto—an American startup founded by former Google engineers—completed the first commercial delivery with an autonomous truck in Colorado, transporting beer for Anheuser-Busch. Around the same time, companies like TuSimple in the U.S. and China, and Embark in the U.S., began developing specialized platforms for autonomous semi trucks on highways. In Europe, Daimler and Volvo launched pilot programs for semi-autonomous platooning, proving that driver-assist and cooperative automation could reduce fuel consumption by up to 10%.
China quickly emerged as a leader in state-backed pilot zones. By 2020, the country had designated autonomous freight corridors around ports and industrial hubs, providing a regulatory and infrastructural foundation for scaling driverless semi trucks. In the U.S., Arizona and Texas became hotspots for commercial testing, with Aurora, Waymo Via, and Kodiak Robotics regularly operating autonomous freight between major cities. Europe, meanwhile, emphasized harmonization of rules, with Germany passing legislation in 2021 to allow Level 4 autonomous driving on public roads—a first for the region.
From an economic perspective, adoption has been gradual but significant. While automated trucking still represents less than 5% of total freight miles in 2025, projections suggest that by 2030, driverless trucks could handle up to 15–20% of long-haul freight in the U.S. and China, with Europe lagging slightly due to stricter regulation. This shift is driven by economics: autonomous trucks can operate nearly 24/7, reducing labor costs, cutting delivery times, and addressing the chronic shortage of truck drivers.
The share of self driving semi trucks relative to human-driven trucks remains small today, but the trend is unmistakable. In the U.S., analysts predict that by 2040, nearly 40% of long-haul miles could be automated. In China, the percentage may climb even higher due to centralized government support and rapid infrastructure upgrades. Europe’s adoption will likely be slower but steadier, aligning with environmental policies that favor efficiency and reduced emissions.
The timeline illustrates how far the industry has come: from experimental convoys in the 1990s to real driver-out operations in 2025. It also highlights the indispensable role of software in this journey. Without robust logistics and truck app development, the vision of widespread autonomous semi trucks would remain science fiction. Instead, thanks to decades of technological evolution, the industry now stands at the cusp of a historic transformation where digital platforms, apps, and AI make autonomy both possible and profitable.

✅ Hashtags
#LogisticsAppDevelopment
#TruckApp
#AutomatedTrucking
#SelfDrivingTrucks
#AutonomousSemiTrucks
#DriverlessTrucks
#ABots
Other articles
Mobile App Development for Startups: Building Scalable Digital Products with A-Bots.com In today’s startup ecosystem, launching without a mobile app is no longer an option. Mobile platforms dominate global markets, shaping how users interact with products and how investors assess growth potential. This article explores the essentials of mobile app development for startups — from MVP design to scalable architectures, from AI-driven personalization to robotics integration. As a mobile app development company for startups, A-Bots.com delivers more than code — we provide strategic guidance, UX expertise, and technical innovation. Whether you want to launch quickly, secure investor trust, or expand globally, our team is ready to transform your idea into a market-ready digital product.
Software Testing Company for IoT Devices | Hire Software Testers In today’s IoT-driven world, testing is not optional—it’s mission-critical. A-Bots.com stands out as a global software testing company, combining development expertise with advanced QA services. From functional validation to scalability, security, and compliance, our team ensures your IoT devices and applications meet the highest standards. Businesses can hire software testers on-demand, gaining access to automation, AI-driven testing, and digital twin simulations without investing in costly in-house labs. Whether you need short-term regression testing or long-term IoT QA outsourcing, A-Bots.com adapts to your project needs. With our hybrid model of human insight and machine efficiency, we transform QA from a secondary task into a strategic advantage. Trust A-Bots.com to deliver not just testing, but reliability, resilience, and market confidence.
Apple Watch for Seniors: Custom Apps and Elder-Care Solutions The phrase apple watch for seniors reflects a growing global trend: using wearables to improve safety, health, and independence for older adults. With Fall Detection, SOS alerts, ECG readings, and medication reminders, Apple Watch already supports elder care. Yet true transformation comes from custom solutions. Tailored watchOS and iOS apps can provide predictive fall-risk monitoring, caregiver dashboards, medication adherence alerts, and seamless integration with clinical systems. For insurers, senior-living providers, and startups, this is not just a technical upgrade but a strategic opportunity in rapidly aging societies where one in five citizens is already over 65. A-Bots.com, with expertise in custom apple watch app development, bridges technology, compliance, and human-centered design. The result is wearable solutions that seniors trust, caregivers depend on, and organizations can scale with confidence.
Mobile App Development for Restaurants | A-Bots.com In today’s digital dining landscape, mobile app development for restaurants is essential. Customers expect apps that manage reservations, ordering, delivery, and loyalty in one seamless flow. Generic templates cannot compete with leaders like Starbucks or Domino’s. A-Bots.com is a trusted restaurant app development company creating bespoke solutions that integrate POS systems, payments, AI personalization, and IoT kitchens. Our expertise allows restaurants to build restaurant apps that increase efficiency, loyalty, and revenue. From boutique cafes to global franchises, we design apps as living systems that adapt to customer behavior and technology trends. Partner with A-Bots.com to create restaurant apps that deliver lasting impact and redefine the dining experience.
App Controlled Coffee Maker: Custom App Development The coffee industry is rapidly embracing connectivity, with app controlled coffee makers and espresso machines becoming central to the smart kitchen revolution. Consumers expect to control brewing, personalize recipes, and monitor devices directly from their phones. Off-the-shelf solutions rarely meet these needs. That’s why A-Bots.com specializes in custom mobile app development for coffee machines with app control. From IoT integration and predictive maintenance to AI-driven personalization and sustainability dashboards, our apps transform coffee makers into digital ecosystems. For manufacturers, restaurants, and startups, this is more than software — it’s a strategic tool for customer loyalty and recurring revenue. Partner with A-Bots.com to shape the future of smart brewing.
Top stories
Copyright © Alpha Systems LTD All rights reserved.
Made with ❤️ by A-BOTS
