
Home
Services
About us
Blog
Contacts
Smart Farming in Controlled Environments: Custom IoT Solutions for Greenhouses and Vertical Farms
1. Introduction: The Future of Farming Is Vertical and Connected
2. Challenges in Traditional Greenhouse and Vertical Farming
3. How IoT Transforms Controlled Environment Agriculture
4. Key Components of a Custom IoT Solution
- 4.1. Sensor Networks: The Eyes and Ears of the System
- 4.2. Actuators: Implementing Decisions
- 4.3. Communication Protocols: Ensuring Seamless Data Flow
- 4.4. Data Processing and Analytics: Turning Data into Actionable Insights
- 4.5. User Interfaces: Bridging Humans and Machines
5. Real-World Case Studies: IoT in Action in Greenhouses and Vertical Farms
6. Challenges and Considerations in IoT Implementation
7. [INTERVIEW] Smart Farming in Action: Inside Custom IoT for Greenhouses and Vertical Farms
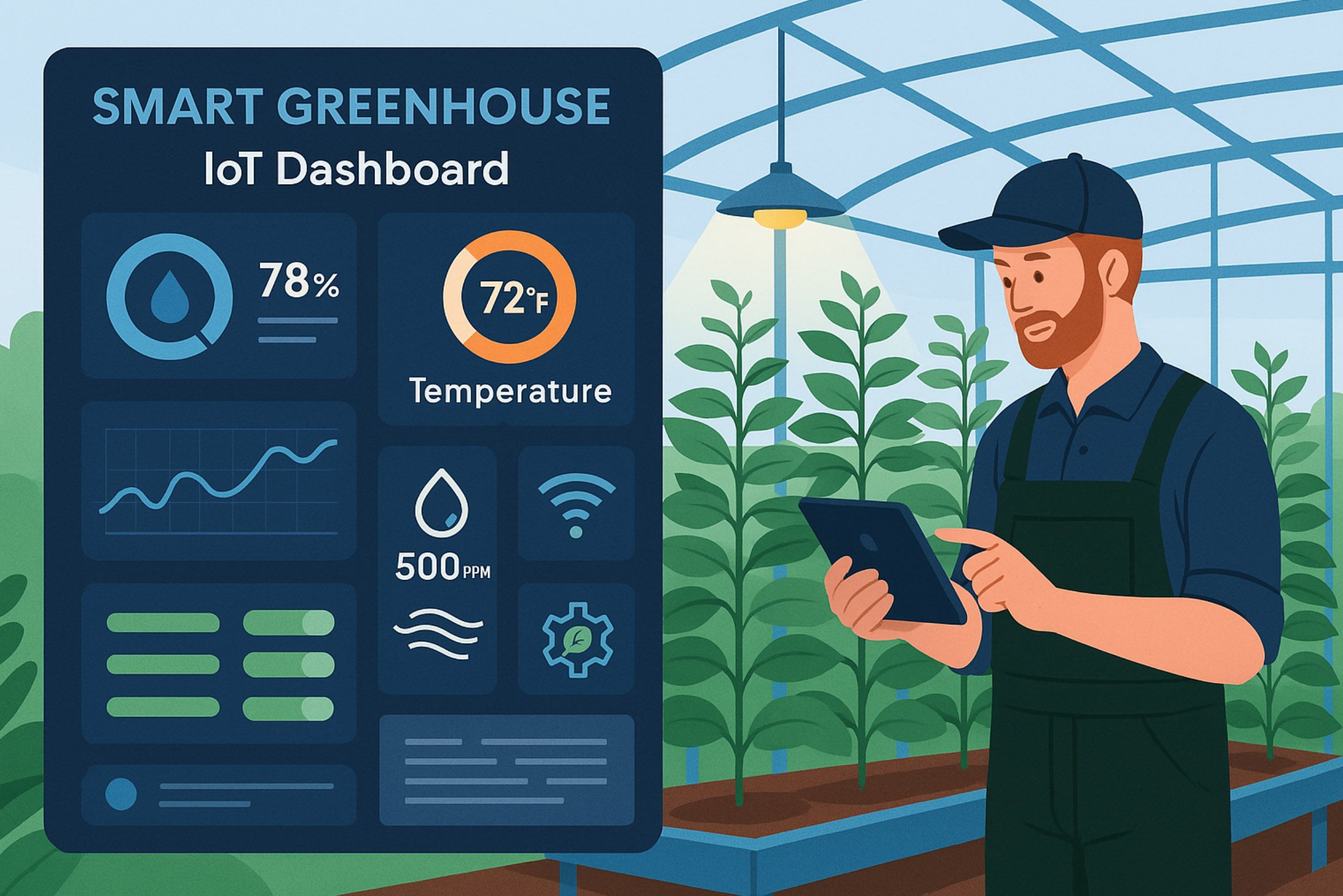
1. Introduction: The Future of Farming Is Vertical and Connected
As the global population continues to rise and arable land becomes increasingly scarce, the agricultural sector faces mounting pressure to produce more food using fewer resources. Traditional farming methods, while foundational, often struggle to meet these demands due to limitations in space, climate variability, and resource inefficiencies. In response, controlled-environment agriculture (CEA) has emerged as a transformative approach, enabling year-round cultivation in optimized conditions (Wikipedia).
CEA encompasses various systems, including greenhouses and vertical farms, that utilize technology to regulate environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, light, and CO₂ levels. By creating ideal growing conditions, these systems can significantly increase crop yields, reduce water usage, and minimize the need for chemical inputs. However, managing these complex environments manually can be labor-intensive and prone to human error.
This is where the Internet of Things (IoT) plays a pivotal role. By integrating IoT technologies into CEA systems, farmers can automate monitoring and control processes, leading to more efficient and precise agricultural practices. Sensors collect real-time data on various environmental parameters, which is then analyzed to make informed decisions about resource allocation and system adjustments. For instance, if sensors detect a drop in humidity, the system can automatically activate misting devices to maintain optimal levels.
The benefits of IoT integration in agriculture are substantial. Studies have shown that smart greenhouse systems can lead to significant improvements in crop quality and resource efficiency. For example, an intelligent agricultural greenhouse control system based on IoT and machine learning demonstrated enhanced crop growth efficiency and yield, accompanied by a reduction in resource wastage (Automation in Agriculture).
Moreover, the scalability of IoT solutions allows for their application in various agricultural settings, from small-scale urban farms to large commercial operations. This adaptability is crucial in addressing the diverse challenges faced by the agricultural sector globally.
In conclusion, the integration of IoT technologies into controlled-environment agriculture represents a significant advancement in modern farming. By enabling precise control over growing conditions, IoT systems contribute to increased productivity, sustainability, and resilience in food production. As we continue to confront the challenges of feeding a growing population amidst environmental constraints, embracing such technological innovations will be essential in shaping the future of agriculture.

2. Challenges in Traditional Greenhouse and Vertical Farming
Controlled-environment agriculture (CEA), encompassing greenhouses and vertical farms, has emerged as a promising solution to the challenges faced by traditional farming methods. By enabling year-round cultivation and optimizing resource usage, CEA offers numerous advantages. However, despite its potential, traditional greenhouse and vertical farming systems encounter several significant challenges that can impede their efficiency and scalability.
High Energy Consumption
One of the most pressing issues in vertical farming is the substantial energy requirement, particularly for artificial lighting and climate control systems. Unlike traditional greenhouses that utilize natural sunlight, vertical farms often rely on LED lighting to provide the necessary spectrum for plant growth. This dependency leads to elevated electricity costs, which can account for a significant portion of operational expenses. For instance, some vertical farms have reported that energy costs constitute up to 40% of their total operating expenses. This financial burden has led to the closure of several high-profile vertical farming ventures, especially in regions with high electricity prices (verticalfarmdaily.com).
Substantial Initial Capital Investment
Establishing a greenhouse or vertical farm requires a considerable upfront investment. Costs associated with constructing specialized facilities, installing advanced climate control systems, and integrating automation technologies can be prohibitive. This financial barrier often deters small-scale farmers and startups from entering the market. Moreover, the return on investment can be uncertain, especially if the farm's output is limited to niche crops with fluctuating market demand.
Technical Complexity and Maintenance
Operating a CEA system demands a high level of technical expertise. Farmers must manage intricate systems that monitor and adjust environmental parameters such as temperature, humidity, CO₂ levels, and nutrient delivery. Maintaining these systems requires specialized knowledge in fields like horticulture, engineering, and data analysis. Additionally, technical malfunctions can lead to significant crop losses if not promptly addressed, emphasizing the need for reliable system design and maintenance protocols.
Limited Crop Diversity
While vertical farms excel in producing leafy greens and herbs, they face challenges in cultivating a broader range of crops. Staple crops like grains and root vegetables are less suited to vertical farming due to their growth requirements and space constraints. This limitation restricts the diversity of produce that vertical farms can offer, potentially impacting their market competitiveness and profitability.
Environmental Impact
Although CEA systems aim to reduce the environmental footprint of agriculture, they are not without ecological concerns. The high energy consumption associated with artificial lighting and climate control contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, particularly if the energy is sourced from fossil fuels. Additionally, the production and disposal of materials used in constructing vertical farms, such as plastics and metals, can have environmental implications. Addressing these issues requires a concerted effort to integrate renewable energy sources and sustainable materials into CEA practices.
Market Acceptance and Consumer Perception
Despite the technological advancements in CEA, consumer acceptance remains a hurdle. Some consumers perceive produce from vertical farms as less natural or inferior in taste compared to traditionally grown crops. Overcoming these perceptions necessitates transparent communication about the benefits of CEA, such as reduced pesticide use, consistent quality, and local production. Educating consumers and building trust are essential for the widespread adoption of CEA produce.
Regulatory and Policy Challenges
CEA operations often navigate a complex landscape of regulations and policies that may not be tailored to their unique practices. Zoning laws, building codes, and agricultural regulations can pose obstacles to establishing and operating vertical farms, especially in urban areas. Advocating for policy frameworks that recognize and support the distinct nature of CEA is crucial for the industry's growth.
In summary, while controlled-environment agriculture presents innovative solutions to modern agricultural challenges, traditional greenhouse and vertical farming systems face significant obstacles. Addressing high energy consumption, substantial capital requirements, technical complexities, limited crop diversity, environmental concerns, consumer perceptions, and regulatory hurdles is essential for the sustainable advancement of CEA. Integrating IoT technologies and adopting holistic strategies can play a pivotal role in overcoming these challenges, paving the way for a more resilient and efficient agricultural future.

3. How IoT Transforms Controlled Environment Agriculture
The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) into Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA) has revolutionized the way we approach modern farming. By leveraging interconnected devices and real-time data analytics, IoT enables precise monitoring and control of environmental conditions within greenhouses and vertical farms, leading to enhanced productivity, resource efficiency, and sustainability.
Precision Monitoring and Control
IoT systems facilitate continuous monitoring of critical environmental parameters such as temperature, humidity, light intensity, CO₂ levels, and soil moisture. Sensors deployed throughout the cultivation environment collect data that is transmitted to centralized platforms, allowing for real-time analysis and adjustments. For instance, if a drop in humidity is detected, the system can automatically activate misting devices to restore optimal levels, ensuring consistent growing conditions.
Automated Resource Management
Automation is a cornerstone of IoT-enabled CEA. By integrating actuators with sensor networks, systems can autonomously regulate irrigation, lighting, and nutrient delivery based on real-time data. This dynamic control minimizes resource wastage and ensures that plants receive precise inputs tailored to their developmental stages. Such precision not only conserves water and energy but also enhances crop quality and yield.
Data-Driven Decision Making
The vast amount of data collected by IoT devices empowers farmers with actionable insights. Advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms can identify patterns and predict potential issues, such as pest infestations or equipment failures, before they escalate. This proactive approach enables timely interventions, reducing crop losses and operational disruptions (en.wikipedia.org).
Scalability and Remote Accessibility
IoT platforms offer scalability, allowing farmers to manage multiple facilities or expand operations without significant infrastructure overhauls. Cloud-based systems provide remote access to real-time data and control functionalities, enabling farmers to monitor and manage their operations from anywhere. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for large-scale enterprises and urban farming initiatives.
Enhanced Sustainability
By optimizing resource utilization and reducing dependency on manual labor, IoT contributes to the sustainability of CEA practices. Efficient energy management, precise water usage, and minimized chemical inputs align with environmental conservation goals. Moreover, the ability to produce high-quality crops year-round in controlled environments reduces the need for long-distance transportation, further lowering the carbon footprint.
In summary, the adoption of IoT technologies in Controlled Environment Agriculture marks a significant advancement in modern farming. By enabling precise environmental control, automating resource management, and facilitating data-driven decisions, IoT enhances the efficiency, productivity, and sustainability of greenhouse and vertical farming operations. As the agricultural sector continues to evolve, the integration of IoT will play a pivotal role in meeting the growing global demand for food while preserving natural resources.

4. Key Components of a Custom IoT Solution for Greenhouses and Vertical Farms
Designing an effective IoT system for controlled-environment agriculture requires a harmonious integration of various hardware and software components. These components work in tandem to monitor, analyze, and optimize the growing conditions within greenhouses and vertical farms. Let's explore the essential elements that constitute a robust IoT solution in this context.
4.1. Sensor Networks: The Eyes and Ears of the System
At the heart of any IoT solution are the sensors that collect real-time data on various environmental parameters. These sensors provide the necessary insights to maintain optimal growing conditions. Key sensors include:Vertical Farming Technology iFarm
- Temperature and Humidity Sensors: Monitor ambient conditions to ensure they remain within the ideal range for plant growth.
- Soil Moisture Sensors: Measure the water content in the soil, aiding in precise irrigation management.
- Light Sensors: Assess the intensity and duration of light exposure, crucial for photosynthesis.
- CO₂ Sensors: Track carbon dioxide levels, which can influence plant metabolism and yield.
- pH and EC Sensors: Evaluate the acidity and electrical conductivity of the soil or nutrient solutions, ensuring optimal nutrient availability.
These sensors can be wired or wireless, with wireless options offering greater flexibility in deployment, especially in large-scale operations.

4.2. Actuators: Implementing Decisions
Actuators are devices that carry out actions based on the data received from sensors. They are responsible for adjusting environmental conditions to maintain optimal growth parameters. Common actuators include:
- Irrigation Systems: Automate watering schedules based on soil moisture readings.
- Ventilation Fans: Regulate air circulation to control temperature and humidity.
- Heating and Cooling Systems: Maintain consistent temperatures regardless of external weather conditions.
- Lighting Systems: Adjust light intensity and duration to simulate natural daylight cycles.
- Nutrient Delivery Systems: Administer precise amounts of fertilizers or nutrients as needed.
The integration of actuators ensures that the greenhouse or vertical farm can respond dynamically to changing conditions, enhancing efficiency and crop yield.
4.3. Communication Protocols: Ensuring Seamless Data Flow
Effective communication between sensors, actuators, and control systems is vital. Various communication protocols facilitate this data exchange: MDPI
-
Wi-Fi and Ethernet: Offer high-speed data transmission, suitable for operations with robust network infrastructure.
-
LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network): Ideal for transmitting data over long distances with low power consumption.
-
Zigbee and Bluetooth: Suitable for short-range communication between devices.
-
Modbus and KNX: Common in industrial settings, providing reliable communication between devices.
Selecting the appropriate protocol depends on factors such as the size of the operation, power availability, and specific use-case requirements.
4.4. Data Processing and Analytics: Turning Data into Actionable Insights
The data collected by sensors must be processed and analyzed to inform decision-making.
-
Edge Computing: Processing data locally at the source to enable real-time responses and reduce latency.
-
Cloud Computing: Storing and analyzing large volumes of data remotely, facilitating long-term trend analysis and remote monitoring.
-
Machine Learning Algorithms: Predicting future conditions and optimizing control strategies based on historical data.
By leveraging these technologies, farmers can make informed decisions that enhance productivity and resource efficiency.

4.5. User Interfaces: Bridging Humans and Machines
User interfaces (UIs) are essential for monitoring system performance and making manual adjustments when necessary.
-
Real-Time Dashboards: Visual representations of current environmental conditions and system statuses.
-
Mobile Applications: Allowing remote access and control via smartphones or tablets.
-
Alerts and Notifications: Informing users of anomalies or required interventions.
A well-designed UI enhances user engagement and ensures that the system remains user-friendly, even for those without technical expertise.
Incorporating these components into a cohesive IoT solution enables greenhouses and vertical farms to operate more efficiently, sustainably, and productively. By harnessing the power of real-time data and automation, farmers can optimize growing conditions, reduce resource consumption, and ultimately increase crop yields.

5. Real-World Case Studies: IoT in Action in Greenhouses and Vertical Farms
To understand the tangible benefits of integrating IoT into controlled-environment agriculture, let's explore several real-world case studies that highlight how these technologies are revolutionizing greenhouses and vertical farms.
AeroFarms: Revolutionizing Urban Agriculture
AeroFarms, based in Newark, New Jersey, operates one of the world's largest indoor vertical farms. By leveraging IoT technologies, they have transformed traditional farming practices into a high-tech operation. Their system utilizes a network of sensors to monitor variables such as temperature, humidity, and nutrient levels in real-time. This data-driven approach allows for precise control over the growing environment, leading to increased crop yields and reduced resource consumption. Notably, AeroFarms reports using 95% less water than conventional farming methods, showcasing the sustainability benefits of IoT integration.
Bowery Farming: Data-Driven Crop Optimization
Bowery Farming, another leader in the vertical farming industry, has developed a proprietary operating system known as BoweryOS. This platform collects data from thousands of sensors placed throughout their facilities, monitoring factors like light intensity, CO₂ levels, and plant growth rates. By analyzing this data, Bowery can make real-time adjustments to optimize plant health and productivity. The result is a consistent supply of high-quality produce grown with minimal environmental impact (Food & Wine).
Trumeter: Enhancing Greenhouse Ventilation
In a case study involving greenhouse operations, Trumeter implemented an IoT-based solution to improve ventilation systems. By installing sensors to monitor temperature and humidity, and integrating these with automated ventilation controls, the greenhouse achieved more stable internal conditions. This not only improved plant health but also led to energy savings by reducing the need for manual intervention and preventing overuse of ventilation equipment. The success of this project underscores the potential for IoT to enhance operational efficiency in greenhouse settings.
Growy: Autonomous Vertical Farming
Growy, a Netherlands-based startup, has taken automation in vertical farming to new heights. Their facilities are equipped with IoT devices and robotics that manage nearly every aspect of the farming process, from planting to harvesting. Sensors continuously collect data on environmental conditions and plant health, which is then used to inform robotic actions. This high level of automation reduces labor costs and increases scalability, making vertical farming more economically viable.
Dusun IoT: Smart Greenhouse Lighting
Dusun IoT has developed a greenhouse monitoring and control system that focuses on optimizing lighting conditions. Their solution uses sensors to detect plant growth stages and adjusts LED lighting spectra accordingly. By tailoring light conditions to the specific needs of plants at different growth phases, the system enhances photosynthesis efficiency and accelerates growth cycles. This targeted approach to lighting demonstrates how IoT can contribute to more sustainable and productive greenhouse operations (dusuniot.com).
These case studies illustrate the diverse applications and benefits of IoT technologies in controlled-environment agriculture. From improving resource efficiency and crop yields to enabling full automation, IoT is at the forefront of transforming how we produce food in greenhouses and vertical farms. As these technologies continue to evolve, we can expect even greater advancements in agricultural productivity and sustainability.

6. Challenges and Considerations in IoT Implementation
Smart farming sounds smart — until you’re knee-deep in hardware that won’t sync, cloud services that lag, and sensors reporting 200% humidity in the middle of Arizona. Behind the clean dashboards and crisp data visualizations, there’s a complex web of challenges that growers must face when integrating IoT systems into greenhouses and vertical farms.
Let’s not romanticize the process. Building a reliable IoT infrastructure isn’t plug-and-play — it’s more like “plug and debug, then debug again, then maybe play.”
Connectivity isn’t just Wi-Fi — it’s a survival game in steel-framed greenhouses and remote agricultural zones. Many greenhouses are built like Faraday cages. Wireless signals bounce, break, and behave badly. Add hundreds of sensors, actuators, and gateways, and you have a network topology that could make NASA sweat. Choosing between Wi-Fi, LoRaWAN, or Zigbee isn’t just a spec sheet decision — it’s about budget, range, reliability, and what happens when a storm knocks out the nearest repeater. Hybrid approaches (e.g., LoRa inside + cellular gateway) are often the most resilient, but also the most complex to maintain.
In a vertical farm in Chicago, engineers spent three months trying to fix network collisions caused by light automation loops interfering with humidity sensor signals. The culprit? An unshielded cable emitting interference at 2.4 GHz — just enough to cripple Zigbee nodes. The fix was elegant: reroute, rewire, reprogram — and then finally, rejoice.
Data security in IoT agriculture is often the last thing considered — until it’s too late. The irony? A vertical farm with AI-controlled microclimates and $2M in crops might still use a Raspberry Pi as its main gateway, running on outdated firmware. Meanwhile, farmers remotely access dashboards with no encryption, from phones that haven’t updated since 2019. In 2022, a U.S.-based hydroponic farm suffered a breach that disabled irrigation for 36 hours. The crops? Gone. The losses? Six figures.
That’s why implementing secure firmware updates, encrypted communications (TLS, VPNs), role-based access, and remote lockout features must be part of the architecture from day one — not a last-minute “we’ll patch it later” discussion. Regulatory frameworks like the U.S. Cybersecurity Improvement Act of 2020 are starting to apply to IoT agriculture too, so being proactive isn’t just smart — it’s legal self-defense.

7. [INTERVIEW] Smart Farming in Action: Inside Custom IoT for Greenhouses and Vertical Farms
Interviewer (I): Thanks for joining us today! Let's dive straight in: Why is IoT becoming essential for greenhouses and vertical farms?
Expert from A-Bots.com (E): Great to be here. In short — because agriculture is becoming data-driven. In greenhouses and vertical farms, you’re dealing with controlled environments where every variable matters: humidity, light, soil nutrients, airflow. You can’t optimize what you don’t measure. IoT gives you the sensors, the control, and the automation to grow smarter — not harder. More information about A-Bots.com services.
I: But aren’t there already a lot of “smart farming” systems on the market?
E: Absolutely, and many are good — but they’re not built around your farm. They often come with fixed sensor kits, fixed dashboards, and limited integration. A vertical farm in Boston won’t have the same requirements as a greenhouse in Arizona. Custom solutions mean we build software around your environment, not the other way around.
I: What are the most common pain points you solve with custom IoT software?
E: One word: visibility. Most clients come to us because they can’t get reliable, real-time data on critical parameters. They’re using spreadsheets, WhatsApp messages, and manual logs. We give them:
- Dashboards with live environmental metrics.
- Alert systems when thresholds are breached.
- Automated actuation of fans, lights, irrigation.
And that’s just the start.
I: Can you share a specific success story?
E: Sure. We worked with a hydroponic vertical farm in Austin. They had four levels of plant trays, and their existing system couldn’t detect light intensity or pH fluctuations at each level. We built a modular IoT setup with distributed sensors, integrated into a custom app. The result? 20% increase in yield and 30% reduction in wasted water within three months.
I: Wow! How do you decide what technology to use — Wi-Fi, LoRa, Zigbee, etc.?
E: We analyze the architecture of the greenhouse or vertical space — materials, layout, distances. In metal-rich environments, Wi-Fi often fails. We might use LoRa for long-range sensor transmission, with edge gateways handling computation locally. It’s always a hybrid, because farms are messy and unpredictable.
I: What kind of automation do your clients usually request?
E: Top requests include:
- Automated irrigation schedules based on real-time soil moisture.
- Dynamic lighting control adjusted by weather forecasts.
- Nutrient dosing tied to growth phases. We’ve even implemented AI models that suggest changes to optimize crop cycles — all from sensor data and historical trends.
I: What role does AI play in smart farming?
E: Increasingly, a big one. Farmers don’t have time to analyze graphs all day. AI helps by:
- Detecting anomalies.
- Forecasting temperature fluctuations.
- Suggesting corrective actions. In one case, our system caught a faulty humidity sensor that could’ve wiped out an entire lettuce crop. The farmer got a push notification before the damage was done.
I: Are these systems expensive to build?
E: Not anymore. Costs have dropped significantly in the last few years. A small greenhouse setup can start from $12,000 to $18,000 for a basic system. And we often build in stages — start with monitoring, then add automation, then AI. This staged rollout keeps budgets flexible.
I: How do you ensure reliability — say, if the internet goes out?
E: Great question. We design for edge-first architecture. That means the system can function independently of the cloud for critical tasks. Irrigation still works. Alerts still go out via SMS. Once the internet’s back — the cloud syncs. Reliability is baked in from day one.
I: And what’s your advice to someone just starting to think about smart farming?
E: Don’t fall into the “shiny dashboard” trap. It’s not about pretty charts — it’s about getting the right data at the right time, and making that data actionable. Start with your real pain points, and build outwards from there. That’s where custom solutions win — because they fit you, not the generic market.
I: Finally, what makes A-Bots.com different?
E: We don’t just code. We ask the right questions:
What do your crops need?
What do your people need?
What does your infrastructure allow?
Then we build an IoT system that’s invisible when it works and indispensable when it matters. That’s smart farming done right.
Hashtags
#SmartFarming
#IoTforAgriculture
#GreenhouseTech
#VerticalFarming
#CustomIoT
#Agritech
#PrecisionFarming
#SmartGreenhouse
#IoTDevelopment
#FarmAutomation
#AgriInnovation
#ABotsTech
Other articles
Custom CRM for Real Estate Developers
Off-the-shelf CRM tools weren’t built for the complexity of real estate development — but we were. This in-depth article explores why custom CRM solutions are redefining how developers manage projects, leads, teams, and revenue. See real-world ROI calculations, key challenges, and expert insights from A-Bots.com, a top CRM development company.
Custom Agriculture App Development for Farmers In 2024, U.S. farmers are more connected than ever — with 82% using smartphones and 85% having internet access. This article explores how mobile applications are transforming everyday operations, from drone-guided field scouting to livestock health tracking and predictive equipment maintenance. It examines why off-the-shelf apps often fail to address specific farm needs and how collaborative, farmer-funded app development is gaining momentum. Through real-world examples and step-by-step guidance, readers will learn how communities of growers can fund, design, and launch custom apps that fit their exact workflows. A-Bots.com offers tailored development services that support both solo farmers and agricultural groups. With offline capabilities, modular design, and support for U.S. and international compliance, these apps grow alongside the farm. Whether you're planting soybeans in Iowa, raising cattle in Texas, or running a greenhouse in California — this article offers the tools and inspiration to build your own farm technology. Discover why more farmers are saying: we don’t wait for the future — we build it.
Custom Drone Mapping Software & Control Apps: Smarter Aerial Solutions by A-Bots.com Custom drone software is revolutionizing how industries operate—from precision agriculture to infrastructure inspection. This article explores why off-the-shelf apps fall short, how AI and modular design shape the future, and how A-Bots.com delivers tailored drone solutions that truly fit. Whether you manage crops, assets, or entire projects, the right software lifts your mission higher.
Top stories
Copyright © Alpha Systems LTD All rights reserved.
Made with ❤️ by A-BOTS
